1.概述
循环引用,顾名思义,N个class相互引用,即classB作为classA的属性、classA作为classB的属性【A.b、B.a】。
前提:充分理解Bean的生命周期中【实例化】和【初始化】
2.三级缓存
// 一级缓存
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
// 二级缓存
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
// 三级缓存
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name to ObjectFactory. */
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}3.核心方法
// 从Spring容器中获取单例
getBean
// 实际从Spring容器中获取单例
->doGetBean
// 从一二三级缓存中获取单例
->getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference)
// 从函数式中获取单例(回调函数lambda表达式)
->getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory)
// 创建Bean
->createBean
// 实际创建Bean
->doCreateBean
// 实例化Bean
->createBeanInstance
// 初始化Bean
->populateBean
// 赋值
->applyPropertyValues
->resolveValueIfNecessary
->resolveReference
->getBean递归
4.例证
public class A {
private String name;
private B b;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public B getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(B b) {
this.b = b;
}
}public class B {
private String name;
private A a;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public A getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(A a) {
this.a = a;
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="a" class="com.sh.basic.source.spring.A">
<property name="name" value="nameA"></property>
<property name="b" ref="b"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="b" class="com.sh.basic.source.spring.B">
<property name="name" value="nameB"></property>
<property name="a" ref="a"></property>
</bean>
</beans>5.流程 BeanDefinition中配置了两个类 先实例化A 再实例化B

5.1 获取A
5.1.1 getBean(a) 获取A
5.1.2 doGetBean(a)
5.1.3 getSingleton(a) 从三级缓存中获取对象
| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 二级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
5.1.4 getSingleton(a,lambda) 没有则创建A
5.1.5 doCreateBean实际创建BeanA
5.1.6 createBeanInstance 实例化A

5.1.7 addSingletonFactory 把A添加到三级缓存
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 二级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 有 | 无 |
5.1.8 populateBean填充属性 给成员变量赋值
5.1.9 applyPropertyValues 给A的成员变量赋值
5.1.10 resolveValueIfNecessary 给A的成员变量b赋值 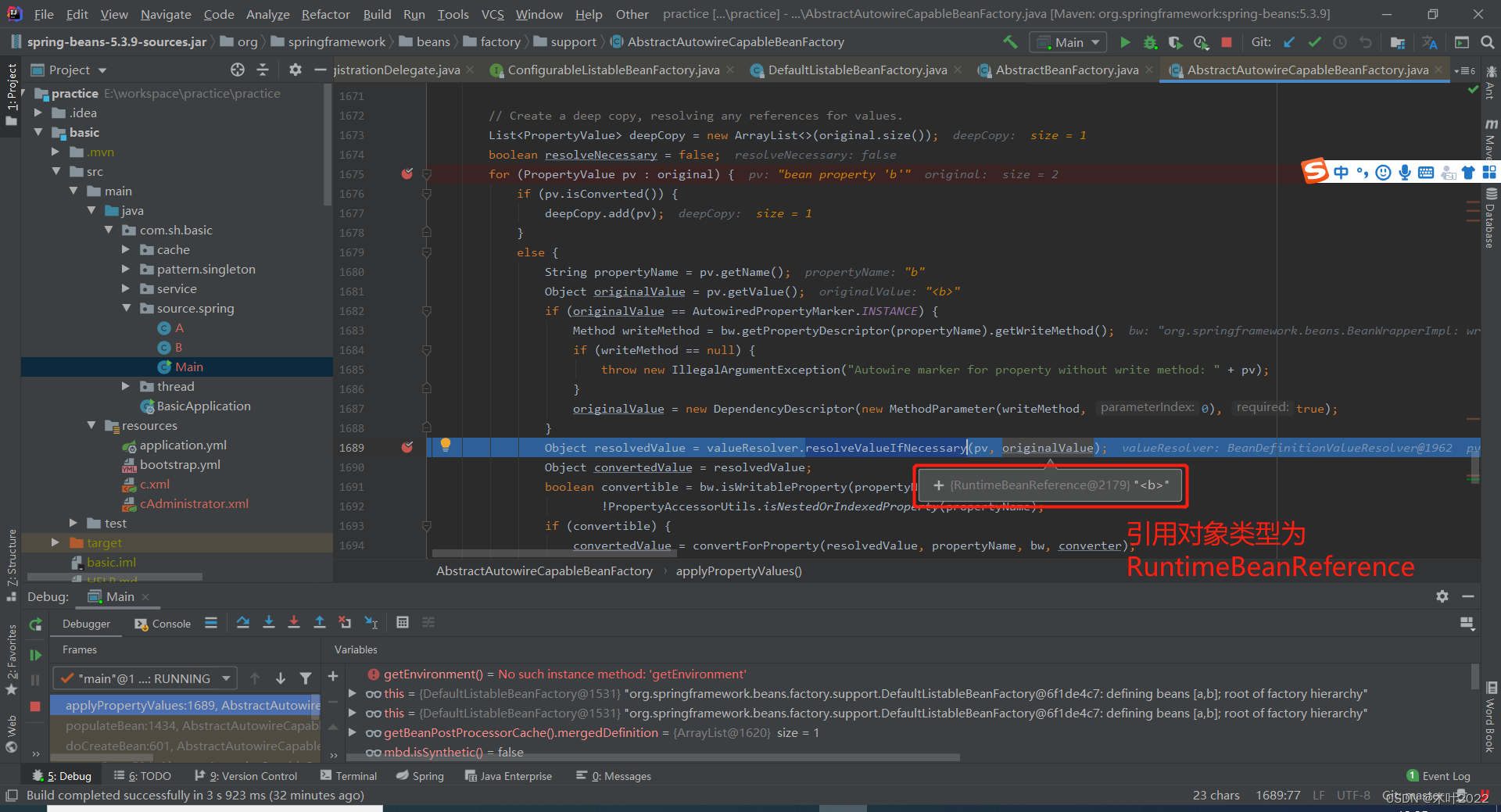
5.1.11 给A的成员变量b赋值时候递归调用getBean(b)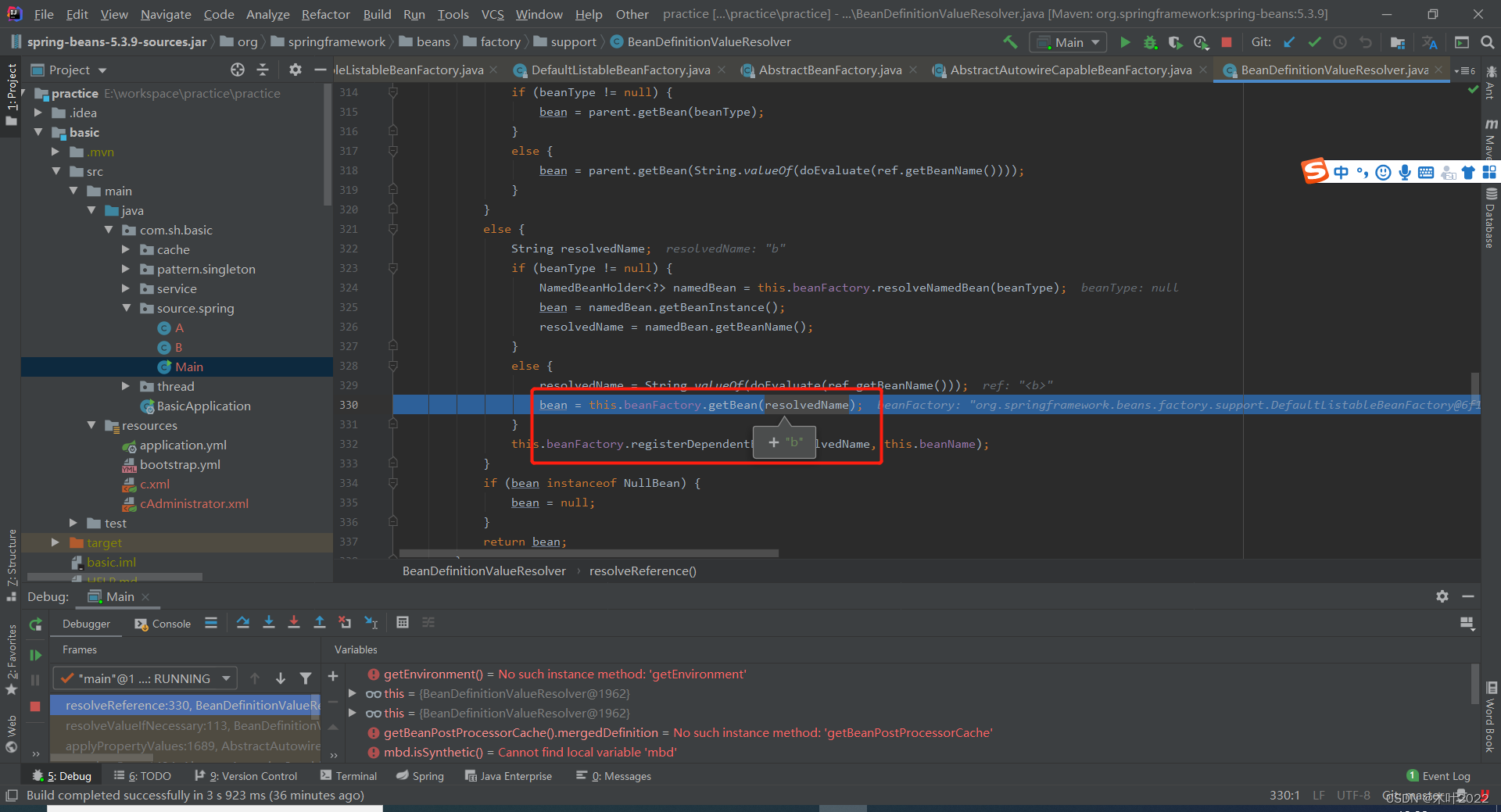
5.2 获取B
5.2.1 getBean(b)
5.2.2 doGetBean(b)
5.2.3 getSingleton(b) 从三级缓存中获取对象
5.2.4 getSingleton(b,lambda) 没有则创建B
5.2.5 doCreateBean实际创建BeanB
5.2.6 createBeanInstance 实例化B
5.2.7 addSingletonFactory 把B添加到三级缓存
| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 二级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 有 | 有 |
5.2.8 populateBean填充属性 给成员变量赋值
5.2.9 applyPropertyValues 给A的成员变量赋值
5.2.10 resolveValueIfNecessary 给A的成员变量b赋值
5.2.11 给B的成员变量a赋值时候递归调用getBean(a)
5.2.12 获取A并返回 三级缓存中存在a,将A加入到二级缓存中,且移出三级缓存
| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 二级缓存 | 有 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 无 | 有 |
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}6.回顾
※ 实例化A getBean(a)->填充属性之前将a添加到三级缓存
| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 二级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 有 | 无 |
但是A的属性中有个b 获取不到 则实例化B getBean(b)->填充属性之前将b添加到三级缓存
| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 二级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 有 | 有 |
但是B的属性中有个a 获取到 a从三级缓存中获取 获取成功则可以给B.a赋值
| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 无 | 无 |
| 二级缓存 | 有 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 有 | 有 |
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}获取a成功之后,即可以给B的a属性赋值,B变成一个完整对象 则addSingleton
| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 无 | 有 |
| 二级缓存 | 有 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 有 | 有 |
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}再回想一下当初为什么会调用到B对象呢,是因为实例化A.b的时候调用b的getBean
b.getBean调用完成之后,还需要给A.b属性赋值 A变成一个完整对象 则addSingleton
| 缓存 | a | b |
| 一级缓存 | 有 | 有 |
| 二级缓存 | 有 | 无 |
| 三级缓存 | 有 | 有 |
























 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








