比较常用和简单。
package com.yzdzy.kotlin.chapter4.dataclass
data class Country(val id: Int, val name: String)
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val china = Country(0,"中国")
println(china)
//参数1
println(china.component1())
//参数2
println(china.component2())
val(id,name)=china
println(id)
println(name)
}输出
Country(id=0, name=中国)
0
中国
0
中国上面课程我们讲到过for循环
for((index,value) in args.withIndex()){
println(index)
println(value)
}点进去withIndex看源码
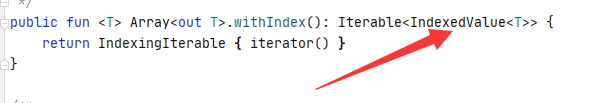
再点进去整个看源码

这就可以说明为啥可以这么写了
for(x in args.withIndex()){
println(x.index)
println(x.value)
}因为x就是一个
IndexedValuecomments可以自定义
package com.yzdzy.kotlin.chapter4.dataclass
class ComponentX {
operator fun component1(): String {
return "您好,我是1"
}
operator fun component2(): Int {
return 2
}
operator fun component3(): String {
return "您好,我是3"
}
operator fun component4(): String {
return "您好,我是4"
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val componentX = ComponentX()
val(a,b,c,d)=componentX;
println("$a,$b,$c,$d")
}结果:您好,我是1,2,您好,我是3,您好,我是4
数据类
-
默认实现copy toString等方法
-
compinentN方法
-
allOpen和noArgs插件
allOpen插件 是为了解决final得问题
noArgs是为了解决。没有无参勾构造的问题
。。data class country使用反编译后的代码
public final class Country {
private final int id;
@NotNull
private final String name;
public final int getId() {
return this.id;
}
@NotNull
public final String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Country(int id, @NotNull String name) {
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(name, "name");
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public final int component1() {
return this.id;
}
@NotNull
public final String component2() {
return this.name;
}
@NotNull
public final Country copy(int id, @NotNull String name) {
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(name, "name");
return new Country(id, name);
}
// $FF: synthetic method
public static Country copy$default(Country var0, int var1, String var2, int var3, Object var4) {
if ((var3 & 1) != 0) {
var1 = var0.id;
}
if ((var3 & 2) != 0) {
var2 = var0.name;
}
return var0.copy(var1, var2);
}
@NotNull
public String toString() {
return "Country(id=" + this.id + ", name=" + this.name + ")";
}
public int hashCode() {
int var10000 = this.id * 31;
String var10001 = this.name;
return var10000 + (var10001 != null ? var10001.hashCode() : 0);
}
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object var1) {
if (this != var1) {
if (var1 instanceof Country) {
Country var2 = (Country)var1;
if (this.id == var2.id && Intrinsics.areEqual(this.name, var2.name)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}没有午餐构造 方法默认使用了final修饰。。我们通过自定义注解配置一下这个部分
要用到两个插件。
像我这种kt入门选手 建议直接性的copy走下面的build。gradle
如果你是kt高手可以copy仅仅需要到的部分 noarg 和allopen相关,
buildscript {
ext.kotlin_version = '1.3.72'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:$kotlin_version"
classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-noarg:$kotlin_version"
classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-allopen:$kotlin_version"
}
}
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'application'
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm' version '1.3.61'
}
apply plugin:"java"
apply plugin:"kotlin"
apply plugin:"kotlin-noarg"
apply plugin:"kotlin-allopen"
mainClassName = "com.yzdzy.kotlin.calc.CalcKt"
group 'com.yzdzy'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
noArg {
annotation("com.yzdzy.kotlin.chapter4.annotations.PoKo")
}
allOpen {
annotation("com.yzdzy.kotlin.chapter4.annotations.PoKo")
}
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk8"
testCompile group: 'junit', name: 'junit', version: '4.12'
}
compileKotlin {
kotlinOptions.jvmTarget = "1.8"
}
compileTestKotlin {
kotlinOptions.jvmTarget = "1.8"
}com.yzdzy.kotlin.chapter4.annotations.PoKo 这个是我们自己新建的其中
com.yzdzy.kotlin.chapter4.annotations.是报名。 PoKo 是.kt文件
内容如下
package com.yzdzy.kotlin.chapter4.annotations
annotation class PoKo

下面就是给刚才最先的Country.kt类 添加注解
@PoKo
data class Country(val id: Int, val name: String)使用反编译 双击shift 输入 show k
召唤反编译工具
再看下我们的country
public class Country {
private final int id;
@NotNull
private final String name;
public int getId() {
return this.id;
}
@NotNull
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Country(int id, @NotNull String name) {
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(name, "name");
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public final int component1() {
return this.getId();
}
@NotNull
public final String component2() {
return this.getName();
}
@NotNull
public final Country copy(int id, @NotNull String name) {
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(name, "name");
return new Country(id, name);
}
// $FF: synthetic method
public static Country copy$default(Country var0, int var1, String var2, int var3, Object var4) {
if (var4 != null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Super calls with default arguments not supported in this target, function: copy");
} else {
if ((var3 & 1) != 0) {
var1 = var0.getId();
}
if ((var3 & 2) != 0) {
var2 = var0.getName();
}
return var0.copy(var1, var2);
}
}
@NotNull
public String toString() {
return "Country(id=" + this.getId() + ", name=" + this.getName() + ")";
}
public int hashCode() {
int var10000 = this.getId() * 31;
String var10001 = this.getName();
return var10000 + (var10001 != null ? var10001.hashCode() : 0);
}
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object var1) {
if (this != var1) {
if (var1 instanceof Country) {
Country var2 = (Country)var1;
if (this.getId() == var2.getId() && Intrinsics.areEqual(this.getName(), var2.getName())) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
public Country() {
}
}多了无参数构造。和取掉了final 完美。一个注解搞定。。就是配置费劲了点。
没点高级android开发工程师的水平估计要配置到天亮。。
但是你遇到了我的博客一样很快!

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










