本文通过示例来描述如何在Python中使用正则表达式来统计文本中的所有数字。
示例中的文本来自命令行的管道数据,
sys.stdin.readlines()主要是因为作者需要在命令行的输出信息中做数字统计。
示例代码1,列出根目录下所有文件或文件夹的名称字符串中包含的数字
import re
for name in sys.stdin.readlines():
items = re.findall("\d+", name)
if(len(items)>0):
print items执行命令:
$ ls /
bin boot cdrom dev etc home initrd.img initrd.img.old lib lib32 lib64 libx32 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin selinux srv sys tmp usr var vmlinuz vmlinuz.old
$ ls / | python test.py
输出结果:
['32']
['64']
['32']
示例代码2:找出管道输出文本中的所有数字,并求和
import sys;
import re
items = []
for name in sys.stdin.readlines():
nums = re.findall("\d+", name)
for num in nums:
items.append(num)
if(len(items)>0):
print items
sumNum = 0
for num in items:
sumNum += int(num)
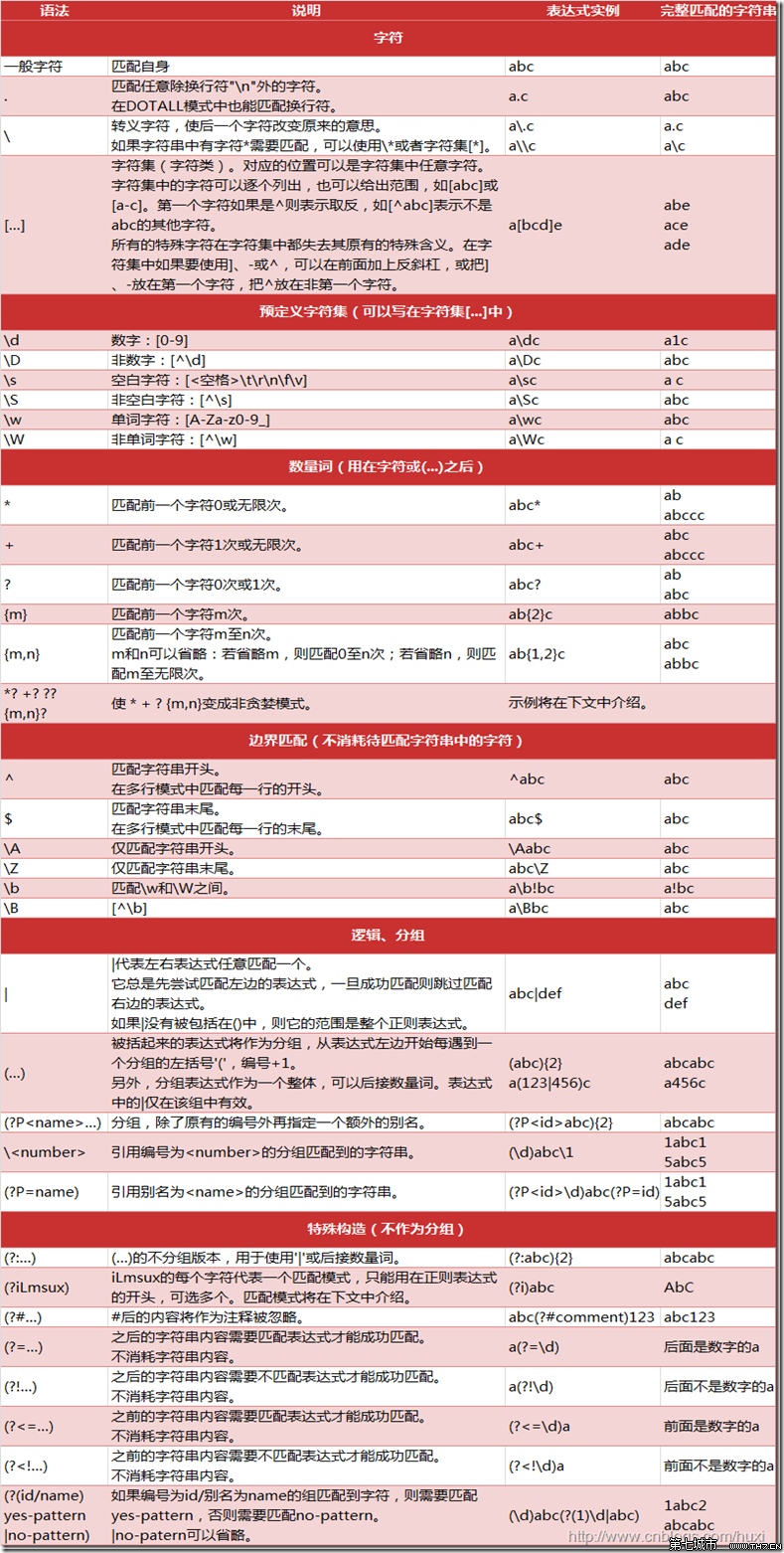
print "Total:",sumNum正则表达式的规则如下图:

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








