转自:http://blog.csdn.net/aesop_wubo/article/details/9117655
为什么要使用选择器
通道处于就绪状态后,就可以在缓冲区之间传送数据。可以采用非阻塞模式来检查通道是否就绪,但非阻塞模式还会做别的任务,当有多个通道同时存在时,很难将检查通道是否就绪与其他任务剥离开来,或者说是这样做很复杂,即使完成了这样的功能,但每检查一次通道的就绪状态,就至少有一次系统调用,代价十分昂贵。当你轮询每个通道的就绪状态时,刚被检查的一个处于未就绪状态的通道,突然处于就绪状态,在下一次轮询之前是不会被察觉的。操作系统拥有这种检查就绪状态并通知就绪的能力,因此要充分利用操作系统提供的服务。在JAVA中,Selector类提供了这种抽象,拥有询问通道是否已经准备好执行每个I/0操作的能力,所以可以利用选择器来很好地解决以上问题。
如何使用选择器
使用选择器时,需要将一个或多个可选择的通道注册到选择器对象中,注册后会返回一个选择键,选择器会记住这些通道以及这些通道感兴趣的操作,还会追踪对应的通道是否已经就绪。调用选择器对象的select( )方法,当有通道就绪时,相关的键会被更新。可以获取选择键的集合,从而找到已经就绪的通道。
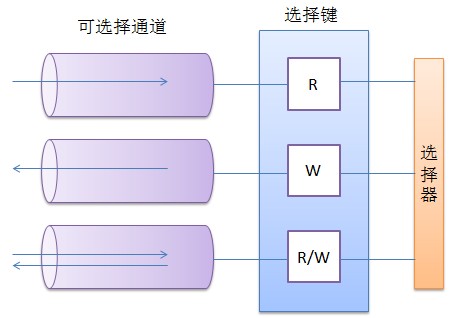
这里提到的选择器、选择键与可选择通道之间的关系如下图所示
先看一段使用选择器的代码
- ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open;
- serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
- serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
- Selector selector = Selector.open();
- serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
- while (true) {
- selector.select();
- Iterator<SelectionKey> itor = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
- while (itor.hasNext()) {
- SelectionKey key = itor.next();
- itor.remove();
- if (key.isAcceptable()) {
- ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
- SocketChannel channel = server.accept();
- channel.configureBlocking(false);
- channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes()));
- channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
- } else if (key.isReadable()) {
- //read();
- }
- }
- }
打开通道
从Selector源码中可以看到,open方法是交给selectorProvider处理的
- public static Selector open() throws IOException {
- return SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
- }
- //WindowsSelectorProvider.java
- public AbstractSelector openSelector() throws IOException {
- <span style="white-space:pre"> </span>return new WindowsSelectorImpl(this);
- }
- //WindowsSelectorImpl.java
- WindowsSelectorImpl(SelectorProvider sp) throws IOException {
- super(sp);
- pollWrapper = new PollArrayWrapper(INIT_CAP);
- wakeupPipe = Pipe.open();
- wakeupSourceFd = ((SelChImpl)wakeupPipe.source()).getFDVal();
- // Disable the Nagle algorithm so that the wakeup is more immediate
- SinkChannelImpl sink = (SinkChannelImpl)wakeupPipe.sink();
- (sink.sc).socket().setTcpNoDelay(true);
- wakeupSinkFd = ((SelChImpl)sink).getFDVal();
- pollWrapper.addWakeupSocket(wakeupSourceFd, 0);
- }
- //PollArrayWrapper.java
- void addWakeupSocket(int fdVal, int index) {
- putDescriptor(index, fdVal);
- putEventOps(index, POLLIN);
- }
注册通道
- public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel,int ops)
- throws ClosedChannelException
注册通道的核心方法是implRegister,仍然以windows为例
- protected void implRegister(SelectionKeyImpl ski) {
- synchronized (closeLock) {
- if (pollWrapper == null)
- throw new ClosedSelectorException();
- growIfNeeded();
- channelArray[totalChannels] = ski;
- ski.setIndex(totalChannels);
- fdMap.put(ski);
- keys.add(ski);
- pollWrapper.addEntry(totalChannels, ski);
- totalChannels++;
- }
- }
- private void growIfNeeded() {
- if (channelArray.length == totalChannels) {
- int newSize = totalChannels * 2; // Make a larger array
- SelectionKeyImpl temp[] = new SelectionKeyImpl[newSize];
- System.arraycopy(channelArray, 1, temp, 1, totalChannels - 1);
- channelArray = temp;
- pollWrapper.grow(newSize);
- }
- if (totalChannels % MAX_SELECTABLE_FDS == 0) { // more threads needed
- pollWrapper.addWakeupSocket(wakeupSourceFd, totalChannels);
- totalChannels++;
- threadsCount++;
- }
- }
implRegister方法设置选择键在数组中的位置,并将其加入已注册的键的集合(keys)中,fdMap是文件描述符到选择键的映射。
选择过程
- protected int doSelect(long timeout) throws IOException {
- if (channelArray == null)
- throw new ClosedSelectorException();
- this.timeout = timeout; // set selector timeout
- processDeregisterQueue();
- if (interruptTriggered) {
- resetWakeupSocket();
- return 0;
- }
- // Calculate number of helper threads needed for poll. If necessary
- // threads are created here and start waiting on startLock
- adjustThreadsCount();
- finishLock.reset(); // reset finishLock
- // Wakeup helper threads, waiting on startLock, so they start polling.
- // Redundant threads will exit here after wakeup.
- startLock.startThreads();
- // do polling in the main thread. Main thread is responsible for
- // first MAX_SELECTABLE_FDS entries in pollArray.
- try {
- begin();
- try {
- subSelector.poll();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- finishLock.setException(e); // Save this exception
- }
- // Main thread is out of poll(). Wakeup others and wait for them
- if (threads.size() > 0)
- finishLock.waitForHelperThreads();
- } finally {
- end();
- }
- // Done with poll(). Set wakeupSocket to nonsignaled for the next run.
- finishLock.checkForException();
- processDeregisterQueue();
- int updated = updateSelectedKeys();
- // Done with poll(). Set wakeupSocket to nonsignaled for the next run.
- resetWakeupSocket();
- return updated;
- }
- protected void implDereg(SelectionKeyImpl ski) throws IOException{
- int i = ski.getIndex();
- assert (i >= 0);
- if (i != totalChannels - 1) {
- // Copy end one over it
- SelectionKeyImpl endChannel = channelArray[totalChannels-1];
- channelArray[i] = endChannel;
- endChannel.setIndex(i);
- pollWrapper.replaceEntry(pollWrapper, totalChannels - 1,
- pollWrapper, i);
- }
- channelArray[totalChannels - 1] = null;
- totalChannels--;
- ski.setIndex(-1);
- if ( totalChannels != 1 && totalChannels % MAX_SELECTABLE_FDS == 1) {
- totalChannels--;
- threadsCount--; // The last thread has become redundant.
- }
- fdMap.remove(ski); // Remove the key from fdMap, keys and selectedKeys
- keys.remove(ski);
- selectedKeys.remove(ski);
- deregister(ski);
- SelectableChannel selch = ski.channel();
- if (!selch.isOpen() && !selch.isRegistered())
- ((SelChImpl)selch).kill();
- }
从channelArray中移除对应的通道,调整通道数和线程数,从map和keys中移除选择键,移除通道上的选择键并关闭通道
adjustThreadsCount这个方法前面提到过,与windows下select有文件描述符限制有关,需要多线程select
- private void adjustThreadsCount() {
- if (threadsCount > threads.size()) {
- // More threads needed. Start more threads.
- for (int i = threads.size(); i < threadsCount; i++) {
- SelectThread newThread = new SelectThread(i);
- threads.add(newThread);
- newThread.setDaemon(true);
- newThread.start();
- }
- } else if (threadsCount < threads.size()) {
- // Some threads become redundant. Remove them from the threads List.
- for (int i = threads.size() - 1 ; i >= threadsCount; i--)
- threads.remove(i).makeZombie();
- }
- }
- public void run() {
- while (true) { // poll loop
- // wait for the start of poll. If this thread has become
- // redundant, then exit.
- if (startLock.waitForStart(this))
- return;
- // call poll()
- try {
- subSelector.poll(index);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- // Save this exception and let other threads finish.
- finishLock.setException(e);
- }
- // notify main thread, that this thread has finished, and
- // wakeup others, if this thread is the first to finish.
- finishLock.threadFinished();
- }
- }
- private synchronized boolean waitForStart(SelectThread thread) {
- while (true) {
- while (runsCounter == thread.lastRun) {
- try {
- startLock.wait();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
- }
- }
- if (thread.isZombie()) { // redundant thread
- return true; // will cause run() to exit.
- } else {
- thread.lastRun = runsCounter; // update lastRun
- return false; // will cause run() to poll.
- }
- }
- }
可以看到这些helper线程创建好后,都阻塞在startLock.wait()上面,待主线程(doSelect方法)调用startLock.startThreads()后,waitForStart方法将返回false
- // Triggers threads, waiting on this lock to start polling.
- private synchronized void startThreads() {
- runsCounter++; // next run
- notifyAll(); // wake up threads.
- }
如果在这期间,有文件描述符准备就绪,poll方法就会返回,不管是主线程返回还是helper线程返回,其他线程都会被唤醒
- private synchronized void waitForHelperThreads() {
- if (threadsToFinish == threads.size()) {
- // no helper threads finished yet. Wakeup them up.
- wakeup();
- }
- while (threadsToFinish != 0) {
- try {
- finishLock.wait();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- // Interrupted - set interrupted state.
- Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
- }
- }
- }
- private synchronized void threadFinished() {
- if (threadsToFinish == threads.size()) { // finished poll() first
- // if finished first, wakeup others
- wakeup();
- }
- threadsToFinish--;
- if (threadsToFinish == 0) // all helper threads finished poll().
- notify(); // notify the main thread
- }
现在把注意力放到updateSelectedKeys方法上,这个方法完成了选择键的更新,来看具体实现
- private int updateSelectedKeys() {
- updateCount++;
- int numKeysUpdated = 0;
- numKeysUpdated += subSelector.processSelectedKeys(updateCount);
- for (SelectThread t: threads) {
- numKeysUpdated += t.subSelector.processSelectedKeys(updateCount);
- }
- return numKeysUpdated;
- }
- private int processSelectedKeys(long updateCount) {
- int numKeysUpdated = 0;
- numKeysUpdated += processFDSet(updateCount, readFds,
- PollArrayWrapper.POLLIN,
- false);
- numKeysUpdated += processFDSet(updateCount, writeFds,
- PollArrayWrapper.POLLCONN |
- PollArrayWrapper.POLLOUT,
- false);
- numKeysUpdated += processFDSet(updateCount, exceptFds,
- PollArrayWrapper.POLLIN |
- PollArrayWrapper.POLLCONN |
- PollArrayWrapper.POLLOUT,
- true);
- return numKeysUpdated;
- }
- private int processFDSet(long updateCount, int[] fds, int rOps,
- boolean isExceptFds){
- int numKeysUpdated = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= fds[0]; i++) {
- int desc = fds[i];
- if (desc == wakeupSourceFd) {
- synchronized (interruptLock) {
- interruptTriggered = true;
- }
- continue;
- }
- MapEntry me = fdMap.get(desc);
- // If me is null, the key was deregistered in the previous
- // processDeregisterQueue.
- if (me == null)
- continue;
- SelectionKeyImpl sk = me.ski;
- // The descriptor may be in the exceptfds set because there is
- // OOB data queued to the socket. If there is OOB data then it
- // is discarded and the key is not added to the selected set.
- if (isExceptFds &&
- (sk.channel() instanceof SocketChannelImpl) &&
- discardUrgentData(desc))
- {
- continue;
- }
- if (selectedKeys.contains(sk)) { // Key in selected set
- if (me.clearedCount != updateCount) {
- if (sk.channel.translateAndSetReadyOps(rOps, sk) &&
- (me.updateCount != updateCount)) {
- me.updateCount = updateCount;
- numKeysUpdated++;
- }
- } else { // The readyOps have been set; now add
- if (sk.channel.translateAndUpdateReadyOps(rOps, sk) &&
- (me.updateCount != updateCount)) {
- me.updateCount = updateCount;
- numKeysUpdated++;
- }
- }
- me.clearedCount = updateCount;
- } else { // Key is not in selected set yet
- if (me.clearedCount != updateCount) {
- sk.channel.translateAndSetReadyOps(rOps, sk);
- if ((sk.nioReadyOps() & sk.nioInterestOps()) != 0) {
- selectedKeys.add(sk);
- me.updateCount = updateCount;
- numKeysUpdated++;
- }
- } else { // The readyOps have been set; now add
- sk.channel.translateAndUpdateReadyOps(rOps, sk);
- if ((sk.nioReadyOps() & sk.nioInterestOps()) != 0) {
- selectedKeys.add(sk);
- me.updateCount = updateCount;
- numKeysUpdated++;
- }
- }
- me.clearedCount = updateCount;
- }
- }
- return numKeysUpdated;
- }
- }
1、忽略wakeupSourceFd,这个文件描述符用于唤醒用的,与用户具体操作无关,所以忽略;
2、过滤fdMap中不存在的文件描述符,因为已被注销;
3、忽略oob data(搜了一下:out of band data指带外数据,有时也称为加速数据, 是指连接双方中的一方发生重要事情,想要迅速地通知对方 ),这也不是用户关心的;
4、如果通道的键还没有处于已选择的键的集合中,那么键的ready集合将被清空,然后表示操作系统发现的当前通道已经准备好的操作的比特掩码将被设置;
5、如果键在已选择的键的集合中。键的ready集合将被表示操作系统发现的当前已经准备好的操作的比特掩码更新。
来看下具体的更新ready集的方法translateAndUpdateReadyOps,不同的通道有不同的实现,以socketChannel为例
- public boolean translateAndUpdateReadyOps(int ops, SelectionKeyImpl sk) {
- return translateReadyOps(ops, sk.nioReadyOps(), sk);
- }
- public boolean translateReadyOps(int ops, int initialOps,
- SelectionKeyImpl sk) {
- int intOps = sk.nioInterestOps(); // Do this just once, it synchronizes
- int oldOps = sk.nioReadyOps();
- int newOps = initialOps;
- if ((ops & PollArrayWrapper.POLLNVAL) != 0) {
- // This should only happen if this channel is pre-closed while a
- // selection operation is in progress
- // ## Throw an error if this channel has not been pre-closed
- return false;
- }
- if ((ops & (PollArrayWrapper.POLLERR
- | PollArrayWrapper.POLLHUP)) != 0) {
- newOps = intOps;
- sk.nioReadyOps(newOps);
- // No need to poll again in checkConnect,
- // the error will be detected there
- readyToConnect = true;
- return (newOps & ~oldOps) != 0;
- }
- if (((ops & PollArrayWrapper.POLLIN) != 0) &&
- ((intOps & SelectionKey.OP_READ) != 0) &&
- (state == ST_CONNECTED))
- newOps |= SelectionKey.OP_READ;
- if (((ops & PollArrayWrapper.POLLCONN) != 0) &&
- ((intOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) &&
- ((state == ST_UNCONNECTED) || (state == ST_PENDING))) {
- newOps |= SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
- readyToConnect = true;
- }
- if (((ops & PollArrayWrapper.POLLOUT) != 0) &&
- ((intOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) &&
- (state == ST_CONNECTED))
- newOps |= SelectionKey.OP_WRITE;
- sk.nioReadyOps(newOps);
- return (newOps & ~oldOps) != 0;
- }
把目光转向selectkey类的几个方法
- public final boolean isAcceptable() {
- return (readyOps() & OP_ACCEPT) != 0;
- }
- public final boolean isConnectable() {
- return (readyOps() & OP_CONNECT) != 0;
- }
- public final boolean isWritable() {
- return (readyOps() & OP_WRITE) != 0;
- }
- public final boolean isReadable() {
- return (readyOps() & OP_READ) != 0;
- }
总结一下doSelect:处理已取消的键集,通过本地方法poll轮询文件描述符,poll方法返回后更新已选择键的ready集。
唤醒
如果线程正阻塞在select方法上,调用wakeup方法会使阻塞的选择操作立即返回
- public Selector wakeup() {
- synchronized (interruptLock) {
- if (!interruptTriggered) {
- setWakeupSocket();
- interruptTriggered = true;
- }
- }
- return this;
- }
- //WindowsSelectorImpl.java
- private void setWakeupSocket() {
- setWakeupSocket0(wakeupSinkFd);
- }
- private native void setWakeupSocket0(int wakeupSinkFd);
- //WindowsSelectorImpl.c
- JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
- Java_sun_nio_ch_WindowsSelectorImpl_setWakeupSocket0(JNIEnv *env, jclass this,
- jint scoutFd)
- {
- /* Write one byte into the pipe */
- send(scoutFd, (char*)&POLLIN, 1, 0);
- }
这里有必要提一下打开通道pipe.open的实现细节,先看看windows的实现
- public static Pipe open() throws IOException {
- return SelectorProvider.provider().openPipe();
- }
- public Pipe openPipe() throws IOException {
- return new PipeImpl(this);
- }
- PipeImpl(final SelectorProvider sp) throws IOException {
- try {
- AccessController.doPrivileged(new Initializer(sp));
- } catch (PrivilegedActionException x) {
- throw (IOException)x.getCause();
- }
- }
- public Void run() throws IOException {
- ServerSocketChannel ssc = null;
- SocketChannel sc1 = null;
- SocketChannel sc2 = null;
- try {
- // loopback address
- InetAddress lb = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
- assert (lb.isLoopbackAddress());
- // bind ServerSocketChannel to a port on the loopback address
- ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
- ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(lb, 0));
- // Establish connection (assumes connections are eagerly
- // accepted)
- InetSocketAddress sa = new InetSocketAddress(lb, ssc.socket().getLocalPort());
- sc1 = SocketChannel.open(sa);
- ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
- long secret = rnd.nextLong();
- bb.putLong(secret).flip();
- sc1.write(bb);
- // Get a connection and verify it is legitimate
- for (;;) {
- sc2 = ssc.accept();
- bb.clear();
- sc2.read(bb);
- bb.rewind();
- if (bb.getLong() == secret)
- break;
- sc2.close();
- }
- // Create source and sink channels
- source = new SourceChannelImpl(sp, sc1);
- sink = new SinkChannelImpl(sp, sc2);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- }
- }
看看sun solaris的实现
- PipeImpl(SelectorProvider sp) {
- int[] fdes = new int[2];
- IOUtil.initPipe(fdes, true);
- FileDescriptor sourcefd = new FileDescriptor();
- IOUtil.setfdVal(sourcefd, fdes[0]);
- source = new SourceChannelImpl(sp, sourcefd);
- FileDescriptor sinkfd = new FileDescriptor();
- IOUtil.setfdVal(sinkfd, fdes[1]);
- sink = new SinkChannelImpl(sp, sinkfd);
- }
- JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
- Java_sun_nio_ch_IOUtil_initPipe(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
- jintArray intArray, jboolean block)
- {
- int fd[2];
- jint *ptr = 0;
- if (pipe(fd) < 0) {
- JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, "Pipe failed");
- return;
- }
- if (block == JNI_FALSE) {
- if ((configureBlocking(fd[0], JNI_FALSE) < 0)
- || (configureBlocking(fd[1], JNI_FALSE) < 0)) {
- JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, "Configure blocking failed");
- }
- }
- ptr = (*env)->GetPrimitiveArrayCritical(env, intArray, 0);
- ptr[0] = fd[0];
- ptr[1] = fd[1];
- (*env)->ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical(env, intArray, ptr, 0);
- }
























 371
371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








