Spring Boot简介
很荣幸刚开始学习java框架就接触到了spring boot,并得到大神的指点,通过查阅资料以及教程学会在实际项目中去使用它,相对于其他框架只有一个字来形容 - “爽”。最近也看了一些资料及招聘信息,用发现弹簧启动的企业越来越多,毋庸置疑,这将会成为下一代的主流框架。春天启动可以说是用用SpringMVC的升级版,去掉了繁琐的配置,可以很容易上手,其最爽的就是他的自动化配置,用了之后再也不想回到以前了,谁用谁知道。网上有很多版本用法但好多都不是我想要的,因此博主再次将其总结记录下来,希望日后可以复习以及给需要的朋友一些帮助,再次声明博主也是学习者所以只能按自己的理解来写,若有不对之处请指教,日后有更深的理解会继续纠正,本篇先项目的构建-使用-部署从头到尾进行简单的讲解。
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。
Spring boot的特点
1.创建独立的Spring应用程序
2.嵌入的Tomcat的,无需部署WAR文件
3.简化的Maven配置
4.自动配置Spring
5.提供生产就绪型功能,如指标,健康检查和外部配置
6.绝对没有代码生成和对XML没有要求配置
Spring boot的优点
spring boot可以支持你快速的开发出restful风格的微服务架构
自动化确实方便,做微服务再合适不过了,单一罐包部署和管理都非常方便。只要系统架构设计合理,大型项目也能用,加上nginx的的负载均衡,轻松实现横向扩展
spring boot要解决的问题,精简配置是一方面,另外一方面是如何方便的让春生态圈和其他工具链整合(比如Redis,电子邮件,elasticsearch)
项目构建
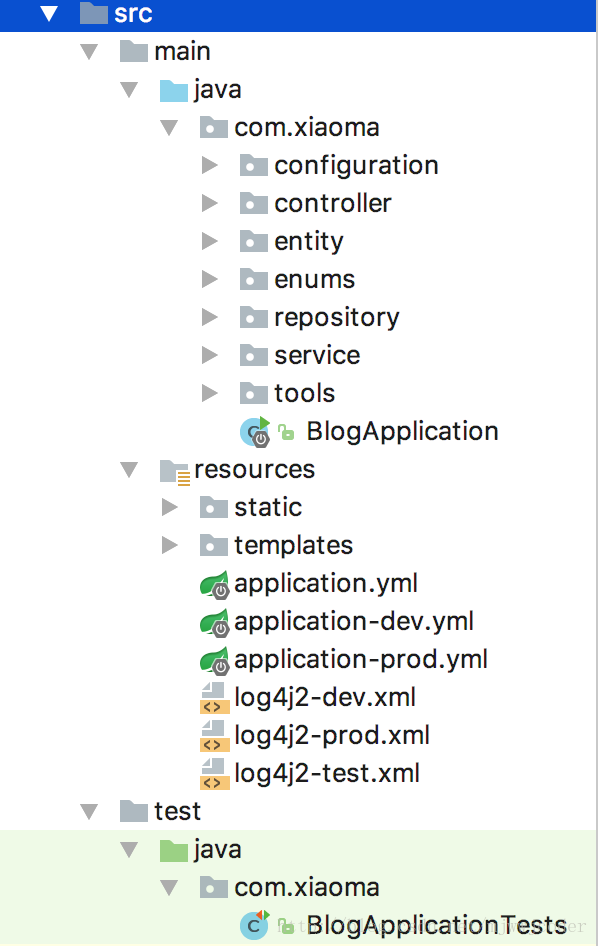
- src / main / java:主程序入口BolgApplication,Spring引导内嵌Tomcat服务器,可以直接通过运行该类来启动应用。
- 的src / main /资源:配置资源文件目录,由于我们是网络项目,因此这里存放一些静态资源文件,静态下存放图片,JS,CSS等,模板下存放JSP,HTML等模板视图文件等.application.yml是配置文件,为原本application.properties中,这里推荐使用YML格式,具体使用可以查阅了解,这里可以配置,访问端口,数据库连接信息等。
- 的src /测试/:单元测试目录,通过Junit4实现项目的单元测试
POM依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>- spring-boot-starter-web:全栈web开发模块,包含嵌入式Tomcat,Spring MVC。
- spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf:thymeleaf视图模板模块,相当于JSP,很好的支持了前后端分离开发。
- 弹簧引导启动测试:通用测试模块,包含了JUnit,Hamcrest,的Mockito。
实现RESTful API
包com.xiaoma.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Created by mj on 2018/1/21.
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String sayHello(){
return "Hello World";
}
}package com.xiaoma;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class BlogApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BlogApplication.class, args);
}
}Spring Boot使用thymeleaf模板
- 打开src/main/resources下的application.yml里面添加如下内容
#设置访问端口
server:
port: 8080
context-path: /
spring:
#设置运行环境
profiles:
active: dev
#环境域名
# domain: xiaomablog.com
#视图模型
thymeleaf:
cache: false
mode: LEGACYHTML5
prefix: classpath:/templates/
suffix: .html
encoding: UTF-8
content-type: text/html
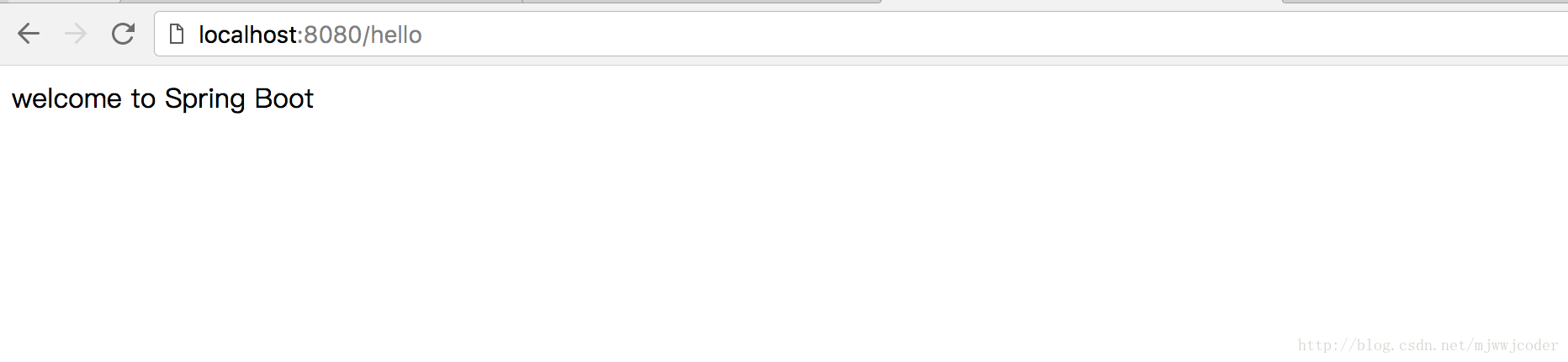
check-template-location: true- 在src/main/resources下的templates下新建index.html文件,内容为:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<body>
<div>
welcome to Spring Boot
</div>
</body>
</html>- 修改HelloController为:
package com.xiaoma.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* Created by mj on 2018/1/21.
*/
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String sayHello(){
return "index";
}
}
Spring Boot自定义参数
book:
name: Spring
author: Boot@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${book.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${book.author}")
private String author;
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String sayHello(){
return name+author;
}
}package com.xiaoma.entity.po;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* Created by mj on 2018/1/21.
*/
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "book")
public class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
省略了getter setter....
}
package com.xiaoma.controller;
import com.xiaoma.entity.po.Book;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Created by mj on 2018/1/21.
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
Book book;
@RequestMapping("hello")
public Book sayHello(){
return book;
}
}
Spring Boot部署
- 以jar包方式部署Spring Boot项目
- 以war包方式部署Spring Boot项目
package com.xiaoma;
import com.xiaoma.configuration.log.GwsLogger;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;
@SpringBootApplication
public class BlogApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BlogApplication.class, args);
System.out.println("========================================xiaomage blog server is started!");
GwsLogger.info("xiaomage blog server is started!");
}
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(this.getClass());
}
}<!--<packaging>jar</packaging>-->
<packaging>war</packaging><dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!-- 如果在使用自带tomcat请注释下面,如果使用第三方tomcat不要注释下面 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>





















 1439
1439

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








