Dynamic DNS (DDNS)? -How it Works and Why Use It?
Dynamic DNS keeps DNS records automatically up to date when an IP address changes.
Dynamic DNS is used in large networks that host internal services, and use their own internal DNS and DHCP servers.
However small companies, and home networks don’t normally have their own DNS server so why would they need Dynamic DNS ?
In this tutorial we look at how dynamic DNS works and how to set it up on a home router.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) -Setup and Use
Dynamic DNS Services are used by small companies and individuals when they want to publish a service on the Internet, and that service is hosted within an internal or home network.
Home networks typically uses a NAT router to connect to the internet which means that devices located on the internal network aren’t accessible from the Internet.
In the following discussion we are going to assume that we want to make a web server located on an internal server available on the internet.
The network diagram below shows the configuration
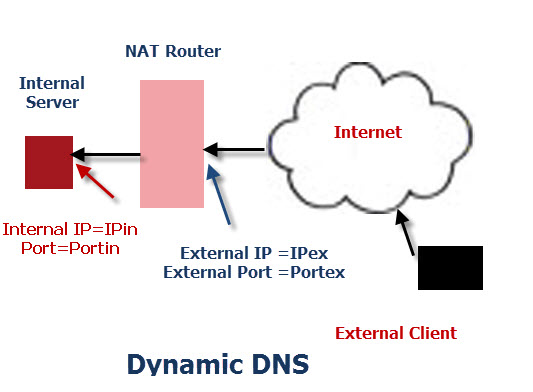
The Internal IP address is assigned to the internal server by the NAT router and via the DHCP service.
However when making a service available on the Internet we will usually give it a static internal IP address.
To make the web service available on the internet we use a technique called port forwarding ( see the port forwarding and Internal vs external IP address tutorials for more details).
Now our web server appears to our external client to be located at IPex and on port Portex.
If we put some typical numbers into this we will see our web server at
Ip Address= 81.157.34.43 and on Port 80
All we need now do is to tell our external client to use these values.
However the external IP address IPex (81.157.34.43) may also be dynamically assigned by the ISP, and we cannot make it static unless we pay for a static address.
In addition, the external client has to remember the IP address.
Dynamic DNS Service
If we now introduce a Dynamic DNS service into the picture.
With Dynamic DNS we assign the web server a name which we can then give to external clients. -This name is fixed and provided by the DDNS service provider.
We then assign the external IP address to the name.
Now because this external IP address will change periodically we will need to update the DNS record periodically.
We could of course do this manually, but that would be very unreliable as you don’t know when it has changed unless you check.
Instead the ability to automatically update the DNS server records is built into most NAT routers.
Here is a screen shot of the Dynamic DNS configuration page of my NAT router (BT Home Hub).
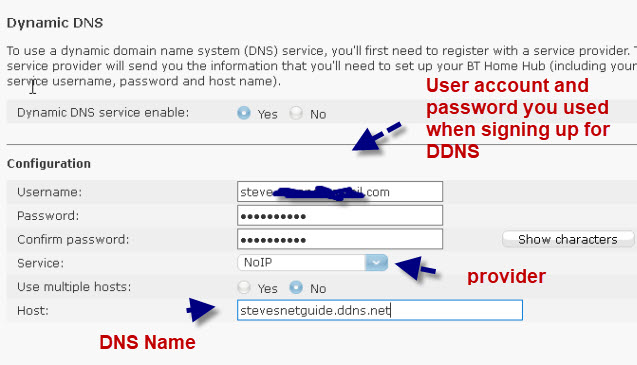
The configuration involves entering the name of your DDNS service provider and your login details.
When you apply it you should get a connected confirmation.
![]()
If you get username/password incorrect check you login details and retry.
Registering with a DDNS Service Provider
Before you can enable Dynamic DNS you will need an account from a DDNS provider.
There are several providers available. Most provide a free service with a premium upgrade.
The main providers all work in a similar way and the registration process is simple.For this tutorial I will use NO-IP.
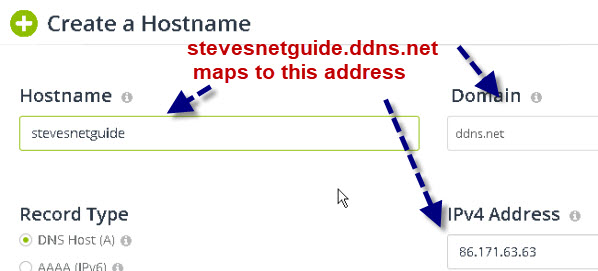
You will need to create a host name for the IP address, and select from one of the available domain names provided by the provider, and enter a hostname.
Below is the name form for No-IP
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) Not Supported on Router!
If your router doesn’t support DDNS updates you can get a DDNS client that you install on a machine on your local network that does the same job.
The only problem with this approach is that the machine needs to be constantly running.
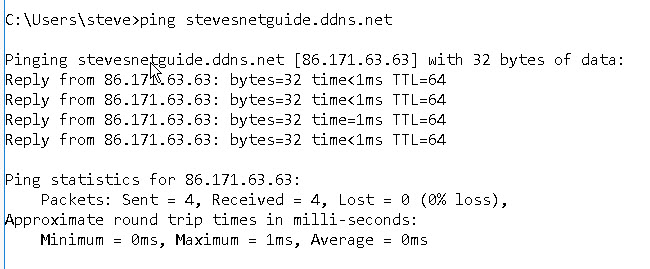
Testing Your configuration
Go to the ping command and test that you can access the IP address by pinging the domain name which consists of the hostname +domain name.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) Video
Here is a video that covers the above:
Common Uses
Although it is used by gamers and tech Geeks it is probably going to see more widespread adoption in remote security/surveillance and control areas.
Without Dynamic DNS how would you access your cameras from the Internet?
Common Questions and Answers
Q-What is the difference between dynamic DNS (DDNS) and DNS?
A- Dynamic DNS is a feature of DNS. Early DNS systems were static and the IP addresses and name mapping were entered manually. Dynamic DNS updates the Name- IP mappings automatically when it changes.
Q- How do I find my external IP address?
A- Go to Google an type what’s my IP address.

Q- Do I need DDNS?
A- Normally no. You only need it when providing services to Internet based clients
Q- Is Dynamic DDNS the same as port forwarding?
A- No- port forwarding makes a service available on an Internet address (external address). DDNS assigns a name to this external address and updates if the address changes.
Q- Does Dynamic DNS use the same port as DNS?
A- yes udp/tcp port 53
Summary
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is very useful if you need to access internal network services from across the Internet.
It isn’t designed for hosting a business website, for that you will need standard web hosting.
Related Articles and Resources:
- DNS for Beginners
- DHCP for Beginners
- Access your Home Network from Anywhere
- Video- Setting up DDNS on Security camera
- NO-IP DDNS provider
Please Let me Know if you found it Useful























 1321
1321

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








