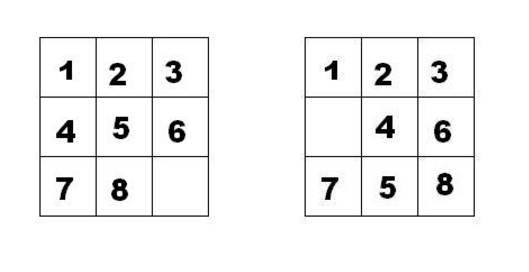
我们把第一个图的局面记为:12345678.
把第二个图的局面记为:123.46758
显然是按从上到下,从左到右的顺序记录数字,空格记为句点。
本题目的任务是已知九宫的初态和终态,求最少经过多少步的移动可以到达。如果无论多少步都无法到达,则输出-1。
123.46758
46758123.
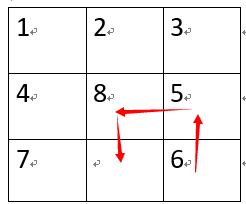
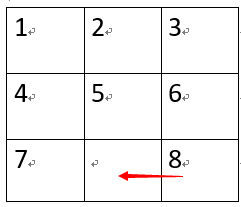
分析:题意说的很清晰,就是移动白块使初状态和末状态一致,移动可以用广搜模拟,但是我们会发现即使白块处于同一个位置,状态仍然可能不一样,以第一组数据初状态为例:
同样是在(2,1)的位置(x,y从0开始),不同的走法状态不一样:
走法1: 走法2:
对应状态分别为(1234857.6) 和(1234567.8) ===》这就要求我们每次移动记录矩阵相应的状态,故需要引入HashMap<String,Integer>(String 存状态,Integer存步数)进行记录,
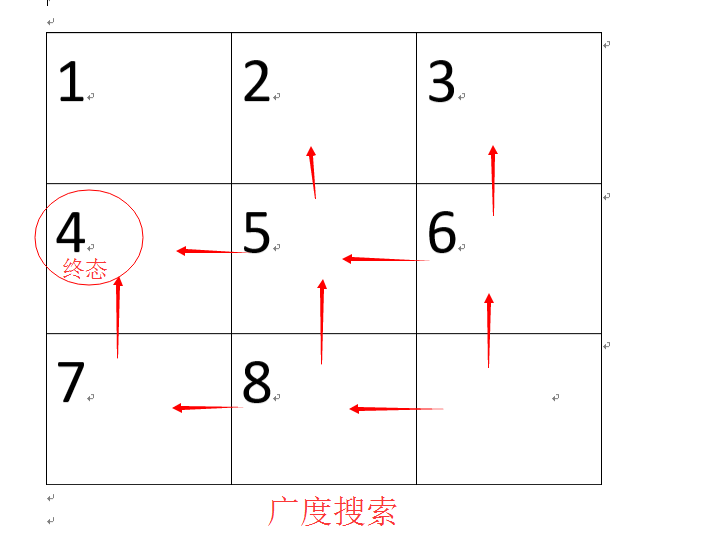
思路:从始态的空白格开始进行广搜,对其上下左右进行广搜,搜一次,对调一次值,将其所对应的状态(如12345678.)放入进行判重,最后只要判断搜到终态空白区域的X,Y且状态一致,就可以得到次数,如果,最后结束仍搜不到,即不可达,输出-1;
搜索图例:
直接搜索:
1.结点(Node)类,里面包含属性,方法:
class Node {
public int x, y;//当前空白格位置坐标
public int sum;//空白格移至当前坐标所需次数
public String s;//此时的矩阵的状态(字符串型,存hashMap时要用)
public char[][] ch;//此时的矩阵的状态(矩阵型)
public Node(int ax, int ay, char[][] a, int sum) {//构造方法
this.x = ax;
this.y = ay;
this.ch = a;
this.sum = sum;
this.s = getString();
}
public char[][] getMap() {//获取矩阵状态
char[][] t = new char[3][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
t[i][j] = ch[i][j];
}
}
return t;
}
private String getString() {//获取字符串型状态
//比StringBuilder和直接String s节省时间
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
sb.append(ch[i][j]);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public String toString() {//调试时方便查看
return "(" + x + "," + y + ") " + sum;
}
}2.Main函数
static Map<String, Integer> map1;//HashMap 判重
static int dir[][] = { { -1, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 } };// 方向数组 上 下 左 右
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (in.hasNext()) {
map1 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
char[] aa = in.next().toCharArray();//读字符串
char[] bb = in.next().toCharArray();//读字符串
char[][] a = new char[3][3];
char[][] b = new char[3][3];
int ax = 0, ay = 0, bx = 0, by = 0, len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {//字符串转3*3二维数组
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
a[i][j] = aa[len];
b[i][j] = bb[len++];
if (a[i][j] == '.') {//记录空白位置始态的坐标
ax = i;
ay = j;
}
if (b[i][j] == '.') {//记录空白位置终态的坐标
bx = i;
by = j;
}
}
}
Node no1 = new Node(ax, ay, a, 0);//始态结点(传入坐标,二维数组及步数)
Node no2 = new Node(bx, by, b, 0);//终态结点
map1.put(no1.s, 0);//将初始的状态存入HashMap
Queue<Node> qNode1 = new LinkedList<Node>();
qNode1.add(no1);//始态入队
int count = BFS(qNode1,no2);
System.out.println(count);
}
in.close();
}3.BFS函数解析:
private static int BFS(Queue<Node> q1, Node no2) {
while (!q1.isEmpty()) {
Node n = q1.poll();
int x = n.x;
int y = n.y;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = x + dir[i][0];
int yy = y + dir[i][1];
if (!(0 <= xx && xx < 3 && 0 <= yy && yy < 3))
continue;
char[][] a = n.getMap();
a[x][y] = a[xx][yy];
a[xx][yy] = '.';
Node t = new Node(xx, yy, a, n.sum + 1);
if(xx == no2.x && yy == no2.y && t.s.equals(no2.s))//搜到终态位置且状态一致
return t.sum;
if (!map1.containsKey(t.s)) {//如果状态不存在,即放入HashMap
q1.add(t);//入队继续判断
map1.put(t.s, t.sum);
}
}
}
return -1;//如果搜索完,说明没找到,返回-1
单向搜索AC代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static Map<String, Integer> map1;//HashMap 判重
static int dir[][] = { { -1, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 } };// 方向数组 上 下 左 右
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (in.hasNext()) {
map1 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
char[] aa = in.next().toCharArray();//读字符串
char[] bb = in.next().toCharArray();//读字符串
char[][] a = new char[3][3];
char[][] b = new char[3][3];
int ax = 0, ay = 0, bx = 0, by = 0, len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {//字符串转3*3二维数组
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
a[i][j] = aa[len];
b[i][j] = bb[len++];
if (a[i][j] == '.') {//记录空白位置始态的坐标
ax = i;
ay = j;
}
if (b[i][j] == '.') {//记录空白位置终态的坐标
bx = i;
by = j;
}
}
}
Node no1 = new Node(ax, ay, a, 0);//始态结点(传入坐标,二维数组及步数)
Node no2 = new Node(bx, by, b, 0);//终态结点
map1.put(no1.s, 0);//将初始的状态存入HashMap
Queue<Node> qNode1 = new LinkedList<Node>();
qNode1.add(no1);//始态入队
int count = BFS(qNode1,no2);
System.out.println(count);
}
in.close();
}
private static int BFS(Queue<Node> q1, Node no2) {
while (!q1.isEmpty()) {
Node n = q1.poll();
int x = n.x;
int y = n.y;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = x + dir[i][0];
int yy = y + dir[i][1];
if (!(0 <= xx && xx < 3 && 0 <= yy && yy < 3))
continue;
char[][] a = n.getMap();
a[x][y] = a[xx][yy];
a[xx][yy] = '.';
Node t = new Node(xx, yy, a, n.sum + 1);
if(xx == no2.x && yy == no2.y && t.s.equals(no2.s))//搜到终态位置且状态一致
return t.sum;
if (!map1.containsKey(t.s)) {//如果状态不存在,即放入HashMap
q1.add(t);//入队继续判断
map1.put(t.s, t.sum);
}
}
}
return -1;//如果搜索完,说明没找到,返回-1
}
}
class Node {
public int x, y;//当前空白格位置坐标
public int sum;//从始态到当前,走了几步
public String s;//此时的矩阵的状态(字符串型,存hashMap时要用)
public char[][] ch;//此时的矩阵的状态(矩阵型)
public Node(int ax, int ay, char[][] a, int sum) {//构造方法
this.x = ax;
this.y = ay;
this.ch = a;
this.sum = sum;
this.s = getString();
}
public char[][] getMap() {//获取矩阵状态
char[][] t = new char[3][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
t[i][j] = ch[i][j];
}
}
return t;
}
private String getString() {//获取字符串型状态
//比StringBuilder和直接String s节省时间
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
sb.append(ch[i][j]);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public String toString() {//调试时方便查看
return "(" + x + "," + y + ") " + sum;
}
}
但是,交上去后发现,单向搜索过于耗时,那么我们就可以用到双向搜索
双向BFS(时间比单向的更快):
定义两个HashMap,map1(始态),map2(终态),始态和终态同时搜索,假设始态的白块要移动到某个位置A,我们先判断一下A点这个位置是否有被终态搜索过,即判断map2是否已经存在该点的状态,如果存在,直接将其步数取出再加上现在所走的步数,即为答案,如果未存在,就把A点的状态存到map1,继续搜索;同理,终态的白块也可以访问map1的状态,这样,就可以实现双向搜索,原理同单向搜索,出口改为map1,map2交界的状态。
双向AC代码:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static Map<String, Integer> map1;
static Map<String, Integer> map2;
static int dir[][] = { { -1, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 } };// 方向数组 上
// 下 左 右
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (in.hasNext()) {
map1 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map2 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
char[] aa = in.next().toCharArray();
char[] bb = in.next().toCharArray();
char[][] a = new char[3][3];
char[][] b = new char[3][3];
int ax = 0, ay = 0, bx = 0, by = 0, len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
a[i][j] = aa[len];
b[i][j] = bb[len++];
if (a[i][j] == '.') {
ax = i;
ay = j;
}
if (b[i][j] == '.') {
bx = i;
by = j;
}
}
}
Node no1 = new Node(ax, ay, a, 0);
Node no2 = new Node(bx, by, b, 0);
map1.put(no1.s, 0);
map2.put(no2.s, 0);
Queue<Node> qNode1 = new LinkedList<Node>();
qNode1.add(no1);
Queue<Node> qNode2 = new LinkedList<Node>();
qNode2.add(no2);
int count = BFS(qNode1, qNode2);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
private static int BFS(Queue<Node> q1, Queue<Node> q2) {
while (!q1.isEmpty() || !q2.isEmpty()) {
Node n;
if (!q1.isEmpty()) {
n = q1.poll();
int x = n.x;
int y = n.y;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = x + dir[i][0];
int yy = y + dir[i][1];
if (!(0 <= xx && xx < 3 && 0 <= yy && yy < 3))
continue;
char[][] a = n.getMap();
a[x][y] = a[xx][yy];
a[xx][yy] = '.';
Node t = new Node(xx, yy, a, n.sum + 1);
if (map2.containsKey(t.s)) {
return t.sum + map2.get(t.s);
}
if (!map1.containsKey(t.s)) {
q1.add(t);
map1.put(t.s, t.sum);
}
}
}
if (!q2.isEmpty()) {
n = q2.poll();
int x = n.x;
int y = n.y;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = x + dir[i][0];
int yy = y + dir[i][1];
if (!(0 <= xx && xx < 3 && 0 <= yy && yy < 3))
continue;
char[][] a = n.getMap();
a[x][y] = a[xx][yy];
a[xx][yy] = '.';
Node t = new Node(xx, yy, a, n.sum + 1);
if (map1.containsKey(t.s)) {
return t.sum + map1.get(t.s);
}
if (!map2.containsKey(t.s)) {
q2.add(t);
map2.put(t.s, t.sum);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
class Node {
public int x, y, sum;
public String s;
public char[][] ch;
public Node(int ax, int ay, char[][] a, int sum) {
this.x = ax;
this.y = ay;
this.ch = a;
this.sum = sum;
this.s = getString();
}
public char[][] getMap() {
char[][] t = new char[3][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
t[i][j] = ch[i][j];
}
}
return t;
}
private String getString() {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
sb.append(ch[i][j]);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public String toString() {
return "(" + x + "," + y + ") " + sum;
}
}






















 1227
1227











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








