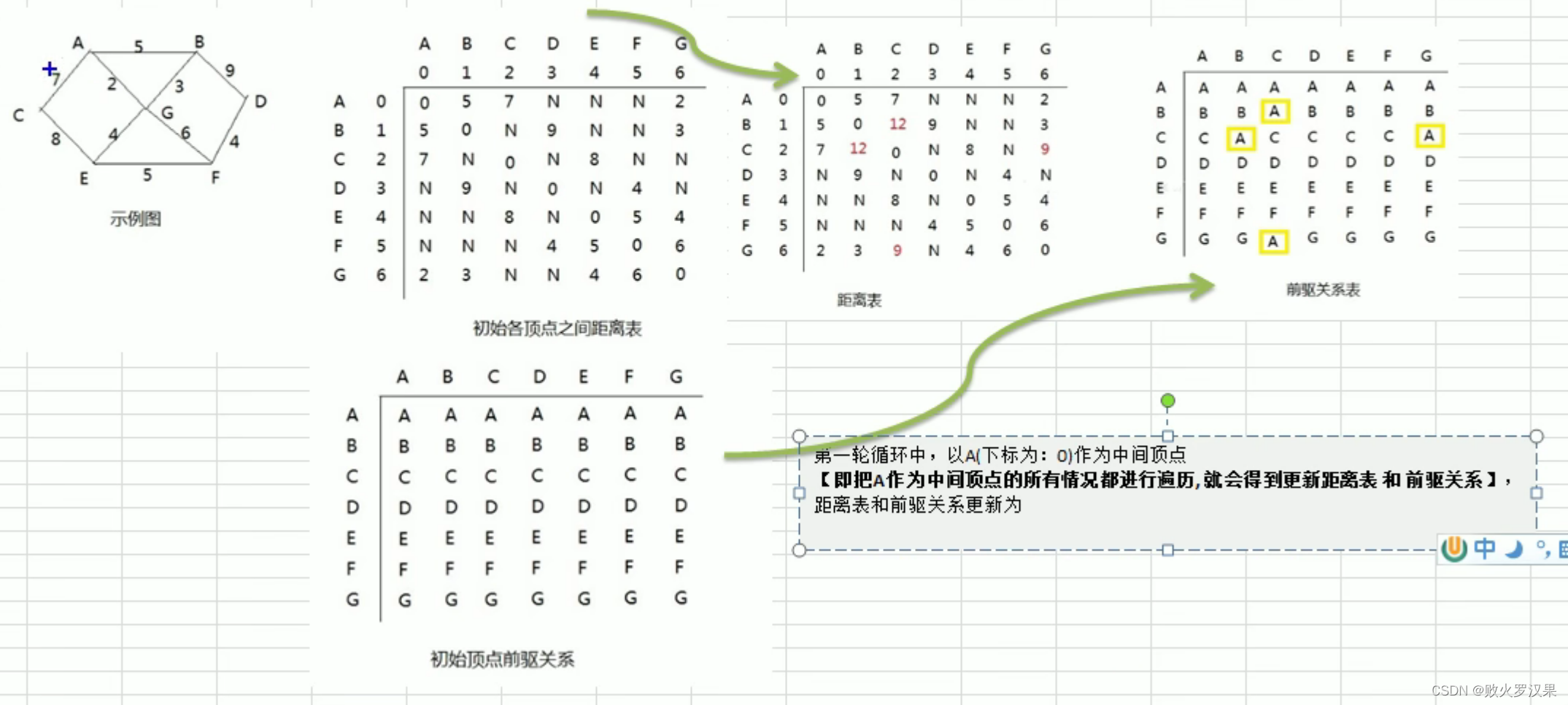
九、弗洛伊德算法

代码实现:
package Algorithm.Floyd;
public class Floyd {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] vertex = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G'};
int[][] matrix = new int[vertex.length][vertex.length];
final int N = 65535;//表示不可链接
matrix[0] = new int[]{0, 5, 7, N, N, N, 2};
matrix[1] = new int[]{5, 0, N, 9, N, N, 3};
matrix[2] = new int[]{7, N, 0, N, 8, N, N};
matrix[3] = new int[]{N, 9, N, 0, N, 4, N};
matrix[4] = new int[]{N, N, 8, N, 0, 5, 4};
matrix[5] = new int[]{N, N, N, 4, 5, 0, 6};
matrix[6] = new int[]{2, 3, N, N, 4, 6, 0};
Graph graph = new Graph(vertex.length, matrix, vertex);
// graph.show();
graph.floyd();
graph.show();
}
}
class Graph {
char[] vertex;//存放顶点的数组
int[][] pre;//保存到达目标顶点的前驱顶点
int[][] dis;//保存从各个顶点出发,到其他顶点的距离
public Graph(int length, int[][] matrix, char[] vertex) {//matrix是初始邻接矩阵,也是初始的dis
this.vertex = vertex;
this.dis = matrix;
this.pre = new int[length][length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
pre[i][j] = i;//存放前驱顶点的下标
}
}
}
public void show() {
for (int i = 0; i < dis.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < dis.length; j++) {
System.out.print(vertex[pre[i][j]]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < dis.length; j++) {
System.out.print(dis[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void floyd(){
int len = 0;//变量保存距离
//对中间顶点的遍历
for (int k = 0; k < dis.length; k++) {
//起始顶点
for (int i = 0; i < dis.length; i++) {
//目标顶点
for (int j = 0; j < dis.length; j++) {
len = dis[i][k]+dis[k][j];
if (len<dis[i][j]){
dis[i][j] = len;
pre[i][j] = pre[k][j];//更新前驱节点对应的下标,k不一定是直接前驱,所以pre[i][j]不能直接等于k
}
}
}
}
}
}
十、骑士周游问题

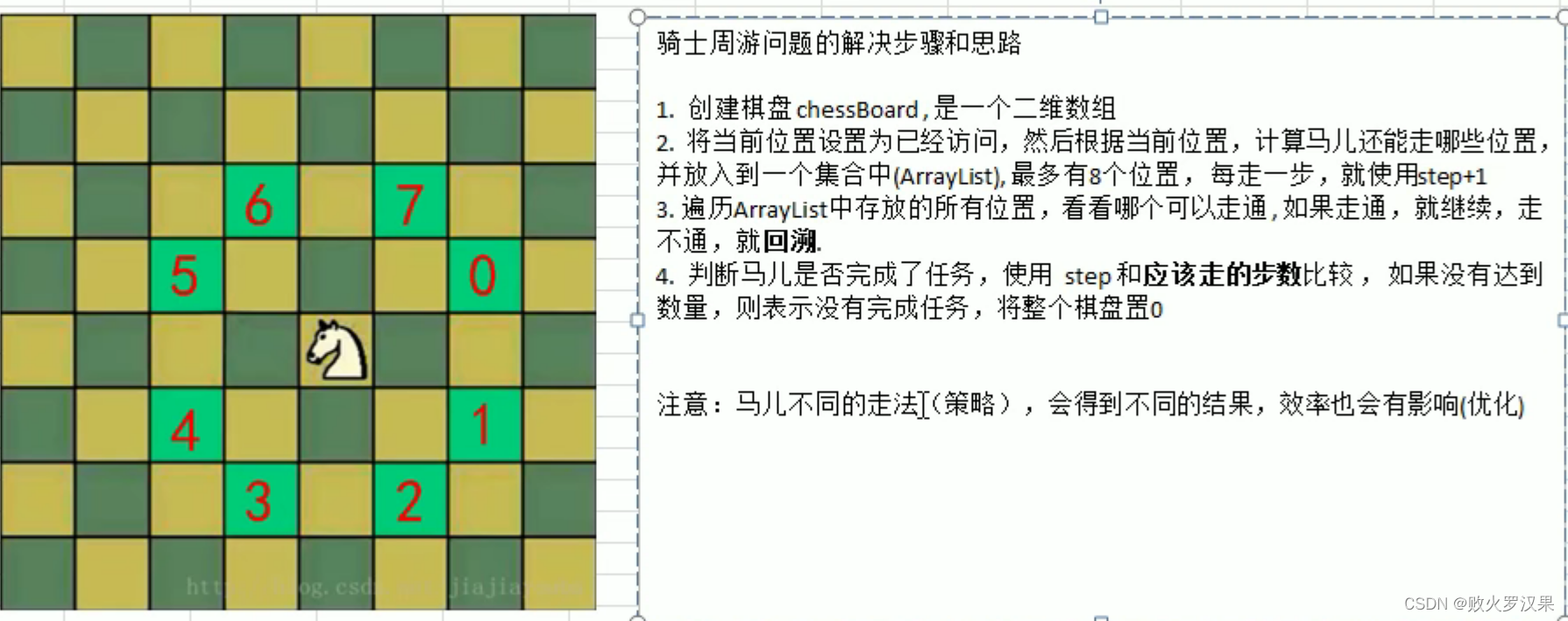
其他思路:不在同行同列同对角线的点
策略优化:选择下一步的下一步选择越少的,效率越高
代码实现:
package Algorithm.Horse;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Horse {
public static int X;//棋盘的列数
public static int Y;//棋盘的行数
public static boolean[] visited;
public static boolean finished;//判断棋盘是否所有位置都被访问成功
public static void main(String[] args) {
Y = 8;
X = 8;
int row = 1;
int column = 1;
int[][] board = new int[Y][X];
visited = new boolean[Y * X];
travel(board, row - 1, column - 1, 1);
for (int[] ints : board) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
}
//需要棋盘、马所在的行和列、当前是第几步
public static void travel(int[][] board, int row, int column, int step) {
board[row][column] = step;
visited[row * X + column] = true;//棋盘上的第多少个格子
//获取当前位置能走的下一个位置的集合
ArrayList<Point> ps = next(new Point(column, row));
sort(ps);
//核心:递归回溯
while (!ps.isEmpty()) {
Point p = ps.remove(0);
if (!visited[p.y * X + p.x]) {
travel(board, p.y, p.x, step + 1);
}
}
if (step < X * Y && !finished) {//任务没有完成,棋盘需要置0(在回溯过程中把每个点都置0了)
//step<X*Y成立的两种情况:1、棋盘目前还没走完 2、棋盘处于回溯
board[row][column] = 0;
visited[row * X + column] = false;
} else {
finished = true;
}
}
//根据当前位置计算马还能走哪些位置
public static ArrayList<Point> next(Point curPoint) {
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<>();//存储可走的点
Point p1 = new Point();
//代表左上角的点是可以走的(棋盘左上角是坐标原点)
//5
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//6
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//7
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//0
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//1
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//2
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//3
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//4
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
return ps;
}
//根据当前的下一步的选择位置进行非递减排序,减少回溯的可能
public static void sort(ArrayList<Point> ps){
ps.sort(new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point o1, Point o2) {
//获取到o1点的下一步的所有位置个数
// int count1 = next(o1).size();
// int count2 = next(o2).size();
// if (count1<count2){
// return -1;
// } else if (count1==count2){
// return 0;
// } else {
// return 1;
// }
return next(o1).size()-next(o2).size();
}
});
}
}






















 406
406











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








