个人主页:Lei宝啊
愿所有美好如期而遇
左值
概念
可以取到地址的值就是左值,并且一般情况下可以修改(const类型左值不可修改)。
左值举例:
//左值
int a = 0;
const int b = 1;
int* p = &a;右值
概念
不能取到地址的值就是右值,并且右值不能被修改。(字面常量,表达式返回值,函数返回值(非左值引用)),我们之前使用的就是左值引用。
右值举例:
int func()
{
return 1 + 1;
}
//右值
10;
a + b;
func();左值引用
概念
int a = 0;
const int b = 1;
int* p = &a;
//左值引用
int& c = a;
const int& d = b;
int*& e = p;右值引用
概念
右值引用就是给右值的引用,给右值取别名。
10;
a + b;
func();
//右值引用
int&& e = 10;
int&& f = a + b;
int&& g = func();互相引用
左值引用右值需要加const,右值引用左值需要将左值先进行move。
//左值引用右值
const int& f = 10;
//右值引用左值
int&& g = move(a);应用与解释
简单来说就是为什么需要右值引用,我们先来看例子:

也就是说,临时对象的产生其实是多余的,所以在没有右值引用时,编译器给出的优化方案就是优化掉临时对象,直接使func中vv拷贝构造main中vv,可即便如此,还是有一次无谓的拷贝,就是func中的vv,他仍要销毁,资源还是浪费了。
接下来使用我们自己实现的string,来对有无右值引用做对比。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <cassert>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
namespace own
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
, _capacity(_size)
{
//cout << "string(char* str)" << endl;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
// s1.swap(s2)
void swap(string& s)
{
::swap(_str, s._str);
::swap(_size, s._size);
::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
// 拷贝构造 -- 左值
string(const string& s)
:_str(nullptr)
{
cout << "string(const string& s) -- 深拷贝" << endl;
_str = new char[s._capacity+1];
strcpy(_str, s._str);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
// 拷贝赋值
// s2 = tmp
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
cout << "string& operator=(const string& s) -- 深拷贝" << endl;
string tmp(s);
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void push_back(char ch)
{
if (_size >= _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
//string operator+=(char ch)
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
private:
char* _str = nullptr;
size_t _size = 0;
size_t _capacity = 0; // 不包含最后做标识的\0
};
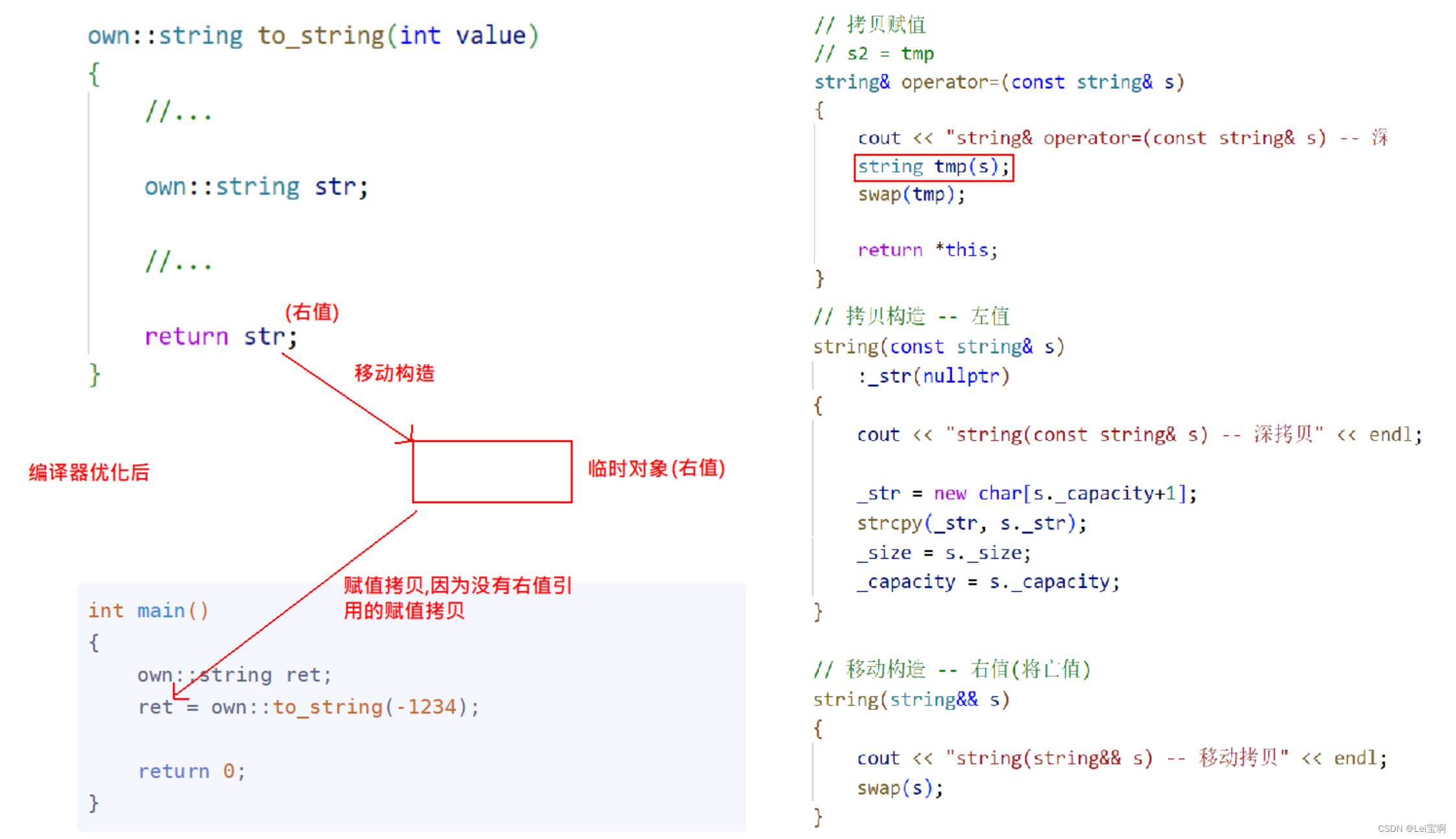
own::string to_string(int value)
{
bool flag = true;
if (value < 0)
{
flag = false;
value = 0 - value;
}
own::string str;
while (value > 0)
{
int x = value % 10;
value /= 10;
str += ('0' + x);
}
if (flag == false)
{
str += '-';
}
std::reverse(str.begin(), str.end());
return str;
}
}
这里博主使用g++编译器,并且关闭了部分优化,在Visual Studio 2022中,优化非常大,我们看不出他的过程,无法更好地进行对比,所以这里在Linux下进行演示,并使用-fno-elide-constructors关闭g++的编译优化。
举例一:仅有左值引用
一:
int main()
{
own::string ret = own::to_string(1234);
return 0;
}
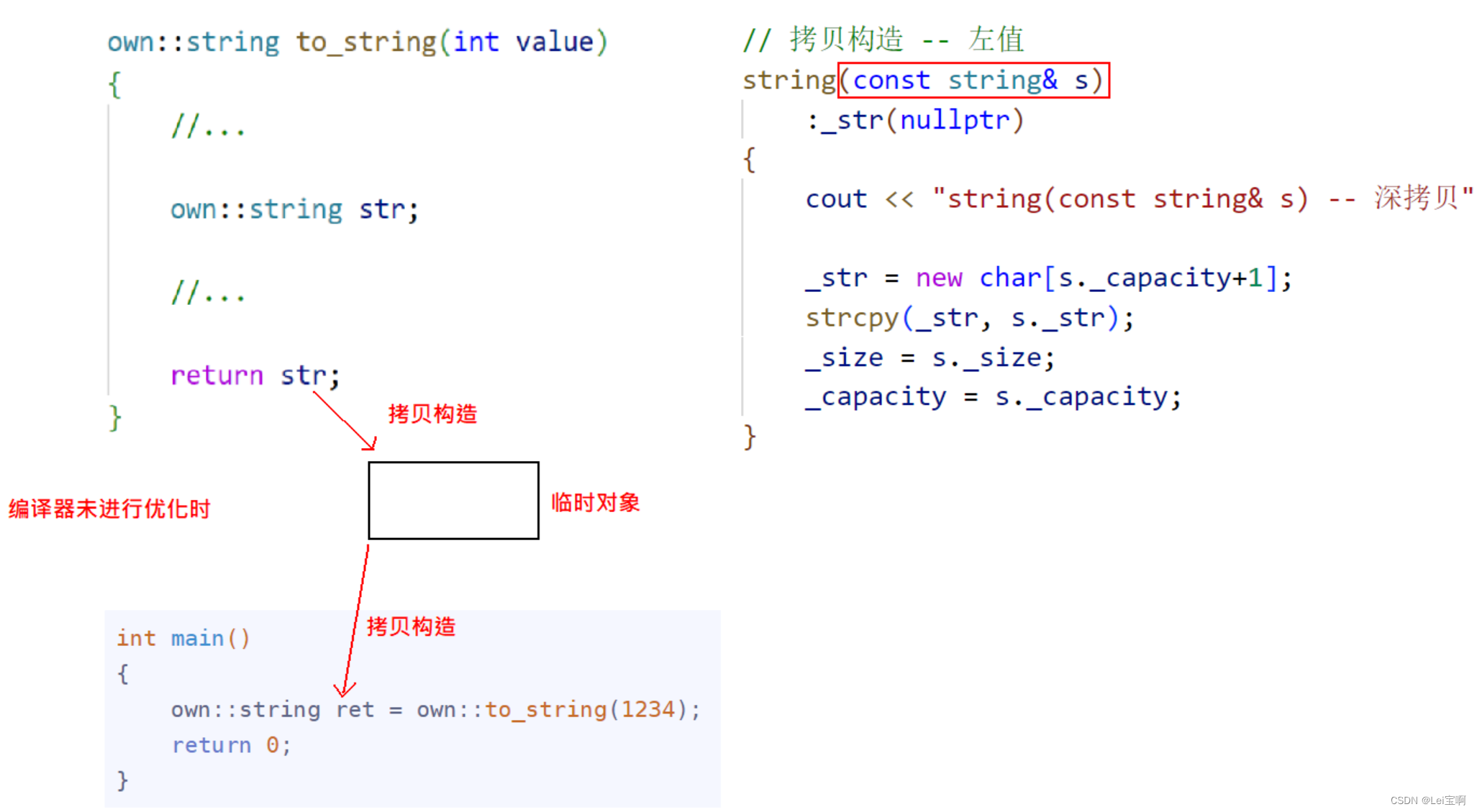
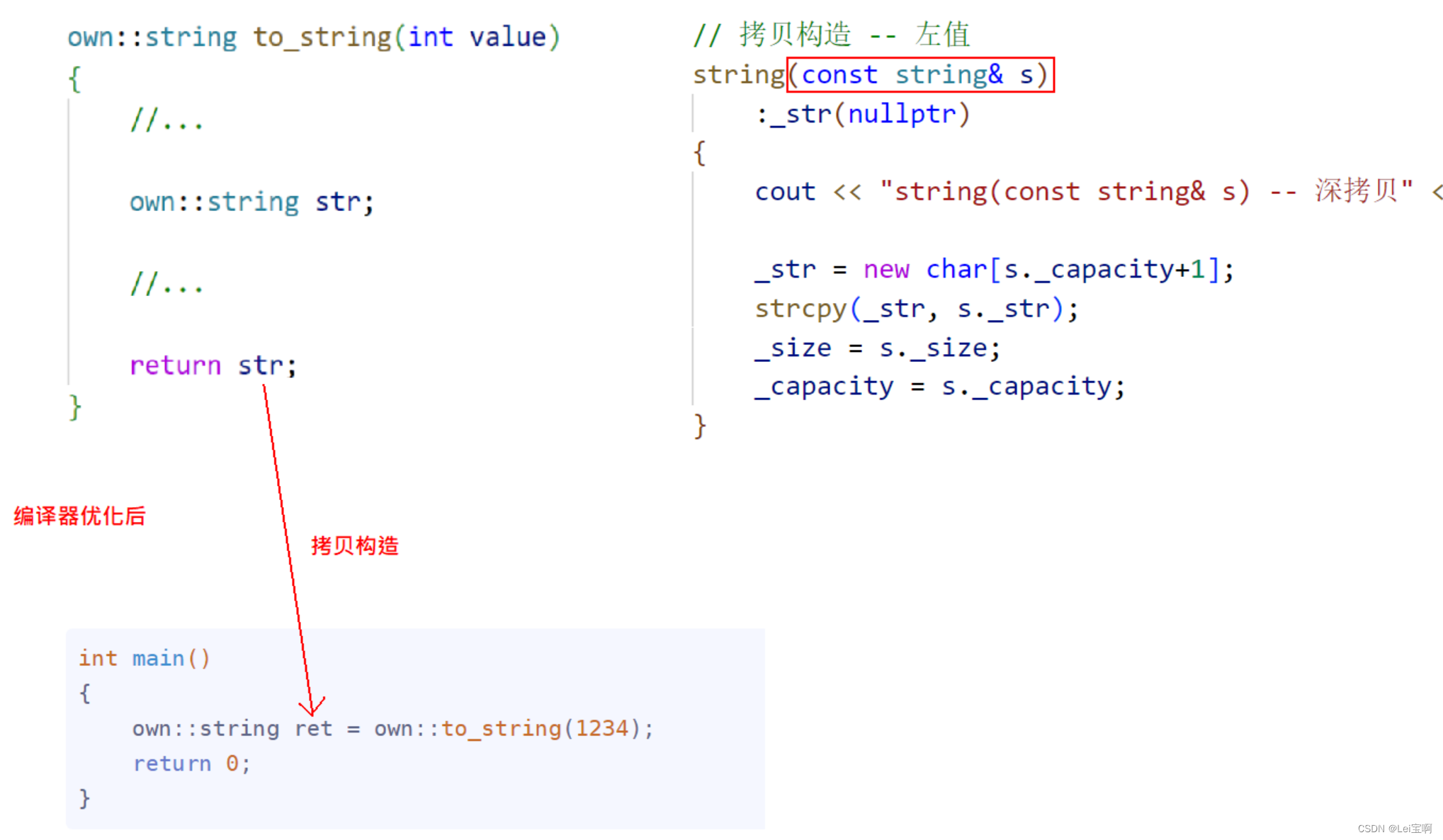
这也就是我们上面得出的结果。
二:
int main()
{
own::string ret;
ret = own::to_string(-1234);
return 0;
}
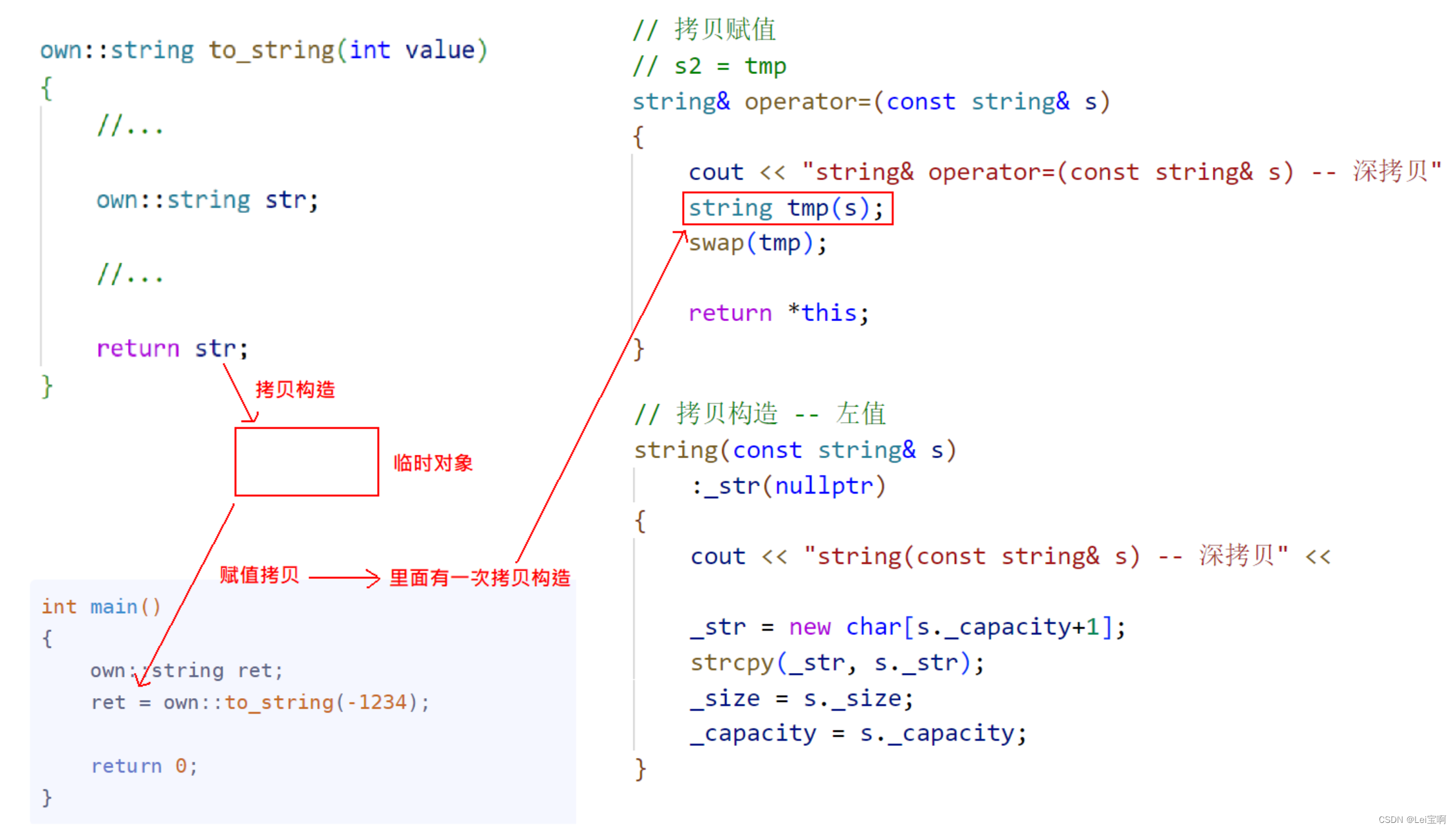 这种编译器是不会优化的,所以一般来说将他们写在一行上。
这种编译器是不会优化的,所以一般来说将他们写在一行上。
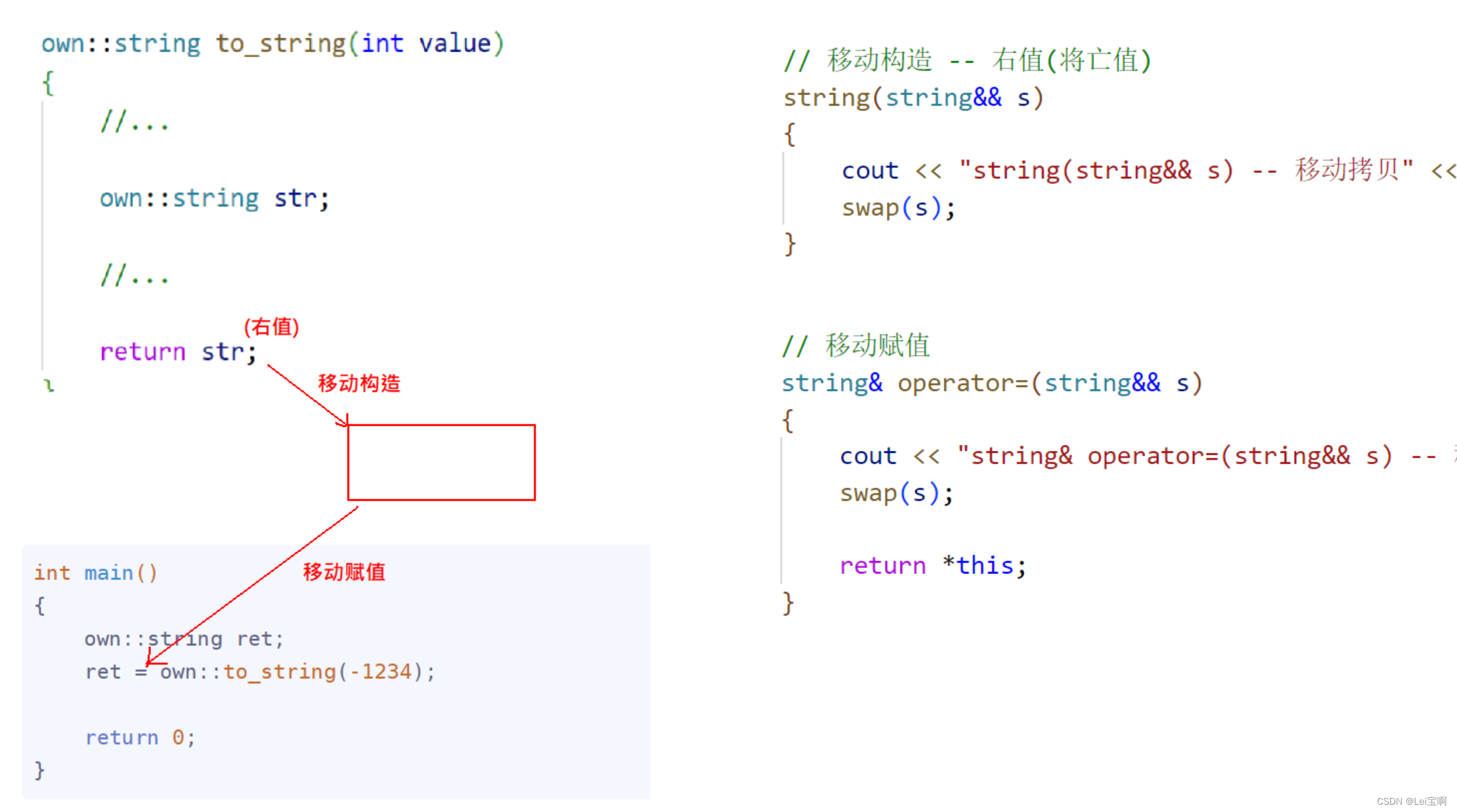
举例二:加入右值引用
// 移动构造 -- 右值(将亡值)
string(string&& s)
{
cout << "string(string&& s) -- 移动拷贝" << endl;
swap(s);
}
我们这里为什么要加入右值引用呢?首先,右值也叫做将亡值,也就是即将销毁的值。我们希望能够将这个将亡值利用起来,拿走他的资源。
我们可以想象一下,可以拿走左值的资源吗?左值引用左值,左值可能仍要被使用,如果这么被swap拿走资源是不可以的,但是将亡值,也就是对右值这样做却是我们希望看到的。
一:
int main()
{
own::string ret = own::to_string(1234);
return 0;
}
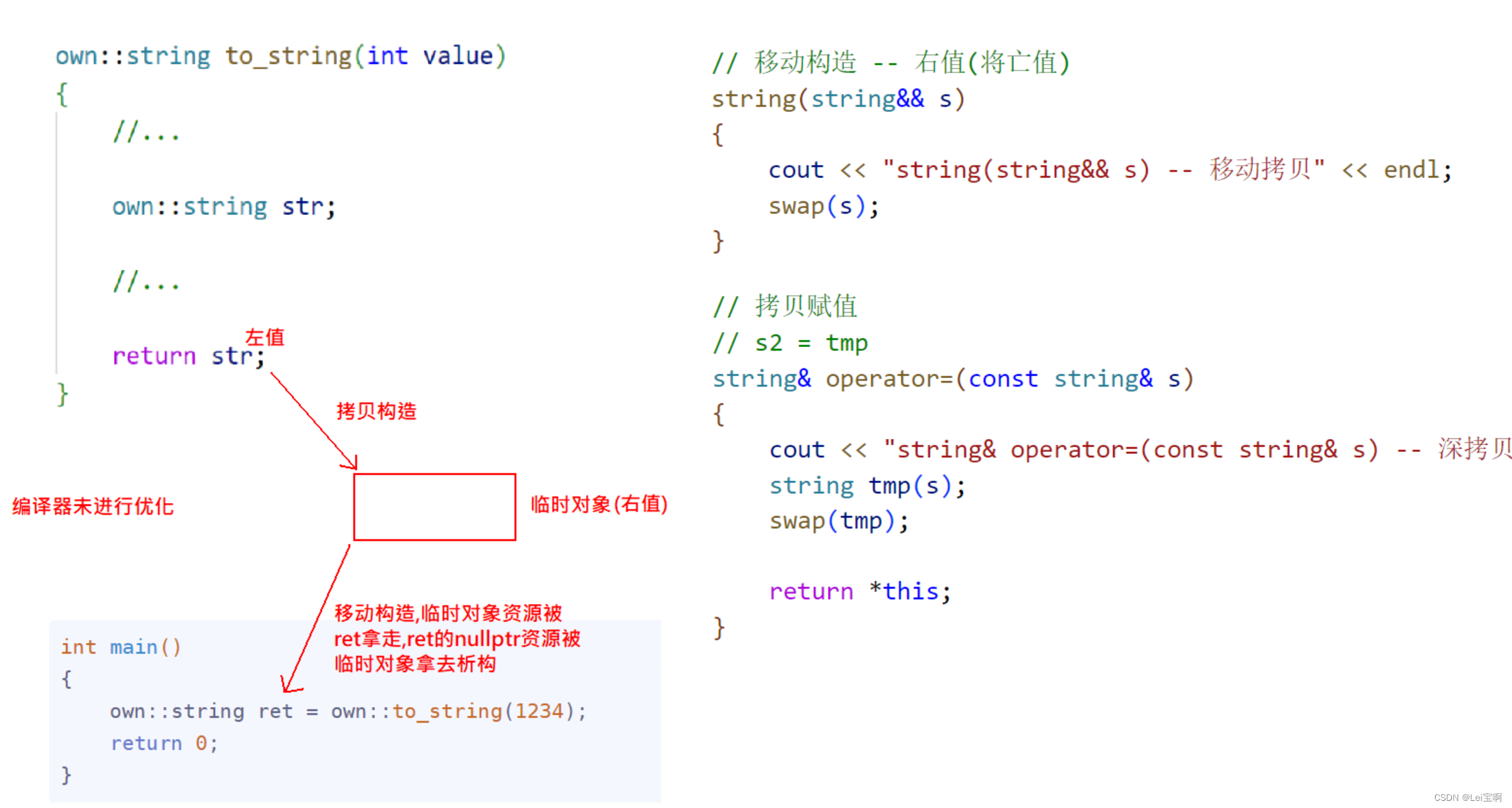

这和我们上面的结果是一致的。
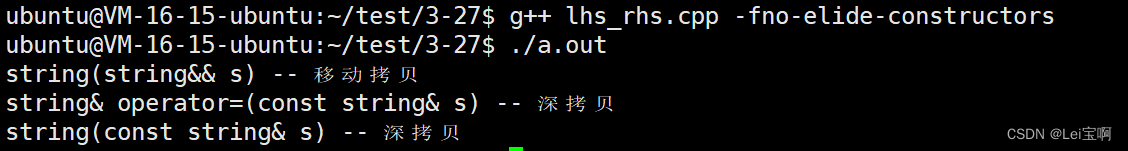
二:
int main()
{
own::string ret;
ret = own::to_string(-1234);
return 0;
}
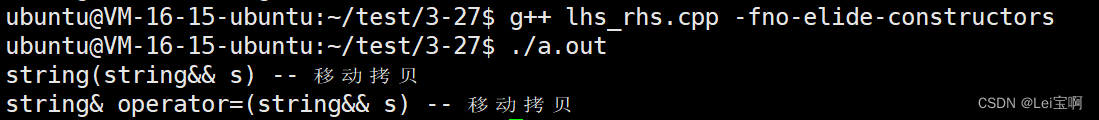
加入移动赋值拷贝
// 移动赋值
string& operator=(string&& s)
{
cout << "string& operator=(string&& s) -- 移动拷贝" << endl;
swap(s);
return *this;
}三:
int main()
{
own::string ret;
ret = own::to_string(-1234);
return 0;
}
看了这么久也许你有一个疑惑,移动构造和移动赋值,都要交换右值的资源,但是右值不是不能被修改吗?
那么这里我们说:右值引用 引用右值后的属性为左值。
也就是说,一个右值,被右值引用后,那个右值引用的属性将变成左值,于是swap中的s属性是左值,也就可以传过去了。























 659
659











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










