在android中,google为开发者提供了一个SmsManager用来管理发送和接收短信的类,类似于WifiManager,先看下SmsManager的常用API
SmsManager常用API
method public java.util.ArrayList<java.lang.String> divideMessage(java.lang.String);一条短信只可容纳70个中文,所以当短信长度超过70个中文字符时程序就要特殊处理了,该方式有个弊端就是用户会分条收到短信。
if (message.length() > 70) {
ArrayList<String> msgs = sms.divideMessage(message);
for (String msg : msgs) {
sms.sendTextMessage(phoneNumber, null, msg, sentPI, deliverPI);
}
}else {
sms.sendTextMessage(phoneNumber, null, message, sentPI, deliverPI);
}
通过sendMultipartTextMessage()方法发送超长短信,这种方式还是发送多条短信,但用户收到的短信会是连在一起的一整条。
if (message.length() > 70) {
ArrayList<String> msgs = sms.divideMessage(message);
ArrayList<PendingIntent> sentIntents = new ArrayList<PendingIntent>();
for(int i = 0;i<msgs.size();i++){
sentIntents.add(sentPI);
}
sms.sendMultipartTextMessage(phoneNumber, null, msgs, sentIntents, null);
} else {
sms.sendTextMessage(phoneNumber, null, message, sentPI, deliverPI);
} 下载彩信
method public void downloadMultimediaMessage(android.content.Context, java.lang.String, android.net.Uri, android.os.Bundle, android.app.PendingIntent);获取一个SmsManager,该SmsManager和默认的subid关联在一起
method public static android.telephony.SmsManager getDefault()获取默认的subid
method public static int getDefaultSmsSubscriptionId();获取和指定subid关联在一起的SmsManager对象
method public static android.telephony.SmsManager getSmsManagerForSubscriptionId(int);getSubscriptionId,是不是获取当前指定的simcard id,如果是双卡设备,用户没有设置默认的接收短信sim卡,则会跳转到SimDialogActivity,选择默认的接收短信subid
method public int getSubscriptionId();发送短信的方法
method public void sendDataMessage(java.lang.String, java.lang.String, short, byte[], android.app.PendingIntent, android.app.PendingIntent);发送一条彩信
method public void sendMultimediaMessage(android.content.Context, android.net.Uri, java.lang.String, android.os.Bundle, android.app.PendingIntent);发送通过divideMessage分割后的长短信
method public void sendMultipartTextMessage(java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.util.ArrayList<java.lang.String>, java.util.ArrayList<android.app.PendingIntent>, java.util.ArrayList<android.app.PendingIntent>);发送一条短信
method public void sendTextMessage(java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.lang.String, android.app.PendingIntent, android.app.PendingIntent);短信的发送流程
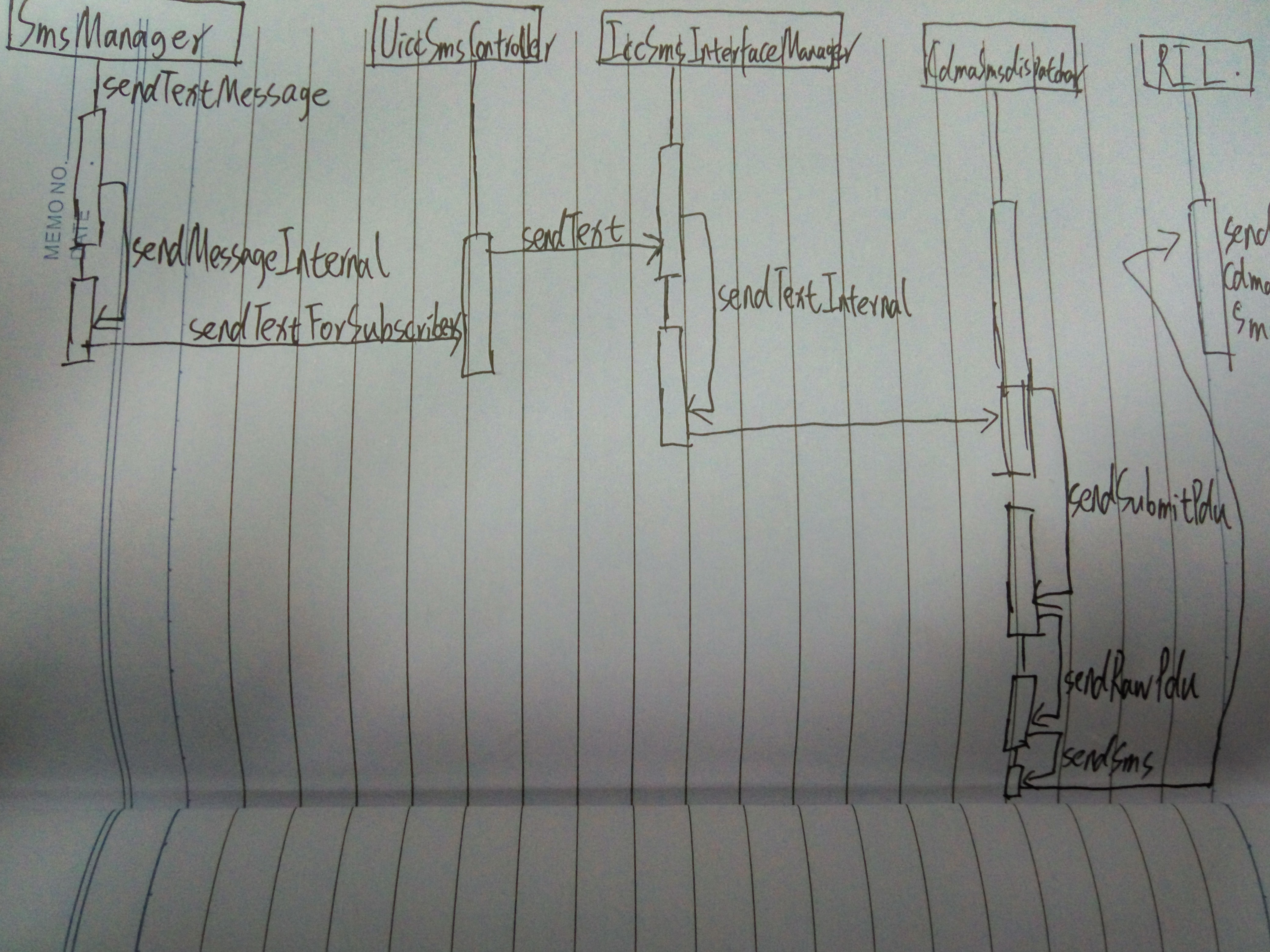
短信啊的发送从sendTextMessage 开始
需要申请”android.permission.SEND_SMS”;权限
destinationAddress 发送的目标号码
scAddress 中心号码,该号码不对时候,会出现发送短信失败,但是不影响接收短信
sentIntent
deliveryIntent 发送短信成功或者失败的时候会发送该pendingIntent对应的广播
deliveryIntent 目标号码接收短信成功或者失败的时候会发送该pendingIntent对应的广播
public void sendTextMessage(
String destinationAddress, String scAddress, String text,
PendingIntent sentIntent, PendingIntent deliveryIntent) {
android.util.SeempLog.record_str(75, destinationAddress);
sendTextMessageInternal(destinationAddress, scAddress, text,
sentIntent, deliveryIntent, true /* persistMessageForCarrierApp*/);
}进一步调用sendTextMessageInternal
private void sendTextMessageInternal(String destinationAddress, String scAddress,
String text, PendingIntent sentIntent, PendingIntent deliveryIntent,
boolean persistMessageForCarrierApp) {
// 检查目标号码是否为空
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(destinationAddress)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid destinationAddress");
}
// 检查短信内容是否为空
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(text)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid message body");
}
try {
ISms iccISms = getISmsServiceOrThrow();
iccISms.sendTextForSubscriber(getSubscriptionId(), ActivityThread.currentPackageName(),
destinationAddress,
scAddress, text, sentIntent, deliveryIntent,
persistMessageForCarrierApp);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// ignore it
}
}
private static ISms getISmsServiceOrThrow() {
ISms iccISms = getISmsService();
if (iccISms == null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Sms is not supported");
}
return iccISms;
}
private static ISms getISmsService() {
return ISms.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService("isms"));
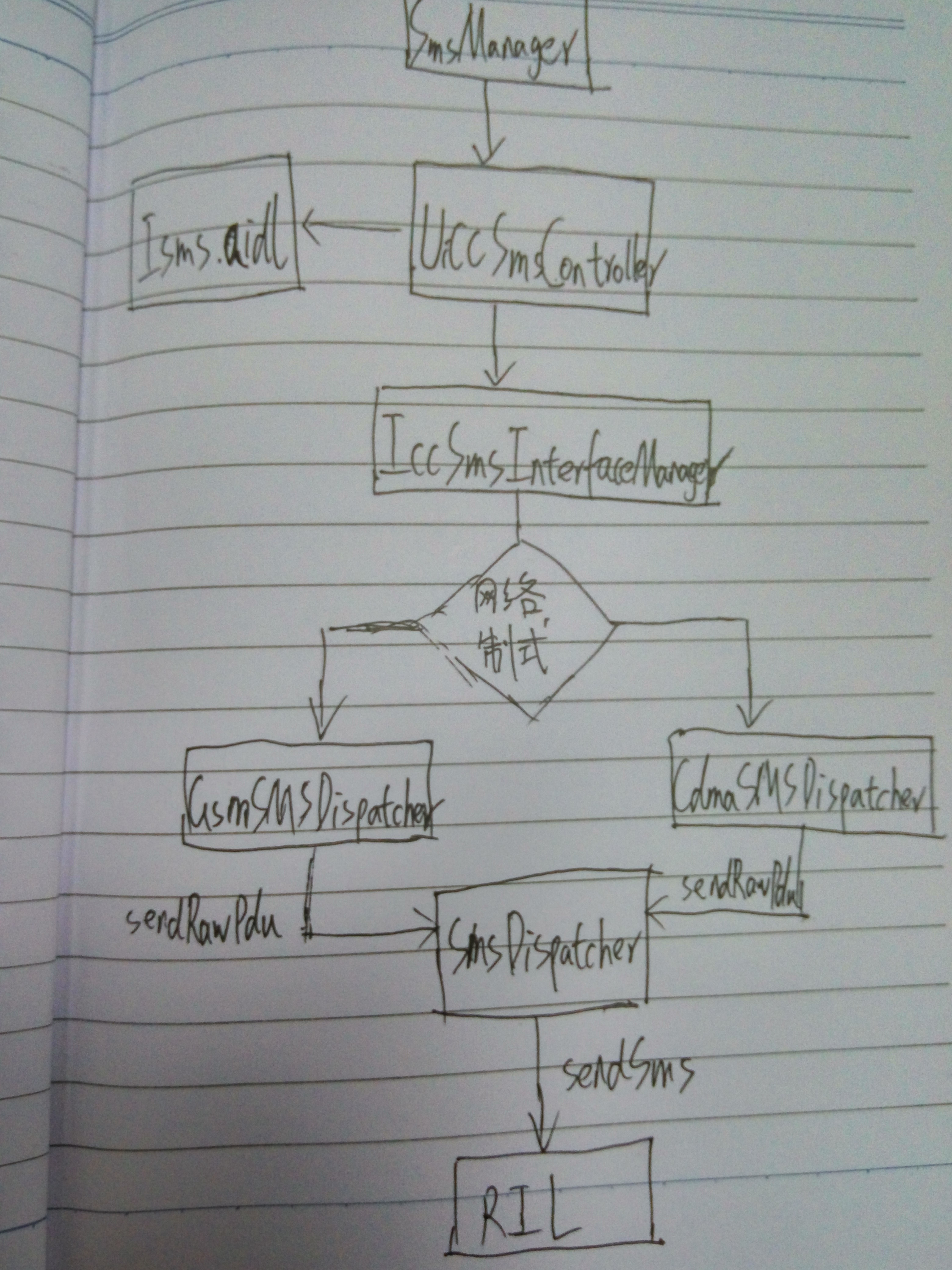
}这里getISmsServiceOrThrow()获取的是一个ISms服务UiccSmsController,UiccSmsController继承自ISms.Stub
frameworks/opt/telephony/src/java/com/android/internal/telephony/UiccSmsController.java
isms service是在UiccSmsController构造方法中添加的
protected UiccSmsController(Phone[] phone){
mPhone = phone;
if (ServiceManager.getService("isms") == null) {
ServiceManager.addService("isms", this);
}
}
UiccSmsController#sendTextForSubscriber
@Override
public void sendTextForSubscriber(int subId, String callingPackage, String destAddr,
String scAddr, String text, PendingIntent sentIntent, PendingIntent deliveryIntent,
boolean persistMessageForNonDefaultSmsApp) {
// 获取具有该subId对应的phone的IccSmsInterfaceManager对象
IccSmsInterfaceManager iccSmsIntMgr = getIccSmsInterfaceManager(subId);
if (iccSmsIntMgr != null) {
iccSmsIntMgr.sendText(callingPackage, destAddr, scAddr, text, sentIntent,
deliveryIntent, persistMessageForNonDefaultSmsApp);
} else {
Rlog.e(LOG_TAG,"sendTextForSubscriber iccSmsIntMgr is null for" +
" Subscription: " + subId);
sendErrorInPendingIntent(sentIntent, SmsManager.RESULT_ERROR_GENERIC_FAILURE);
}
}可以看到上面首先获取具有该subId对应的phone的IccSmsInterfaceManager对象,然后通过IccSmsInterfaceManager#sendText进一步发送短信
private @Nullable IccSmsInterfaceManager getIccSmsInterfaceManager(int subId) {
// 当前subId不可用,用户没有激活
if (!isActiveSubId(subId)) {
return null;
}
int phoneId = SubscriptionController.getInstance().getPhoneId(subId) ;
//Fixme: for multi-subscription case
if (!SubscriptionManager.isValidPhoneId(phoneId)
|| phoneId == SubscriptionManager.DEFAULT_PHONE_INDEX) {
phoneId = 0;
}
try {
// mPhone是在PhoneFactory中初始化并赋值的,Phone是一个接口,具体实现是在PhoneProxy中
return (IccSmsInterfaceManager)
((PhoneProxy)mPhone[(int)phoneId]).getIccSmsInterfaceManager();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
Rlog.e(LOG_TAG, "Exception is :"+e.toString()+" For subscription :"+subId );
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
Rlog.e(LOG_TAG, "Exception is :"+e.toString()+" For subscription :"+subId );
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
小插曲phone的初始化
从上面的代码可以看到phone是一个很重要的对象,其对于发送短信是不可或缺的,关于phone对象初始化是从PhoneFactory开始的
frameworks/opt/telephony/src/java/com/android/internal/telephony/PhoneFactory.java
public class PhoneFactory {
....
static private PhoneProxy[] sProxyPhones = null;
public static void makeDefaultPhones(Context context) {
makeDefaultPhone(context);
}
/**
* FIXME replace this with some other way of making these
* instances
*/
public static void makeDefaultPhone(Context context) {
synchronized (sLockProxyPhones) {
if (!sMadeDefaults) {
....
sContext = context;
int numPhones = TelephonyManager.getDefault().getPhoneCount();
int[] networkModes = new int[numPhones];
// 1. 为sProxyPhones数组初始化
sProxyPhones = new PhoneProxy[numPhones];
// 初始化sCommandsInterfaces
sCommandsInterfaces = new RIL[numPhones];
for (int i = 0; i < numPhones; i++) {
try {
networkModes[i] = TelephonyManager.getIntAtIndex(
context.getContentResolver(),
Settings.Global.PREFERRED_NETWORK_MODE , i);
} catch (SettingNotFoundException snfe) {
networkModes[i] = RILConstants.PREFERRED_NETWORK_MODE;
}
// 为sCommandsInterfaces赋值,最终发送短信其实就是通过RIL实现的
sCommandsInterfaces[i] = new RIL(context, networkModes[i],
cdmaSubscription, i);
}
// Instantiate UiccController so that all other classes can just
// call getInstance()
mUiccController = UiccController.make(context, sCommandsInterfaces);
for (int i = 0; i < numPhones; i++) {
PhoneBase phone = null;
int phoneType = TelephonyManager.getPhoneType(networkModes[i]);
if (phoneType == PhoneConstants.PHONE_TYPE_GSM) {
phone = TelephonyPluginDelegate.getInstance().makeGSMPhone(context,
sCommandsInterfaces[i], sPhoneNotifier, i);
} else if (phoneType == PhoneConstants.PHONE_TYPE_CDMA) {
phone = TelephonyPluginDelegate.getInstance().makeCDMALTEPhone(context,
sCommandsInterfaces[i], sPhoneNotifier, i);
}
// 2. 为sProxyPhones赋值,这里是Phone接口的实现类,PhoneProxy
sProxyPhones[i] = TelephonyPluginDelegate.getInstance().makePhoneProxy(phone);
}
mProxyController = ProxyController.getInstance(context, sProxyPhones,
mUiccController, sCommandsInterfaces);
// Set the default phone in base class.
// FIXME: This is a first best guess at what the defaults will be. It
// FIXME: needs to be done in a more controlled manner in the future.
sProxyPhone = sProxyPhones[0];
sCommandsInterface = sCommandsInterfaces[0];
// Default phone must be ready before ImsPhone is created
// because ImsService might need it when it is being opened.
for (int i = 0; i < numPhones; i++) {
sProxyPhones[i].startMonitoringImsService();
}
}
}
}
....
}
可以看到关于phone的初始化是在PhoneFactory#makeDefaultPhone中进行的,那么makeDefaultPhone其实是在PhoneGlobals#onCreate调用的呦。
packages/services/Telephony/src/com/android/phone/PhoneGlobals.java
public class PhoneGlobals extends ContextWrapper {
if (mCM == null) {
// 初始化phone数组
PhoneFactory.makeDefaultPhones(this);
// Start TelephonyDebugService After the default phone is created.
Intent intent = new Intent(this, TelephonyDebugService.class);
startService(intent);
mCM = CallManager.getInstance();
for (Phone phone : PhoneFactory.getPhones()) {
// 注册当前phone
mCM.registerPhone(phone);
}
// Create the NotificationMgr singleton, which is used to display
// status bar icons and control other status bar behavior.
notificationMgr = NotificationMgr.init(this);
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(EVENT_START_SIP_SERVICE);
// Create an instance of CdmaPhoneCallState and initialize it to IDLE
cdmaPhoneCallState = new CdmaPhoneCallState();
cdmaPhoneCallState.CdmaPhoneCallStateInit();
// before registering for phone state changes
mPowerManager = (PowerManager) getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
mWakeLock = mPowerManager.newWakeLock(PowerManager.FULL_WAKE_LOCK, LOG_TAG);
// lock used to keep the processor awake, when we don't care for the display.
mPartialWakeLock = mPowerManager.newWakeLock(PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK
| PowerManager.ON_AFTER_RELEASE, LOG_TAG);
mKeyguardManager = (KeyguardManager) getSystemService(Context.KEYGUARD_SERVICE);
// get a handle to the service so that we can use it later when we
// want to set the poke lock.
mPowerManagerService = IPowerManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService("power"));
// Get UpdateLock to suppress system-update related events (e.g. dialog show-up)
// during phone calls.
mUpdateLock = new UpdateLock("phone");
if (DBG) Log.d(LOG_TAG, "onCreate: mUpdateLock: " + mUpdateLock);
CallLogger callLogger = new CallLogger(this, new CallLogAsync());
callGatewayManager = CallGatewayManager.getInstance();
// Create the CallController singleton, which is the interface
// to the telephony layer for user-initiated telephony functionality
// (like making outgoing calls.)
callController = CallController.init(this, callLogger, callGatewayManager);
// Create the CallerInfoCache singleton, which remembers custom ring tone and
// send-to-voicemail settings.
//
// The asynchronous caching will start just after this call.
callerInfoCache = CallerInfoCache.init(this);
// Monitors call activity from the telephony layer
callStateMonitor = new CallStateMonitor(mCM);
phoneMgr = PhoneInterfaceManager.init(this, PhoneFactory.getDefaultPhone());
configLoader = CarrierConfigLoader.init(this);
// Create the CallNotifer singleton, which handles
// asynchronous events from the telephony layer (like
// launching the incoming-call UI when an incoming call comes
// in.)
notifier = CallNotifier.init(this, callLogger, callStateMonitor);
PhoneUtils.registerIccStatus(mHandler, EVENT_SIM_NETWORK_LOCKED);
// register for MMI/USSD
mCM.registerForMmiComplete(mHandler, MMI_COMPLETE, null);
// register connection tracking to PhoneUtils
PhoneUtils.initializeConnectionHandler(mCM);
// 注册监听对应的广播
IntentFilter intentFilter =
new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_AIRPLANE_MODE_CHANGED);
intentFilter.addAction(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_ANY_DATA_CONNECTION_STATE_CHANGED);
intentFilter.addAction(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_SIM_STATE_CHANGED);
intentFilter.addAction(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_RADIO_TECHNOLOGY_CHANGED);
intentFilter.addAction(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_SERVICE_STATE_CHANGED);
intentFilter.addAction(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_EMERGENCY_CALLBACK_MODE_CHANGED);
registerReceiver(mReceiver, intentFilter);
//set the default values for the preferences in the phone.
PreferenceManager.setDefaultValues(this, R.xml.network_setting, false);
PreferenceManager.setDefaultValues(this, R.xml.call_feature_setting, false);
// Make sure the audio mode (along with some
// audio-mode-related state of our own) is initialized
// correctly, given the current state of the phone.
PhoneUtils.setAudioMode(mCM);
}
....
}
}接上面IccSmsInterfaceManager.sendText
public void sendText(String callingPackage, String destAddr, String scAddr,
String text, PendingIntent sentIntent, PendingIntent deliveryIntent,
boolean persistMessageForNonDefaultSmsApp) {
// 检查当前应用包是否具有Manifest.permission.SEND_SMS权限,如果没有则抛出一个SecurityException
mPhone.getContext().enforceCallingPermission(
Manifest.permission.SEND_SMS,
"Sending SMS message");
sendTextInternal(callingPackage, destAddr, scAddr, text, sentIntent, deliveryIntent,
persistMessageForNonDefaultSmsApp);
}
private void sendTextInternal(String callingPackage, String destAddr, String scAddr,
String text, PendingIntent sentIntent, PendingIntent deliveryIntent,
boolean persistMessageForNonDefaultSmsApp) {
if (Rlog.isLoggable("SMS", Log.VERBOSE)) {
log("sendText: destAddr=" + destAddr + " scAddr=" + scAddr +
" text='"+ text + "' sentIntent=" +
sentIntent + " deliveryIntent=" + deliveryIntent);
}
if (!isAllowedToSendMsgByPolicy()) {
if (sentIntent != null) {
try {
sentIntent.send(SmsManager.RESULT_ERROR_GENERIC_FAILURE);
} catch (CanceledException ce) {
}
}
return;
}
if (mAppOps.noteOp(AppOpsManager.OP_SEND_SMS, Binder.getCallingUid(),
callingPackage) != AppOpsManager.MODE_ALLOWED) {
return;
}
if (!persistMessageForNonDefaultSmsApp) {
// Only allow carrier app to skip auto message persistence.
enforceCarrierPrivilege();
}
destAddr = filterDestAddress(destAddr);
// mDispatcher是SMSDispatcher类型,具体实现类是ImsSMSDispatcher
mDispatcher.sendText(destAddr, scAddr, text, sentIntent, deliveryIntent,
null/*messageUri*/, callingPackage, persistMessageForNonDefaultSmsApp,
-1, false, -1);
}通过判断网络制式,分别调用GsmSMSDispatcher和CdmaSMSDispatcher的sendText()方法。
@Override
protected void sendText(String destAddr, String scAddr, String text, PendingIntent sentIntent,
PendingIntent deliveryIntent, Uri messageUri, String callingPkg,
boolean persistMessage, int priority, boolean isExpectMore, int validityPeriod) {
Rlog.d(TAG, "sendText");
if (isCdmaMo()) {
mCdmaDispatcher.sendText(destAddr, scAddr,
text, sentIntent, deliveryIntent, messageUri, callingPkg, persistMessage,
priority, isExpectMore, validityPeriod);
} else {
mGsmDispatcher.sendText(destAddr, scAddr,
text, sentIntent, deliveryIntent, messageUri, callingPkg, persistMessage,
priority, isExpectMore, validityPeriod);
}
}以CdmaSMSDispatcher为例
@Override
protected void sendText(String destAddr, String scAddr, String text, PendingIntent sentIntent,
PendingIntent deliveryIntent, Uri messageUri, String callingPkg,
boolean persistMessage, int priority, boolean isExpectMore, int validityPeriod) {
// 将当前的参数封装成pdu
SmsMessage.SubmitPdu pdu = SmsMessage.getSubmitPdu(
scAddr, destAddr, text, (deliveryIntent != null), null, priority);
if (pdu != null) {
HashMap map = getSmsTrackerMap(destAddr, scAddr, text, pdu);
// 根据封装后的pdu,获取一个SmsTracker
SmsTracker tracker = getSmsTracker(callingPkg, map, sentIntent, deliveryIntent,
getFormat(), messageUri, isExpectMore, text, true /*isText*/, validityPeriod,
persistMessage);
String carrierPackage = getCarrierAppPackageName();
if (carrierPackage != null) {
TextSmsSender smsSender = new TextSmsSender(tracker);
smsSender.sendSmsByCarrierApp(carrierPackage, new SmsSenderCallback(smsSender));
} else {
// 通过sendSubmitPdu进一步发送短信,在sendSubmitPdu中会调用sendRawPdu(tracker);
sendSubmitPdu(tracker);
}
} else {
if (sentIntent != null) {
try {
sentIntent.send(SmsManager.RESULT_ERROR_GENERIC_FAILURE);
} catch (CanceledException ex) {
Rlog.e(TAG, "Intent has been canceled!");
}
}
}
}
@Override
protected void sendSubmitPdu(SmsTracker tracker) {
if (SystemProperties.getBoolean(TelephonyProperties.PROPERTY_INECM_MODE, false)) {
if (VDBG) {
Rlog.d(TAG, "Block SMS in Emergency Callback mode");
}
tracker.onFailed(mContext, SmsManager.RESULT_ERROR_NO_SERVICE, 0/*errorCode*/);
return;
}
// sendRawPdu是父类SMSDispatcher的方法
sendRawPdu(tracker);
}
SMSDispatcher#sendRawPdu
protected void sendRawPdu(SmsTracker tracker) {
HashMap map = tracker.mData;
// 获取pdu
byte pdu[] = (byte[]) map.get("pdu");
// 是否可以发送短信
if (mSmsSendDisabled) {
Rlog.e(TAG, "Device does not support sending sms.");
tracker.onFailed(mContext, RESULT_ERROR_NO_SERVICE, 0/*errorCode*/);
return;
}
// pdu是否为空
if (pdu == null) {
Rlog.e(TAG, "Empty PDU");
tracker.onFailed(mContext, RESULT_ERROR_NULL_PDU, 0/*errorCode*/);
return;
}
// Get calling app package name via UID from Binder call
PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager();
String[] packageNames = pm.getPackagesForUid(Binder.getCallingUid());
if (packageNames == null || packageNames.length == 0) {
// Refuse to send SMS if we can't get the calling package name.
Rlog.e(TAG, "Can't get calling app package name: refusing to send SMS");
tracker.onFailed(mContext, RESULT_ERROR_GENERIC_FAILURE, 0/*errorCode*/);
return;
}
// Get package info via packagemanager
PackageInfo appInfo;
try {
// XXX this is lossy- apps can share a UID
appInfo = pm.getPackageInfo(packageNames[0], PackageManager.GET_SIGNATURES);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
Rlog.e(TAG, "Can't get calling app package info: refusing to send SMS");
tracker.onFailed(mContext, RESULT_ERROR_GENERIC_FAILURE, 0/*errorCode*/);
return;
}
// checkDestination() returns true if the destination is not a premium short code or the
// sending app is approved to send to short codes. Otherwise, a message is sent to our
// handler with the SmsTracker to request user confirmation before sending.
if (checkDestination(tracker)) {
// check for excessive outgoing SMS usage by this app
if (!mUsageMonitor.check(appInfo.packageName, SINGLE_PART_SMS)) {
sendMessage(obtainMessage(EVENT_SEND_LIMIT_REACHED_CONFIRMATION, tracker));
return;
}
// 通过CdmaSMSDispatcher.sendSms(tracker)发送短信
sendSms(tracker);
}
}
- 获取pdu
- 判断是否可以发送短信
- 判断pdu是否为空
- 通过CdmaSMSDispatcher.sendSms(tracker)发送短信
@Override
protected void sendSms(SmsTracker tracker) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = tracker.mData;
// byte[] smsc = (byte[]) map.get("smsc"); // unused for CDMA
byte[] pdu = (byte[]) map.get("pdu");
Rlog.d(TAG, "sendSms: "
+ " isIms()=" + isIms()
+ " mRetryCount=" + tracker.mRetryCount
+ " mImsRetry=" + tracker.mImsRetry
+ " mMessageRef=" + tracker.mMessageRef
+ " SS=" + mPhone.getServiceState().getState());
sendSmsByPstn(tracker);
}
@Override
protected void sendSmsByPstn(SmsTracker tracker) {
int ss = mPhone.getServiceState().getState();
// if sms over IMS is not supported on data and voice is not available...
if (!isIms() && ss != ServiceState.STATE_IN_SERVICE) {
tracker.onFailed(mContext, getNotInServiceError(ss), 0/*errorCode*/);
return;
}
// 构造一个消息,表示发送完成
Message reply = obtainMessage(EVENT_SEND_SMS_COMPLETE, tracker);
byte[] pdu = (byte[]) tracker.mData.get("pdu");
int currentDataNetwork = mPhone.getServiceState().getDataNetworkType();
boolean imsSmsDisabled = (currentDataNetwork == TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EHRPD
|| (mPhone.getServiceStateTracker().isRatLte(currentDataNetwork)
&& !mPhone.getServiceStateTracker().isConcurrentVoiceAndDataAllowed()))
&& mPhone.getServiceState().getVoiceNetworkType()
== TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_1xRTT
&& ((CDMAPhone) mPhone).mCT.mState != PhoneConstants.State.IDLE;
if (0 == tracker.mImsRetry && !isIms()) {
mCi.sendCdmaSms(pdu, reply);
}
else if (!mImsSMSDispatcher.isImsSmsEnabled()) {
mCi.sendCdmaSms(pdu, reply);
mImsSMSDispatcher.enableSendSmsOverIms(true);
}
else {
mCi.sendImsCdmaSms(pdu, tracker.mImsRetry, tracker.mMessageRef, reply);
// increment it here, so in case of SMS_FAIL_RETRY over IMS
// next retry will be sent using IMS request again.
tracker.mImsRetry++;
}
}
上面的代码最终是通过mCi的sendCdmaSms或者sendImsCdmaSms进一步发送短信的,mCi是CommandsInterface接口,具体实现类也是在PhoneFactory中和Phone对象一并初始化的,其实就是RIL中,
到现在为止短信的发送流程就结束了。

























 6505
6505











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








