其实并查集顾名思义就是有“合并集合”和“查找集合”两种操作的关于数据结构的一种算法。
概述
性质
并查集算法不支持分割一个集合。
算法
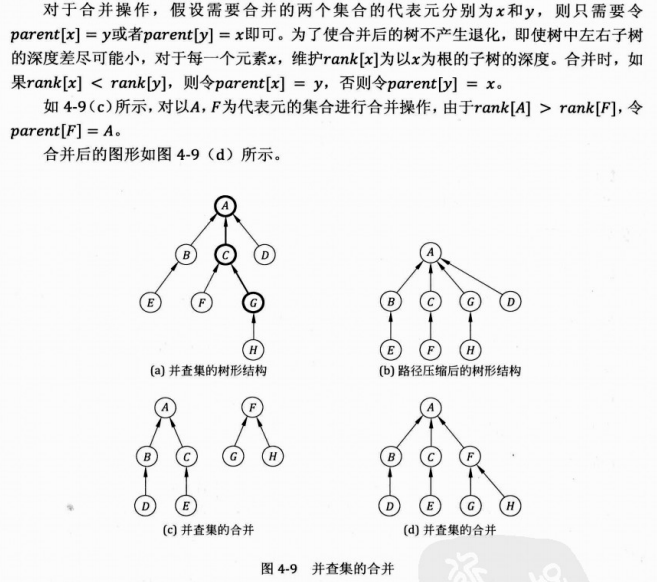
用集合中的某个元素来代表这个集合,该元素称为集合的代表元。
一个集合内的所有元素组织成以代表元为根的树形结构。
对于每一个元素 parent[x]指向x在树形结构上的父亲节点。如果x是根节点,则令parent[x] = x。
对于查找操作,假设需要确定x所在的的集合,也就是确定集合的代表元。可以沿着parent[x]不断在树形结构中向上移动,直到到达根节点。
判断两个元素是否属于同一集合,只需要看他们的代表元是否相同即可。路径压缩
为了加快查找速度,查找时将x到根节点路径上的所有点的parent设为根节点,该优化方法称为压缩路径。
使用该优化后,平均复杂度可视为Ackerman函数的反函数,实际应用中可粗略认为其是一个常数。
用途
1、维护无向图的连通性。支持判断两个点是否在同一连通块内,和判断增加一条边是否会产生环。(不理解)
2、用在求解最小生成树的Kruskal算法里。
reference
《ACM国际大学生程序设计竞赛 知识与入门 俞勇主编》
三个操作
一般来说,一个并查集一三个操作。
初始化
包括对所有单个的数据建立一个单独的集合(即根据题目的意思自己建立的最多可能有的集合,为下面的合并查找操作提供操作对象)
在每一个单个的集合里面,有三个东西。
1,集合所代表的数据。(这个初始值根据需要自己定义,不固定)
2,这个集合的层次通常用rank表示(一般来说,初始化的工作之一就是将每一个集合里的rank置为0)。
3,这个集合的类别parent(有的人也喜欢用set表示)(其实就是一个指针,用来指示这个集合属于那一类,合并过后的集合,他们的parent指向的最终值一定是相同的。)
(有的简单题里面集合的数据就是这个集合的标号,也就是说只包含2和3,1省略了)。
初始化的时候,一个集合的parent都是这个集合自己的标号。没有跟它同类的集合,那么这个集合的源头只能是自己了。
(最简单的集合就只含有这三个东西了,当然,复杂的集合就是把3指针这一项添加内容,如PKU食物链那题,我们还可以添加enemy指针,表示这个物种集合的天敌集合;food指针,表示这个物种集合的食物集合。随着指针的增加,并查集操作起来也变得复杂,题目也就显得更难了)
结构体表示法
有的人是建立一个结构体把集合表示出来,如:
#define MAX 10000
struct Node
{
int data;
int rank;
int parent;
}node[MAX];数组表示法
有的人则是弄很多相同大小的数组,如:
int set[max];//集合index的类别,或者用parent表示
int rank[max];//集合index的层次,通常初始化为0
int data[max];//集合index的数据类型
//初始化集合
void Make_Set(int i)
{
set[i]=i;//初始化的时候,一个集合的parent都是这个集合自己的标号。没有跟它同类的集合,那么这个集合的源头只能是自己了。
rank[i]=0;
}一般来说,题目简单用数组,题目复杂用结构体,因为结构体有条理,数组可以少打几个字。
查找函数
就是找到parent指针的源头,可以把函数命名为get_parent(或者find_set,这个随你喜欢,以便于理解为主)
如果集合的parent等于集合的编号(即还没有被合并或者没有同类),那么自然返回自身编号。
如果不同(即经过合并操作后指针指向了源头(合并后选出的rank高的集合))那么就可以调用递归函数,如下面的代码:
/**
*查找集合i(一个元素是一个集合)的源头(递归实现)。
如果集合i的父亲是自己,说明自己就是源头,返回自己的标号;
否则查找集合i的父亲的源头。
**/
int get_parent(int x)
{
if(node[x].parent==x)
return x;
return get_parent(node[x].parent);
}数组的话就是:
//查找集合i(一个元素是一个集合)的源头(递归实现)
int Find_Set(int i)
{
//如果集合i的父亲是自己,说明自己就是源头,返回自己的标号
if(set[i]==i)
return set[i];
//否则查找集合i的父亲的源头
return Find_Set(set[i]);
}合并集合函数
这就是所谓并查集的并了。至于怎么知道两个集合是可以合并的,那就是题目的条件了。先看代码:
void Union(int a,int b)
{
a=get_parent(a);
b=get_parent(b);
if(node[a].rank>node[b].rank)
node[b].parent=a;
else
{
node[a].parent=b;
if(node[a].rank==node[b].rank)
node[b].rank++;
}
}再给出数组显示的合并函数:
void Union(int i,int j)
{
i=Find_Set(i);
j=Find_Set(j);
if(i==j) return ;
if(rank[i]>rank[j]) set[j]=i;
else
{
if(rank[i]==rank[j]) rank[j]++;
set[i]=j;
}
}
下面给个leetcode的样题与code
Number of Islands II
Given a n,m which means the row and column of the 2D matrix and an array of pair A( size k). Originally, the 2D matrix is all 0 which means there is only sea in the matrix. The list pair has k operator and each operator has two integer A[i].x, A[i].y means that you can change the grid matrix[A[i].x][A[i].y] from sea to island. Return how many island are there in the matrix after each operator.
Example
Given n = 3, m = 3, array of pair A = [(0,0),(0,1),(2,2),(2,1)].
return [1,1,2,2].
Note
0 is represented as the sea, 1 is represented as the island. If two 1 is adjacent, we consider them in the same island. We only consider up/down/left/right adjacent.
解法:带路径压缩的并查集算法
public class Solution{
public List<Integer> numberofislandsii(int m, int n,Point[] operations){
HashMap<Integer,Integer> fathermapping=new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(m*n);
int cnt=0;
List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<Integer>(operations.length);
int[] dx={0,1,0,-1};
int[] dy={1,0,-1,0};
for(Point op:operations){
int p=op.x*m+op.y;
int fp=findfather(fathermapping,p);
if(p==fp) cnt++;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int xx=op.x+dx[i];
int yy=op.y+dy[i];
if(xx<0||xx>m||yy<0||yy>n) continue;
int q=xx*m+yy;
if(fathermapping.containsKey(q)){
int fq=findfather(fathermapping,q);
if(fp!=fq){
cnt--;
fathermapping.replace(fq, fp);
}
}
}
ans.add(cnt);
}
return ans;
}
public int findfather(HashMap<Integer,Integer> fathermapping,int q){
if(!fathermapping.containsKey(q)){
fathermapping.put(q, q);
return q;
}
int res=q,temp;
while(res!=fathermapping.get(res)){
res=fathermapping.get(res);
}
while(q!=fathermapping.get(q)){
temp=fathermapping.get(q);
fathermapping.replace(q, res);
q=temp;
}
return q;
}
}
}
class Point{
int x;
int y;
public Point(int x,int y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}






















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








