Java中容器是非常重要的概念。Java API(java.util包内)所提供的一系列类的实例,用于在程序中存放对象。
1136(1个图1个类3个知识点6个接口)
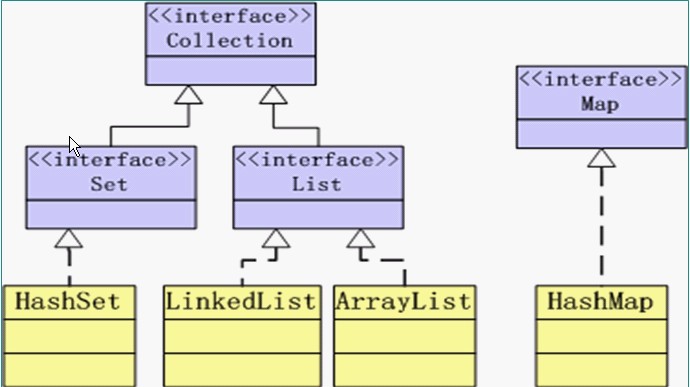
Collection接口--定义了存取一组对象的方法,其子接口Set和List分别定义了存储方式。
a.Set中的数据对象是没有顺序且不可以重复(重复指的是相互equals)
b.List中的数据对象有顺序且可以重复
Map接口定义了存储“键(key)--值(value)映射对”的方法。
例子1:
import java.util.*;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Collection c = new ArrayList();//为什么不写ArrayList al = new ArrayList(); 提供最大的灵活性,方便日后修改代码
//可以放入不同类型的对象
c.add("hello");
c.add(new Name("f1","11"));
c.add(new Integer(100));//必须装<span style="color:#ff0000;">对象</span>,不能是基础类型
System.out.println(c.size());
System.out.println(c);
}
}
class Name
{
public String fName;
public String lName;
public Name(String string, String string2) {
fName = string;
lName = string2;
}
public String toString(){
return fName +" "+ lName;
}
}输出结果:
3
[hello, f1 11, 100]
例子2:
import java.util.*;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Collection c = new HashSet();
//可以放入不同类型的对象
c.add("hello");
c.add(new Name("f1","11"));
c.add(new Integer(100));//必须装对象,不能是基础类型
c.remove("hello");
c.remove(new Integer(100));
System.out.println(c.remove(new Name("f1","11")));
System.out.println(c);
}
}
class Name
{
public String fName;
public String lName;
public Name(String string, String string2) {
fName = string;
lName = string2;
}
public String toString(){
return fName +" "+ lName;
}
}
输出结果:
false
[f1 11]分析:
两个new出来的f1 11是不同的两个对象,不相等,删除无法完成。
容器类对象在调用remove、contains等方法时需要比较对象是否相等,这会涉及到对象类型的equals方法和hashCode方法;对于自定义的类型,需要重写equals和hashCode方法以实现自定义的对象相等规则。
注意:相等的对象应该具有相等的hash codes。
例子2(续)--重写equals和hashCode方法之后 删除完成:
import java.util.*;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Collection c = new HashSet();
//可以放入不同类型的对象
c.add("hello");
c.add(new Name("f1","11"));
c.add(new Integer(100));//必须装对象,不能是基础类型
c.remove("hello");
c.remove(new Integer(100));
System.out.println(c.remove(new Name("f1","11")));
System.out.println(c);
}
}
class Name
{
public String fName;
public String lName;
public Name(String string, String string2) {
fName = string;
lName = string2;
}
public String toString(){
return fName +" "+ lName;
}
//重写equals和hashCode方法
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj instanceof Name){
Name name = (Name)obj;
return (fName.equals(name.fName)) && (lName.equals(name.lName));
}
return super.equals(obj);
}
public int hashCode(){
return fName.hashCode();
}
}
输出结果:
true
[]
Iterator 接口(遍历)
1)所有实现了Collection接口的容器类都有一个iterator方法用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象。
2)Iteratord对象称作迭代器,用以方便的实现对容器内元素的遍历操作
3)Iterator接口定义的方法:
boolean hasNext(); //判断游标右边是否有元素
Object next(); //返回游标右边的元素并将游标移动到下一个位置
void remove(); //删除游标左面的元素,在执行完next之后该操作只能执行一次
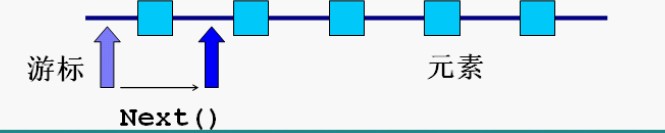
说明:
可以将Iterator看作是一个游标(或者指针),当第一次拿到这个Iterator时,游标停在第一个元素的左边。
例子3:
import java.util.*;
public class TestIterator {
public static void main(String[] args){
/* Collection c = new HashSet();
c.add(new Name("f1","11"));
c.add(new Name("f2","12"));
c.add(new Name("f3","13"));
Iterator i = c.iterator();//很关键,多态
while(i.hasNext()){
Name n = (Name)i.next();
System.out.print(n.getFirstName()+" ");
}*/
Collection c = new HashSet();
c.add(new Name("fff1","1111"));
c.add(new Name("f2","13"));
c.add(new Name("fff3","1113"));
for(Iterator i = c.iterator();i.hasNext();){
Name name = (Name)i.next();
if(name.getFirstName().length()<3){
i.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(c);
}
}
class Name{
public String firstName,lastName;
public Name(String s1,String s2){
firstName = s1;
lastName= s2;
}
public String getFirstName(){
return firstName;
}
public String toString(){
return firstName +" " +lastName;
}
}
输出结果:
[fff3 1113, fff1 1111]Set接口
1)Set接口是Collection接口的子接口,Set接口没有提供额外的方法,但Sun规定实现Set接口的容器类中的元素是没有顺序的,而且不可以重复。
2)Set容器可以与数学中的”集合“的概念相对应。
3)J2SDK API中所提供的Set容器类有HashSet,TreeSet等。
例子4:
import java.util.*;
/*
* 测试HashSet的retainAll()和addAll()
*/
public class TestSet {
public static void main(String[] args){
/*Set s= new HashSet();
s.add("hello");
s.add("world");
s.add(new Integer(100));
s.add("world");
System.out.println(s);*/
Set s1 = new HashSet();
Set s2 = new HashSet();
s1.add("a");s1.add("b");s1.add("c");s1.add("d");
s2.add("e");s2.add("f");s2.add("a");s2.add("c");
Set sn = new HashSet(s1);
sn.retainAll(s2);
Set su = new HashSet(s1);<pre name="code" class="java">[c, a]
[f, d, e, b, c, a]
su.addAll(s2);System.out.println(sn);System.out.println(su);}}
输出结果:
[c, a]
[f, d, e, b, c, a]
List接口
1)List接口是Connection接口的子接口,实现List接口的容器类中的元素是有顺序的,而且可以重复。
2)List容器中的元素都对应一个整数型的序号记载其在容器中的位置,可以根据序号存取容器中的元素。
3)J2SDK所提供的List容器类有ArrayList,LinkedList等
Object get(int index);
Object set(int index,Object element);//返回被替代的旧元素
void add(int index,Object element);
int indexOf(Object o);
int lastIndexOf(Object o);
例子4:
import java.util.*;
public class TestList {
public static void main(String[] args){
List l1 = new LinkedList();
for(int i = 0;i <= 5;i++){
l1.add("a" + i);
}
l1.add(3,"a100");
System.out.println(l1);
l1.set(6,"a200");
System.out.println(l1);
System.out.println((String)l1.get(2));
System.out.println(l1.indexOf("a3"));
l1.remove(1);
System.out.println(l1);
}
}
输出结果:
[a0, a1, a2, a100, a3, a4, a5]
[a0, a1, a2, a100, a3, a4, a200]
a2
4
[a0, a2, a100, a3, a4, a200]
类java.util.Collections提供了一系列静态方法实现了基于List容器的一些常用算法。
例子5:
import java.util.*;
public class TestConnections {
public static void main(String[] args){
List l1 = new LinkedList();
for(int i = 0;i <=9;i++){
l1.add("a" + i);
}
System.out.println(l1);
Collections.shuffle(l1);//随机排序
System.out.println(l1);
Collections.reverse(l1);//逆序排序
System.out.println(l1);
Collections.sort(l1);//排序
System.out.println(l1);
System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(l1, "a4"));
}
}
输出结果:
[a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9]
[a2, a3, a1, a0, a4, a6, a8, a5, a7, a9]
[a9, a7, a5, a8, a6, a4, a0, a1, a3, a2]
[a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9]
4
排序中是怎么比较两个对象的大小呢(比如9只猫怎么比较大小)-- Comparable 接口
所有可以”排序"的类都实现了java.lang.Comparable 接口,Comparable接口中只有一个方法
public int compareTo(Object obj);该方法:
返回 0 表示 this == obj;
返回正数表示this > obj;
返回负数表示this < obj;
实现了Comparable接口的类通过实现comparaTo方法从而确定该类对象的排序方式。
例子6:
import java.util.*;
public class TestIterator {
public static void main(String[] args){
List l1 = new LinkedList();
l1.add(new Name("Karl","M"));
l1.add(new Name("Steven","Lee"));
l1.add(new Name("John","O"));
l1.add(new Name("Tom","M"));
System.out.println(l1);
Collections.sort(l1);
System.out.println(l1);
}
}
class Name implements Comparable{
public String firstName,lastName;
public Name(String s1,String s2){
firstName = s1;
lastName= s2;
}
public String getFirstName(){
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName(){
return lastName;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj instanceof Name){
Name name = (Name)obj;
return (firstName.equals(name.firstName))&&(lastName.equals(name.lastName));
}
return super.equals(obj);
}
public int hashCode(){
return firstName.hashCode();
}
public String toString(){
return firstName +" " +lastName;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Name n = (Name) o;
int lastCmp = lastName.compareTo(n.lastName);
return lastCmp != 0 ? lastCmp : firstName.compareTo(n.firstName);
}
}输出结果:
[Karl M, Steven Lee, John O, Tom M]
[Steven Lee, Karl M, Tom M, John O]
衡量标准:读的效率和改的效率
1)Array读快改慢
2)Linked改快读慢
3)Hash两者之间
Map接口
1)实现Map接口的类用来存储键值对。
2)Map接口的实现类有HashMap和TreeMap等
3)Map类中存储的键值对通过键来标识,所以键值不能重复。
例子7:import java.util.*;
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args){
Map m1 = new HashMap();
Map m2 = new HashMap();
m1.put("one", new Integer(1));
m1.put("two",new Integer(2));
m1.put("three",new Integer(3));
m2.put("A", new Integer(1));
m2.put("B", new Integer(2));
System.out.println(m1.size());
System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one"));
System.out.println(m2.containsValue(new Integer(1)));
if(m1.containsKey("two")){
int i =((Integer) m1.get("two")).intValue();
System.out.println(i);
}
Map m3 = new HashMap(m1);
m3.putAll(m2);
System.out.println(m3);
}
}
输出结果:
3
true
true
2
{two=2, A=1, B=2, one=1, three=3}
上面的程序可以简化为:
import java.util.*;
/*
* 测试包装类的自动打包与解包
*/
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args){
Map m1 = new HashMap();
Map m2 = new HashMap();
//m1.put("one", new Integer(1));
m1.put("one", 1);
//m1.put("two",new Integer(2));
m1.put("two", 2);
//m1.put("three",new Integer(3));
m1.put("three", 3);
//m2.put("A", new Integer(1));
m2.put("A",1);
//m2.put("B", new Integer(2));
m2.put("B", 2);
System.out.println(m1.size());
System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one"));
System.out.println(m2.containsValue(new Integer(1)));
if(m1.containsKey("two")){
//int i =((Integer) m1.get("two")).intValue();
int i = (Integer)m1.get("two");
System.out.println(i);
}
Map m3 = new HashMap(m1);
m3.putAll(m2);
System.out.println(m3);
}
}






















 5379
5379

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








