二维数组例子,直接复制去吧。
int[][] arr = new int[8][];
arr[0] = new int[]{9, 12};
arr[1] = new int[]{1, 10};
arr[2] = new int[]{4, 11};
arr[3] = new int[]{8, 12};
arr[4] = new int[]{3, 9};
arr[5] = new int[]{6, 9};
arr[6] = new int[]{6, 7};
arr[7] = new int[]{1, 5};
先对数组进行排序
以x start 升序
如果 x start 相同,以 x end 升序
Arrays.sort(points, (o1, o2) -> {
if (o1[0] == o2[0]) {
return o1[1] - o2[1];
} else {
return o1[0] - o2[0];
}
});
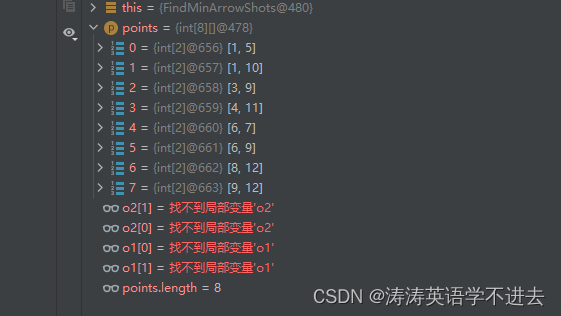
这个排序有个弊端。对[[-2147483646,-2147483645],[2147483646,2147483647]]这个测例会溢出。
这个是二维数组的单关键字升序
Arrays.sort(points, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
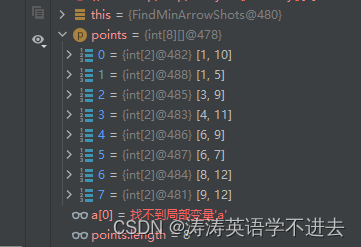
第三种方式是第一种的改进,防止溢出的。
Arrays.sort(points, (o1, o2) -> {
if (o1[0] == o2[0]) {
// 升序 o1[1]-o2[1] <0
// 即 o1[1]<o2[1]
// Integer.compare(o1[1], o2[1])
// 如果 o1[1]<o2[1]
// Integer.compare(o1[1], o2[1]) 返回 -1 也<0
return Integer.compare(o1[1], o2[1]);
} else {
return Integer.compare(o1[0], o2[0]);
}
});
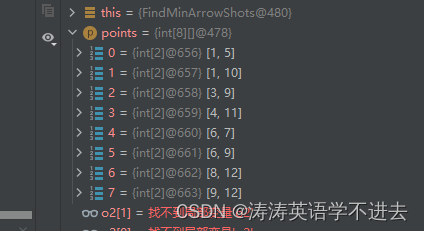
二维数组根据不同列进行升序降序选择。






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








