前言
在 C++ 中有个扩展库 ext,里面有一些黑科技(hash, splay, binomial_heap 等等),
在 Windows 环境中,我们运行 Dev-C++ 并在头文件写 #include<bits/extc++.h> 时,经常会收到 [Error] iconv.h: No such file or directory 的编译报错。
所以为了代替他,我们会写很多
#include<ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>#include<ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>诸如此类。这不失为一个解决方案,但是万能头显然更加方便快捷。
现在我们来试着解决这个问题。
Step 1
找到您电脑上头文件的存储位置。通常为 C:\Program Files (x86)\Dev-Cpp\MinGW64\lib\gcc\x86_64-w64-mingw32\4.9.2\include\c++。
如果找不到可以新建一个 cpp 文件,开头写上 #include<iostream> 然后 Ctrl+左键点一下就可以知道文件目录了。
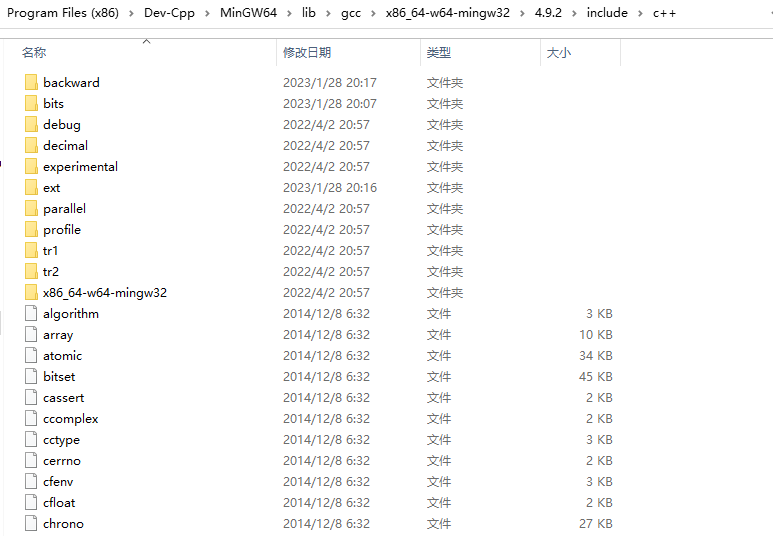
Step 2
在此目录下新建一个 iconv.h 文件,把下列内容复制进去:
/* Copyright (C) 1999-2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This file is part of the GNU LIBICONV Library.
The GNU LIBICONV Library is free software; you can redistribute it
and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Library General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2
of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
The GNU LIBICONV Library is distributed in the hope that it will be
useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Library General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Library General Public
License along with the GNU LIBICONV Library; see the file COPYING.LIB.
If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. *//* When installed, this file is called "iconv.h". */#ifndef_LIBICONV_H#define_LIBICONV_H#define_LIBICONV_VERSION0x0110/* version number: (major<<8) + minor */extern__declspec(dllimport)int _libiconv_version;/* Likewise *//* We would like to #include any system header file which could define
iconv_t, 1. in order to eliminate the risk that the user gets compilation
errors because some other system header file includes /usr/include/iconv.h
which defines iconv_t or declares iconv after this file, 2. when compiling
for LIBICONV_PLUG, we need the proper iconv_t type in order to produce
binary compatible code.
But gcc's #include_next is not portable. Thus, once libiconv's iconv.h
has been installed in /usr/local/include, there is no way any more to
include the original /usr/include/iconv.h. We simply have to get away
without it.
Ad 1. The risk that a system header file does
#include "iconv.h" or #include_next "iconv.h"
is small. They all do #include <iconv.h>.
Ad 2. The iconv_t type is a pointer type in all cases I have seen. (It
has to be a scalar type because (iconv_t)(-1) is a possible return value
from iconv_open().) *//* Define iconv_t ourselves. */#undeficonv_t#defineiconv_tlibiconv_ttypedefvoid* iconv_t;/* Get size_t declaration.
Get wchar_t declaration if it exists. */#include<stddef.h>/* Get errno declaration and values. */#include<errno.h>/* Some systems, like SunOS 4, don't have EILSEQ. Some systems, like BSD/OS,
have EILSEQ in a different header. On these systems, define EILSEQ
ourselves. */#ifndefEILSEQ#defineEILSEQ#endif#ifdef__cplusplusextern"C"{#endif/* Allocates descriptor for code conversion from encoding ‘fromcode’ to
encoding ‘tocode’. */#ifndefLIBICONV_PLUG#defineiconv_openlibiconv_open#endifextern iconv_t iconv_open(constchar* tocode,constchar* fromcode);/* Converts, using conversion descriptor ‘cd’, at most ‘*inbytesleft’ bytes
starting at ‘*inbuf’, writing at most ‘*outbytesleft’ bytes starting at
‘*outbuf’.
Decrements ‘*inbytesleft’ and increments ‘*inbuf’ by the same amount.
Decrements ‘*outbytesleft’ and increments ‘*outbuf’ by the same amount. */#ifndefLIBICONV_PLUG#defineiconvlibiconv#endifextern size_t iconv(iconv_t cd,char** inbuf, size_t *inbytesleft,char** outbuf, size_t *outbytesleft);/* Frees resources allocated for conversion descriptor ‘cd’. */#ifndefLIBICONV_PLUG#defineiconv_closelibiconv_close#endifexterninticonv_close(iconv_t cd);#ifdef__cplusplus}#endif#ifndefLIBICONV_PLUG/* Nonstandard extensions. */#if1#if0/* Tru64 with Desktop Toolkit C has a bug: <stdio.h> must be included before
<wchar.h>.
BSD/OS 4.0.1 has a bug: <stddef.h>, <stdio.h> and <time.h> must be
included before <wchar.h>. */#include<stddef.h>#include<stdio.h>#include<time.h>#endif#include<wchar.h>#endif#ifdef__cplusplusextern"C"{#endif/* A type that holds all memory needed by a conversion descriptor.
A pointer to such an object can be used as an iconv_t. */typedefstruct{void* dummy1[28];#if1
mbstate_t dummy2;#endif} iconv_allocation_t;/* Allocates descriptor for code conversion from encoding ‘fromcode’ to
encoding ‘tocode’ into preallocated memory. Returns an error indicator
(0 or -1 with errno set). */#defineiconv_open_intolibiconv_open_intoexterninticonv_open_into(constchar* tocode,constchar* fromcode,
iconv_allocation_t* resultp);/* Control of attributes. */#defineiconvctllibiconvctlexterninticonvctl(iconv_t cd,int request,void* argument);/* Hook performed after every successful conversion of a Unicode character. */typedefvoid(*iconv_unicode_char_hook)(unsignedint uc,void* data);/* Hook performed after every successful conversion of a wide character. */typedefvoid(*iconv_wide_char_hook)(wchar_t wc,void* data);/* Set of hooks. */structiconv_hooks{
iconv_unicode_char_hook uc_hook;
iconv_wide_char_hook wc_hook;void* data;};/* Fallback function. Invoked when a small number of bytes could not be
converted to a Unicode character. This function should process all
bytes from inbuf and may produce replacement Unicode characters by calling
the write_replacement callback repeatedly. */typedefvoid(*iconv_unicode_mb_to_uc_fallback)(constchar* inbuf, size_t inbufsize,void(*write_replacement)(constunsignedint*buf, size_t buflen,void* callback_arg),void* callback_arg,void* data);/* Fallback function. Invoked when a Unicode character could not be converted
to the target encoding. This function should process the character and
may produce replacement bytes (in the target encoding) by calling the
write_replacement callback repeatedly. */typedefvoid(*iconv_unicode_uc_to_mb_fallback)(unsignedint code,void(*write_replacement)(constchar*buf, size_t buflen,void* callback_arg),void* callback_arg,void* data);#if1/* Fallback function. Invoked when a number of bytes could not be converted to
a wide character. This function should process all bytes from inbuf and may
produce replacement wide characters by calling the write_replacement
callback repeatedly. */typedefvoid(*iconv_wchar_mb_to_wc_fallback)(constchar* inbuf, size_t inbufsize,void(*write_replacement)(constwchar_t*buf, size_t buflen,void* callback_arg),void* callback_arg,void* data);/* Fallback function. Invoked when a wide character could not be converted to
the target encoding. This function should process the character and may
produce replacement bytes (in the target encoding) by calling the
write_replacement callback repeatedly. */typedefvoid(*iconv_wchar_wc_to_mb_fallback)(wchar_t code,void(*write_replacement)(constchar*buf, size_t buflen,void* callback_arg),void* callback_arg,void* data);#else/* If the wchar_t type does not exist, these two fallback functions are never
invoked. Their argument list therefore does not matter. */typedefvoid(*iconv_wchar_mb_to_wc_fallback)();typedefvoid(*iconv_wchar_wc_to_mb_fallback)();#endif/* Set of fallbacks. */structiconv_fallbacks{
iconv_unicode_mb_to_uc_fallback mb_to_uc_fallback;
iconv_unicode_uc_to_mb_fallback uc_to_mb_fallback;
iconv_wchar_mb_to_wc_fallback mb_to_wc_fallback;
iconv_wchar_wc_to_mb_fallback wc_to_mb_fallback;void* data;};/* Requests for iconvctl. */#defineICONV_TRIVIALP0/* int *argument */#defineICONV_GET_TRANSLITERATE1/* int *argument */#defineICONV_SET_TRANSLITERATE2/* const int *argument */#defineICONV_GET_DISCARD_ILSEQ3/* int *argument */#defineICONV_SET_DISCARD_ILSEQ4/* const int *argument */#defineICONV_SET_HOOKS5/* const struct iconv_hooks *argument */#defineICONV_SET_FALLBACKS6/* const struct iconv_fallbacks *argument *//* Listing of locale independent encodings. */#defineiconvlistlibiconvlistexternvoidiconvlist(int(*do_one)(unsignedint namescount,constchar*const* names,void* data),void* data);/* Canonicalize an encoding name.
The result is either a canonical encoding name, or name itself. */externconstchar*iconv_canonicalize(constchar* name);/* Support for relocatable packages. *//* Sets the original and the current installation prefix of the package.
Relocation simply replaces a pathname starting with the original prefix
by the corresponding pathname with the current prefix instead. Both
prefixes should be directory names without trailing slash (i.e. use ""
instead of "/"). */externvoidlibiconv_set_relocation_prefix(constchar*orig_prefix,constchar*curr_prefix);#ifdef__cplusplus}#endif#endif#endif/* _LIBICONV_H */Step 3
保存。再次编译时可以顺利通过。
使用 critical 子句,使用这个子句主要是用于创建临界区和 OpenMP 提供的运行时库函数的作用是一致的,只不过这种方法是直接通过编译指导语句实现的,更加方便一点,加锁和解锁的过程编译器会帮我们实现。
使用 atomic 指令,这个主要是通过原子指令,主要是有处理器提供的一些原子指令实现的。
OpenMP 给我们提供了 omp_lock_t 和 omp_nest_lock_t 两种数据结构实现简单锁和可重入锁。
在本篇文章当中主要讨论 OpenMP 当中的互斥操作,在下一篇文章当中主要讨论 OpenMP 当中原子操作的实现原理,并且查看程序编译之后的汇编指令。
自定义线程之间的同步 barrier
在实际的写程序的过程当中我们可能会有一种需求就是需要等待所有的线程都执行完成之才能够进行后面的操作,这个时候我们就可以自己使用 barrier 来实现这个需求了。
比如我们要实现下面的一个计算式:
data=1!+2!+...+n!n
现在我们计算 n = 16 的时候上面的表达式的值:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <omp.h>
int factorial(int n)
{
int s = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
s *= i;
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
int data[16];
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(16) default(none) shared(data)
{
int id = omp_get_thread_num();
data[id] = factorial(id + 1);
// 等待上面所有的线程都完成的阶乘的计算
#pragma omp barrier
long sum = 0;
#pragma omp single
{
for(int i = 0; i < 16; ++i)
{
sum += data[i];
}
printf("final value = %lf\n", (double) sum / 16);
}
}
return 0;
}在上面的代码当中我们首先让 16 个线程都计算完成对应的阶乘结果之后然后在求和进行除法操作,因此在进行除法操作之前就需要将所有的阶乘计算完成,在这里我们就可以使用 #pragma omp barrier 让所有的线程到达这个同步点之后才继续完成后执行,这样就保证了在进行后面的任务的时候所有线程计算阶乘的任务已经完成。
定义临界区 critical
在并发程序当中我们经常会有这样的需求,比如不同的线程需要对同一个数据进行求和操作,当然这个操作我们也可以通过 atomic constuct 来完成,但是在本篇文章当中我们使用临界区来完成,在下一篇完成当中我们将仔细分析 OpenMP 当中的原子操作。
比如我们现在有一个数据 data,然后每个线程需要对这个数据进行加操作。























 5617
5617











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










