1、getBoundingClientRect()
这个方法返回一个矩形对象,包含四个属性:left、top、right和bottom。分别表示元素各边与页面上边和左边的距离。
var box=document.getElementById(‘box’); // 获取元素
alert(box.getBoundingClientRect().top); // 元素上边距离页面上边的距离
alert(box.getBoundingClientRect().right); // 元素右边距离页面左边的距离
alert(box.getBoundingClientRect().bottom); // 元素下边距离页面上边的距离
alert(box.getBoundingClientRect().left); // 元素左边距离页面左边的距离
注意:IE、Firefox3+、Opera9.5、Chrome、Safari支持,在IE中,默认坐标从(2,2)开始计算,导致最终距离比其他浏览器多出两个像素,我们需要做个兼容。
document.documentElement.clientTop; // 非IE为0,IE为2
document.documentElement.clientLeft; // 非IE为0,IE为2
functiongGetRect (element) {
var rect = element.getBoundingClientRect();
var top = document.documentElement.clientTop;
var left= document.documentElement.clientLeft;
return{
top : rect.top - top,
bottom : rect.bottom - top,
left : rect.left - left,
right : rect.right - left
}
}
分别加上外边据、内边距、边框和滚动条,用于测试所有浏览器是否一致。
给个例子看一下:
现在我要获取
("body")[0].getBoundingClientRect()【补充个知识点:将jquery对象变成dom对象,就是
(“”)[0],如果将dom对象变成jquery对象就是在前面加上$】
这是body现在的大小
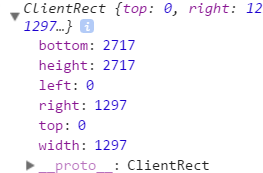
这是body获取到上,下,左,右的距离
body其实是从左上角计算的,这样充分理解了意义之后才可以使用它。
window.innerHeight在本机的电脑上是不改变的,就是屏幕的高度。我们可以通过比较$(“body”)[0].getBoundingClientRect().bottom与window.innerHeight之间的大小,确定这个时候有没有滚动条出现。然后再做其他的处理。






















 5341
5341

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








