One tradition of welcoming the New Year is launching fireworks into the sky. Usually a launched firework flies vertically upward for some period of time, then explodes, splitting into several parts flying in different directions. Sometimes those parts also explode after some period of time, splitting into even more parts, and so on.
Limak, who lives in an infinite grid, has a single firework. The behaviour of the firework is described with a recursion depth n and a duration for each level of recursion t1, t2, ..., tn. Once Limak launches the firework in some cell, the firework starts moving upward. After covering t1 cells (including the starting cell), it explodes and splits into two parts, each moving in the direction changed by 45 degrees (see the pictures below for clarification). So, one part moves in the top-left direction, while the other one moves in the top-right direction. Each part explodes again after covering t2 cells, splitting into two parts moving in directions again changed by 45 degrees. The process continues till the n-th level of recursion, when all 2n - 1existing parts explode and disappear without creating new parts. After a few levels of recursion, it's possible that some parts will be at the same place and at the same time — it is allowed and such parts do not crash.
Before launching the firework, Limak must make sure that nobody stands in cells which will be visited at least once by the firework. Can you count the number of those cells?
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 30) — the total depth of the recursion.
The second line contains n integers t1, t2, ..., tn (1 ≤ ti ≤ 5). On the i-th level each of 2i - 1 parts will cover ti cells before exploding.
Print one integer, denoting the number of cells which will be visited at least once by any part of the firework.
4 4 2 2 3
39
6 1 1 1 1 1 3
85
1 3
3
For the first sample, the drawings below show the situation after each level of recursion. Limak launched the firework from the bottom-most red cell. It covered t1 = 4 cells (marked red), exploded and divided into two parts (their further movement is marked green). All explosions are marked with an 'X' character. On the last drawing, there are 4 red, 4 green, 8 orange and 23 pink cells. So, the total number of visited cells is4 + 4 + 8 + 23 = 39.
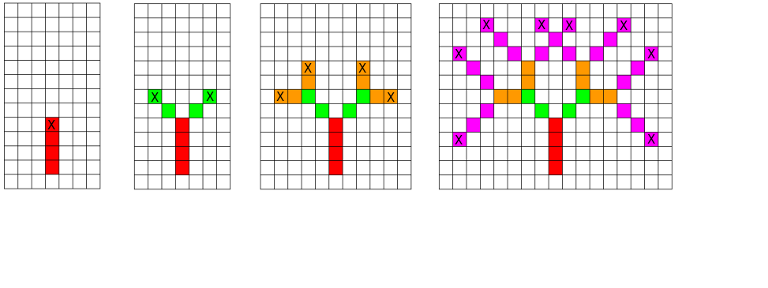
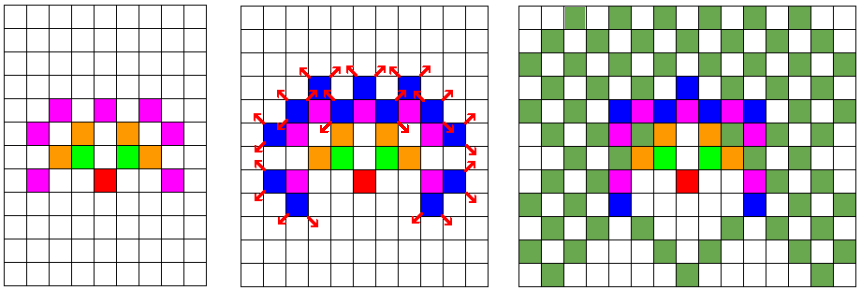
For the second sample, the drawings below show the situation after levels 4, 5 and 6. The middle drawing shows directions of all parts that will move in the next level.
题目大意(来自某群):
有一个烟花,总共有n<=30层,每一层的爆炸延时是t[i]<=5,也就是穿过t[i]个单位长度后爆炸,每一次爆炸都会分成两半,然后方向是与当前发射方向夹角为正负45度,烟花没有碰撞体积,问有多少个格子被至少一个烟花穿过
思路;
观察t【i】的范围比较小的特点,我们判断出,最后炸出来的图最大500*500也够了,所以我们尝试暴力,一共对于30层烟花进行暴力,时间是足够的,接下来考虑模拟的过程:
①一共其具有8个方向,分别判断出其爆炸后能够得到的状态即可。
②因为一个格子会存有多个方向的炸药,那么我们如果暴力用vector无脑存的话,对于一个格子会存入相当多的情况,那么我么考虑剪枝,对于一个格子,最多也就八种炸的方式,那么我们对于一个格子重复的方向,去重处理即可。
Ac代码(好挫啊):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int map[505][505];
vector<int >vis[505][505];
vector<int >vis2[505][505];
int use[10];
int a[50];
int x,y,x2,y2;
void cal(int val)
{
if(val==0)x=-1,y=-1,x2=-1,y2=1;
if(val==1)x=0,y=-1,x2=-1,y2=0;
if(val==2)x=1,y=-1,x2=-1,y2=-1;
if(val==3)x=1,y=0,x2=0,y2=-1;
if(val==4)x=1,y=1,x2=1,y2=-1;
if(val==5)x=0,y=1,x2=1,y2=0;
if(val==6)x=-1,y=1,x2=1,y2=1;
if(val==7)x=-1,y=0,x2=0,y2=1;
return ;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
for(int z=1;z<=n;z++)
{
if(z==1)
{
for(int i=250;i>=1;i--)
{
if(a[z]>0)
{
map[i][250]=1;
if(a[z]==1)
{
vis[i][250].push_back(0);
}
}
a[z]--;
}
}
else
{
for(int i=1;i<=500;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=500;j++)
{
if(vis[i][j].size()==0)continue;
for(int d=0;d<vis[i][j].size();d++)
{
for(int k=1;k<=a[z];k++)
{
cal(vis[i][j][d]);
map[i+k*x][j+k*y]=1;
map[i+k*x2][j+k*y2]=1;
if(k==a[z])
{
vis2[i+k*x][j+k*y].push_back((vis[i][j][d]+1)%8);
if(vis[i][j][d]!=0)
vis2[i+k*x2][j+k*y2].push_back(vis[i][j][d]-1);
else vis2[i+k*x2][j+k*y2].push_back(7);
}
}
}
vis[i][j].clear();
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=500;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=500;j++)
{
if(vis2[i][j].size()>0)
{
memset(use,0,sizeof(use));
for(int d=0;d<vis2[i][j].size();d++)
{
if(use[vis2[i][j][d]]==1)continue;
vis[i][j].push_back(vis2[i][j][d]);
use[vis2[i][j][d]]=1;
}
vis2[i][j].clear();
}
}
}
}
}
int output=0;
for(int i=1;i<=500;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=500;j++)
{
if(map[i][j]==1)output++;
}
}
printf("%d\n",output);
}
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








