Thrift指南:http://diwakergupta.github.io/thrift-missing-guide/
Defining Services
service Twitter {
// A method definition looks like C code. It has a return type, arguments,
void ping(),
// The 'oneway' modifier indicates that the client only makes a request and does not wait for any response at all.
oneway void zip()
}
在strom.thrift中找到
service Nimbus {
void submitTopology(1: string name, 2: stringuploadedJarLocation, 3: string jsonConf, 4: StormTopology topology) throws (1:AlreadyAliveException e, 2: InvalidTopologyException ite);
void killTopology(1: string name) throws (1:NotAliveException e);
void activate(1: string name) throws (1:NotAliveException e);
string beginFileUpload();
void uploadChunk(1: string location, 2:binary chunk);
void finishFileUpload(1: string location);
// returns json
string getNimbusConf();
// stats functions
ClusterSummary getClusterInfo();
TopologyInfo getTopologyInfo(1: string id)throws (1: NotAliveException e);
//returns json
string getTopologyConf(1: string id) throws(1: NotAliveException e);
StormTopology getTopology(1: string id)throws (1: NotAliveException e);
StormTopology getUserTopology(1: string id)throws (1: NotAliveException e);
}
客户端:backtype.storm.generated.Nimbus的iface接口
服务器端:backtype.storm.daemon.nimbus.cljservice-handler (reify Nimbus$Iface
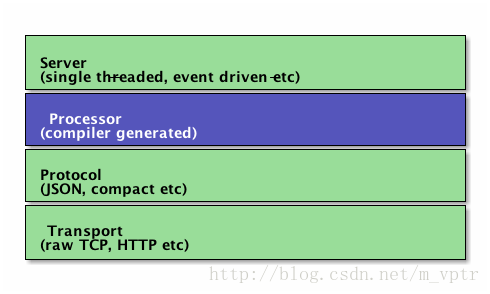
Thrift network stack:
The Transport layer provides a simpleabstraction for reading/writing from/to the network. This enables Thrift todecouple the underlying transport from the rest of the system(serialization/deserialization, for instance).
//org.apache.thrift7.transport.TTransport
The Protocol abstraction defines a mechanism tomap in-memory data structures to a wire-format. In other words, a protocolspecifies how datatypes use the underlying Transport to encode/decodethemselves.
//org.apache.thrift7.protocol.TProtocol接口
A Processor encapsulates the ability toread data from input streams and write to output streams. The input and outputstreams are represented by Protocol objects.
//org.apache.thrift7.TProcessor
public interfaceTProcessor{
bool process(TProtocol in, TProtocol out)throws TException
}
Service-specific processor implementations aregeneratedby the compiler. The Processor essentially reads data from the wire (using theinput protocol),delegatesprocessing to thehandler(implemented by the user) and writes theresponseover the wire (using the output protocol).
A Server pullstogether all of the various features described above:
· Create a transport
· Create input/outputprotocols for the transport
· Create a processorbased on the input/output protocols
· Wait for incomingconnections and hand them off to the processor
服务器端Server的代码:
(defnlaunch-server! [conf nimbus]
(validate-distributed-mode! conf)
(let[service-handler(service-handler confnimbus)
options (->(TNonblockingServerSocket.(int(conf NIMBUS-THRIFT-PORT)))
(THsHaServer$Args.) //主
(.workerThreads 64)->args.workerThreads
(.protocolFactory(TBinaryProtocol$Factory.))
(.processor(Nimbus$Processor. service-handler))
)
server (THsHaServer. options)] ->newTHsHaServer(Args -> THsHaServer$Args)
与网络栈的对应关系:
Server->THsHaServer
Processor -> Nimbus$Processor
Protocol ->TBinaryProtocol
Transport -> TNonblockingServerSocket
参考文档:
Thrift指南:http://diwakergupta.github.io/thrift-missing-guide/
























 4928
4928

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








