实验目的
掌握词典编码的基本原理,用C/C++/Python等语言编程实现LZW解码器并分析编解码算法。
实验内容
1.LZW编码原理和实现算法
LZW的编码思想是不断地从字符流中提取新的字符串,通俗地理解为新“词条”,然后用“代号”也就是码字表示这个“词条”。这样一来,对字符流的编码就变成了用码字去替换字符流,生成码字流,从而达到压缩数据的目的。LZW编码是围绕称为词典的转换表来完成的。LZW编码器通过管理这个词典完成输入与输出之间的转换。LZW编码器的输入是字符流,字符流可以是用8位ASCII字符组成的字符串,而输出是用n位(例如12位)表示的码字流。LZW编码算法的步骤如下:
步骤1:将词典初始化为包含所有可能的单字符,当前前缀P初始化为空。
步骤2:当前字符C=字符流中的下一个字符。
步骤3:判断P+C是否在词典中
(1)如果“是”,则用C扩展P,即让P=P+C,返回到步骤2。
(2)如果“否”,则
输出与当前前缀P相对应的码字W;
将P+C添加到词典中;
令P=C,并返回到步骤2
2.LZW解码原理和实现算法
LZW解码算法开始时,译码词典和编码词典相同,包含所有可能的前缀根。具体解码算法如下:
步骤1:在开始译码时词典包含所有可能的前缀根。
步骤2:令CW:=码字流中的第一个码字。
步骤3:输出当前缀-符串string.CW到码字流。
步骤4:先前码字PW:=当前码字CW。
步骤5:当前码字CW:=码字流的下一个码字。
步骤6:判断当前缀-符串string.CW 是否在词典中。
(1)如果”是”,则把当前缀-符串string.CW输出到字符流。
当前前缀P:=先前缀-符串string.PW。
当前字符C:=当前前缀-符串string.CW的第一个字符。
把缀-符串P+C添加到词典。
(2)如果”否”,则当前前缀P:=先前缀-符串string.PW。
当前字符C:=当前缀-符串string.CW的第一个字符。
输出缀-符串P+C到字符流,然后把它添加到词典中。
步骤7:判断码字流中是否还有码字要译。
(1)如果”是”,就返回步骤4。
(2)如果”否”,结束。
实验步骤
1.首先调试LZW的编码程序,以一个文本文件作为输入,得到输出的LZW编码文件。
2. 以实验步骤一得到的编码文件作为输入,编写LZW的解码程序。在写解码程序时需要对关键语句加上注释,并说明进行何操作。在实验报告中重点说明当前码字在词典中不存在时应如何处理并解释原因。
3. 选择至少十种不同格式类型的文件,使用LZW编码器进行压缩得到输出的压缩比特流文件。对各种不同格式的文件进行压缩效率的分析。
代码分析:
int suffix; //当前的字符的尾缀字符
int parent; //指当前节点所对应的母节点
int firstchild; //指当前节点的第一个孩子节点,也就是母节点下属产生的第一个节点
int nextsibling; //指下一个兄弟节点,即下一个同级节点
初始化字典:
void InitDictionary( void){
int i;
for( i=0; i<256; i++){//尾缀字符suffix数组中包含的是默认的ascii码所对应的256的字符
dictionary[i].suffix = i;//尾缀字符
dictionary[i].parent = -1;//母节点
dictionary[i].firstchild = -1;//孩子节点
dictionary[i].nextsibling = i+1;//下一个兄弟节点
}
dictionary[255].nextsibling = -1;
next_code = 256;//标记新写入dictionary的索引
}
添加新的字符串
void AddToDictionary( int character, int string_code){
int firstsibling, nextsibling;
if( 0>string_code) return;
dictionary[next_code].suffix = character;
dictionary[next_code].parent = string_code;
dictionary[next_code].nextsibling = -1;
dictionary[next_code].firstchild = -1;
firstsibling = dictionary[string_code].firstchild;
if( -1<firstsibling){ // the parent has child
nextsibling = firstsibling;
//找到前缀为string_code的表的末尾
while( -1<dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling )
nextsibling = dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling;
dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling = next_code;
}else{// no child before, modify it to be the first
dictionary[string_code].firstchild = next_code;
}
next_code ++;
}
编码过程:
void LZWEncode( FILE *fp, BITFILE *bf){
int character;
int string_code;
int index;
unsigned long file_length;
fseek( fp, 0, SEEK_END);
file_length = ftell( fp);
fseek( fp, 0, SEEK_SET);//计算需要编码的文件的长度大小
BitsOutput( bf, file_length, 4*8);
InitDictionary();
string_code = -1;
while( EOF!=(character=fgetc( fp))){//从fp中逐个取出字符,每次读一个字节
index = InDictionary( character, string_code);
if( 0<=index){ // string+character in dictionary 在词典中,进行赋值操作
string_code = index;
}else{ // string+character not in dictionary 不在词典中,需创建一个新的
output( bf, string_code);
if( MAX_CODE > next_code){ // free space in dictionary
// add string+character to dictionary
AddToDictionary( character, string_code);
}
string_code = character;
}
}
output( bf, string_code);
}
解码过程:
pW表示之前刚刚解码的记号;cW表示当前新读进来的记号,用Str(cW)和Str(pW)表示它们解码出来的原字符串。
void LZWDecode( BITFILE *bf, FILE *fp){
int character;
int new_code, last_code;//new_code是CW,last_code是PW
int phrase_length;//每一次解码的长度
unsigned long file_length;//文件总长度
file_length = BitsInput( bf, 4*8);//读出输入的需要解码的文件的长度
if( -1 == file_length) file_length = 0;
InitDictionary();//初始化解码词典
last_code = -1;//第一个码字前的值是空的
while( 0<file_length){
new_code = input( bf);
//判断更新之后的CW是否在词典中
if( new_code >= next_code)//若成立,不在词典中
{ // this is the case CSCSC( not in dict)
d_stack[0] = character;//将character赋给d_stack[0]
phrase_length = DecodeString( 1, last_code);
}else//在词典中
{
phrase_length = DecodeString( 0, new_code);
}
character = d_stack[phrase_length-1];//找到dstack里的最后一个字符
while( 0<phrase_length){
phrase_length --;//判断解压缩多少位到文件中
fputc( d_stack[ phrase_length], fp);
file_length--;//文件剩余未解压缩的量
}
if( MAX_CODE>next_code){// add the new phrase to dictionary
AddToDictionary( character, last_code);
}
last_code = new_code;
}
}
读出文件长度,初始化解码词典;
判断cW是否位于词典中,因为解码比编码有一步的延迟,当new_code >= next_code时,字符不存在于词典中,cW的映射为即将加入的P+C,cW的第一个字符就是pW的第一个字符;
将倒序存入的堆栈逆序取出并输出到文件中;
判断词典中是否还有剩余空间。
主函数:
int main( int argc, char **argv){
FILE *fp;
BITFILE *bf;
if( 4>argc){//输入的参数个数必须要大于等于三,否则会出现以下内容
fprintf( stdout, "usage: \n%s <o> <ifile> <ofile>\n", argv[0]);
fprintf( stdout, "\t<o>: E or D reffers encode or decode\n");
fprintf( stdout, "\t<ifile>: input file name\n");
fprintf( stdout, "\t<ofile>: output file name\n");
return -1;
}
if( 'E' == argv[1][0]){ // do encoding
fp = fopen( argv[2], "rb");
bf = OpenBitFileOutput( argv[3]);//argv[3]是在命令参数中设置的输出的地址和文件名
if( NULL!=fp && NULL!=bf){
LZWEncode( fp, bf);
fclose( fp);
CloseBitFileOutput( bf);
fprintf( stdout, "encoding done\n");
}
}else if( 'D' == argv[1][0]){ // do decoding
bf = OpenBitFileInput( argv[2]);
fp = fopen( argv[3], "wb");//argv[3]是在命令参数中设置的输出的地址和文件名
if( NULL!=fp && NULL!=bf){
LZWDecode( bf, fp);
fclose( fp);
CloseBitFileInput( bf);
fprintf( stdout, "decoding done\n");
}
}else{ // otherwise
fprintf( stderr, "not supported operation\n");
}
return 0;
}
设置命令参数:


实验结果分析

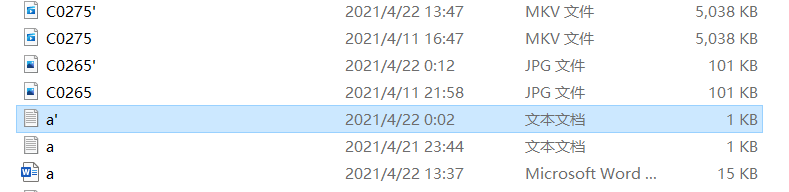
| 文件类型 | 编码前文件大小 | 编码后文件大小 | 压缩效率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| .tif | 4505KB | 5390KB | -19.64% |
| .tga | 6837KB | 8207KB | -20.04% |
| .png | 3874KB | 4749KB | -22.59% |
| .bmp | 6992KB | 8479KB | -21.27% |
| .wmv | 7077KB | 7359KB | -3.98% |
| .mp4 | 94216KB | 111317KB | -18.15% |
| .mkv | 5038KB | 6203KB | -23.12% |
| .jpg | 101KB | 140KB | -38.61% |
| .yuv | 96KB | 69KB | 28.13% |
| .txt | 1KB | 1KB | 0 |
根据结果可以看出,不是所有类型文件经过LZW编码器编码后都得到了压缩,若字符串重复概率低、词典中的字符串不再出现,都会影响压缩效率。





















 765
765











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








