写在前面,本文百分之70来自saltstack官方文档摘抄,百分之20来自网络其他博文
saltstack官方文档目录:http://docs.saltstack.cn/zh_CN/latest/contents.html
入门篇
使用pip安装
因为Salt已经进入 PyPI , 所以可以使用pip安装,尽管多数用户优先使用RPMs安装(可以从 EPEL 安装)。从pip安装很简单:
pip install salt
警告
如果从pip安装(或者使用 setup.pyinstall 从源码安装),需要注意 yum-utils 被Salt依赖,用于管理软件包。同样的,如果Python依赖没有安装,你需要额外安装库/工具来构建一些依赖。更多信息点这里。
从EPEL安装
从0.9.4版本开始,Salt已经在 EPEL 中可用。使用yum即可安装。Salt可以在所有主流的基于RHEL的发行版中使用,包括CentOS, Scientific Linux,Oracle Linux和Amazon Linux。报告任何bugs或者issues在issue tracker。
在RHEL6上,Jinja包 'python-jinja2' 从EPEL移动到"RHEL Server Option Channel"中去. 在RHEL6平台上安装salt时请确保该仓库处于enabled状态.
1. RHEL中开启EPEL
在你的系统中如果EPEL当前并不是enabled状态,你可以通过如下命令启用它.
对于RHEL 5:
rpm -Uvh http://mirror.pnl.gov/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
对于RHEL 6:
rpm -Uvh http://ftp.linux.ncsu.edu/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
简单配置
Master
配置master开机自动启动:
chkconfig salt-master on
启动Master:
service salt-master start
Minion
配置Minion开机自动启动:
chkconfig salt-minion on
启动Minion:
service salt-minion start
==========
Salt Minion仅仅需要知道一条信息就可以运行,Master的网络位置
默认情况下minion将会查找DNS解析 salt 作为master,最简单的途径是搭建一个内部的DNS将salt 解析到Salt Master IP上。
否则,需要编辑minion配置文件配置 master 选项指向Salt Master的DNS名或IP:
注解
默认配置文件路径位于/etc/salt下。大多数平台会遵守这个约定,但是像FreeBSD和Microsoft Windows这样的平台会将这个文件放在不同的路径。
/etc/salt/minion:
master: saltmaster.example.com
现在已经能够找到master了,同master一样以相同方式启动minion;使用平台init系统或者直接通过命令行。
以daemon模式运行
salt-minion -d
在前台以debug模式运行
salt-minion -l debug
当minion启动后,它会产生一个 id 值,除非已经在之前的运行过程中产生过并且缓存在配置路径下,默认是/etc/salt 。minion用这个值作为名称尝试去master进行验证。尝试下面几步操作,以便找到一个不是localhost 的值:
-
运行Python函数"socket.getfqdn()"
-
核对"/etc/hostname"(仅针对非Windows系统)
-
核对"/etc/hosts"(在Windows主机上是"%WINDIR%system32driversetchosts") 上的包括"127.0.0.0/8"在内的所有主机名。
如果以上都不能产生除"localhost"以外的id,那么就会按顺序检测minion上的IP地址列表(排除"127.0.0.0/8"在内)。如果存在,就会使用第一个公网路由IP地址,否则就会使用第一个私网路由IP地址。
如果所有这些都失败了,那么就会使用"localhost"作为备选。
现在minion已经运行了,它会产生秘钥对并且尝试连接master。下一步就是折回master服务器接受新minion的公钥。
使用salt-key
Salt通过公钥加密和认证minions。想要让minion从master端接受命令,minions的密钥需要被master接受。
salt-key 命令时用来管理master上所有的密钥的。列出master上的密钥:
salt-key -L
The keys that have been rejected, accepted, and pending acceptance are listed.The easiest way to accept the minion key is to accept all pending keys:
salt-key -A
注解
Keys should be verified! The secure thing to do before accepting a key isto runsalt-key -f minion-id to print the fingerprint of the minion'spublic key. This fingerprint can then be compared against the fingerprintgenerated on the minion.
On the master:
# salt-key -f foo.domain.com
Unaccepted Keys:
foo.domain.com: 39:f9:e4:8a:aa:74:8d:52:1a:ec:92:03:82:09:c8:f9
On the minion:
# salt-call key.finger --local
local:
39:f9:e4:8a:aa:74:8d:52:1a:ec:92:03:82:09:c8:f9
If they match, approve the key with salt-key -a foo.domain.com.
测试
现在minion已经连接到master并且通过认证,master可以发送命令到minion。
Salt命令允许执行海量的函数库,并且可以针对特殊的minions和minions组为目标执行。
salt 命令包含命令选项,目标说明,要执行的函数,和函数的参数。
一个简单的入门级命令看起来像是这样:
salt '*' test.ping
* 是指向所有minions的目标。
test.ping 告诉minon运行 test.ping 函数。
In the case of test.ping, test refers to a execution module. ping refers to theping function contained in the aforementionedtestmodule.
注解
Execution modules are the workhorses of Salt. They do the work on thesystem to perform various tasks, such as manipulating files and restartingservices.
运行这条命令的结果将会是master指示所有的minions并行执行 test.ping 并返回结果。
这不是真正的ICMP ping,而是一个简单的函数返回 True。使用 test.ping 是确认一个minion是否连接正常的好方法。
注解
每个minion使用唯一的minion ID注册自身,但是也能够通过使用minion配置中的 id 选项来明确定义。
Of course, there are hundreds of other modules that can be called just astest.ping can. For example, the following would return disk usage on alltargeted minions:
salt '*' disk.usage
函数
函数概况
Salt拥有一个巨大的函数库可用于执行,而且Salt函数是自带文档说明的。在minions上执行 sys.doc 函数可以查看哪些函数可用:
salt '*' sys.doc
这会显示一个非常大的可用函数和函数文档列表。
注解
模块文档也可以 在线 查看。
这些函数覆盖从shell命令到包管理到数据库服务器操作等所有内容。它们包含强大的系统管理API,而这则是Salt配置管理和很多其他部分的核心。
注解
Salt拥有很多插件系统。这些函数通过文档:`执行模块 </ref/modules/all/index>`的"salt"命令可用。
了解一些有帮助的函数
文档`cmd </ref/modules/all/salt.modules.cmdmod>`模块包含在minions上执行shell命令的函数,比如模块`cmd.run <salt.modules.cmdmod.run>`和模块`cmd.run_all <salt.modules.cmdmod.run_all>`:
salt '*' cmd.run 'ls -l /etc'
pkg 函数会自动将本地系统包管理器映射到相同的salt函数。这意味着 pkg.install 在基于Red Hat系统上将使用 yum 而在Debian系统上则使用apt 来安装包,等等。
salt '*' pkg.install vim
注解
一些自定义的Linux和其他发行版的衍生版可能不能被Salt正确检测。如果上述命令返回 pkg.install is not available的错误信息,那么你可能就需要重写pkg provider。这个过程在 这里 有详解。
模块函数`network.interfaces <salt.modules.network.interfaces>` 将会列出minion上的所有接口,以及它们的IP地址,子网掩码,MAC地址等:
salt '*' network.interfaces
Changing the Output Format
The default output format used for most Salt commands is called the nestedoutputter, but there are several other outputters that can be used to changethe way the output is displayed. For instance, thepprint outputter can beused to display the return data using Python'spprint module:
root@saltmaster:~# salt myminion grains.item pythonpath --out=pprint
{'myminion': {'pythonpath': ['/usr/lib64/python2.7',
'/usr/lib/python2.7/plat-linux2',
'/usr/lib64/python2.7/lib-tk',
'/usr/lib/python2.7/lib-tk',
'/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages',
'/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/gst-0.10',
'/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/gtk-2.0']}}
The full list of Salt outputters, as well as example output, can be foundhere.
salt-call
The examples so far have described running commands from the Master using thesalt command, but when troubleshooting it can be more beneficial to loginto the minion directly and usesalt-call.
Doing so allows you to see the minion log messages specific to the command youare running (which arenot part of the return data you see when running thecommand from the Master usingsalt), making it unnecessary to tail theminion log. More information onsalt-call and how to use it can be foundhere.
grains是minion启动时加载的,在运行过程中不会发生变化,所以是静态数据。grains中包含诸如运行的内核版本,操作系统等信息。
Salt使用一个叫做 :doc:`Grains <../targeting/grains>`的系统来建立关于minions的静态数据。这个数据包含了关于操作系统运行状态,CPU架构等信息。grains系统贯穿Salt用于发送平台数据到许多组件和用户。
Grains can also be statically set, this makes it easy to assign values tominions for grouping and managing.
A common practice is to assign grains to minions to specify what the role orroles a minion might be. These static grains can be set in the minionconfiguration file or via thegrains.setvalfunction.
Targeting
Salt allows for minions to be targeted based on a wide range of criteria. Thedefault targeting system uses globular expressions to match minions, hence ifthere are minions namedlarry1, larry2,curly1, and curly2, aglob oflarry* will match larry1 and larry2, and a glob of *1will match larry1 and curly1.
除了通配符之外还有许多其他的目标系统可以使用,这些系统包括:
-
正则表达式
-
使用PCRE引擎的正则表达式的目标
grains是minion启动时加载的,在运行过程中不会发生变化,所以是静态数据。grains中包含诸如运行的内核版本,操作系统等信息。
-
基于grains数据的目标: Targeting with Grains
Pilar
-
基于pilar数据的目标: Targeting with Pillar
IP
-
基于IP地址/子网/范围的目标
杂合
-
创建基于多个目标的逻辑目标规则: Targeting with Compound
节点组
-
节点组目标: Targeting with Nodegroup
目标的概念不仅在可以Salt命令行上使用,而且在很多其他的区域同样可以运行,包括state系统和用于ACLs和用户权限的系统。
传递参数
很多函数可以通过命令行接收参数:
salt '*' pkg.install vim
这个例子传递参数 vim 给pkg.install函数。因为很多函数可以仅仅通过一个字符串接受更复杂的输入,传递的参数通过YAML解析,允许更复杂的数据通过命令行发送:
salt '*' test.echo 'foo: bar'
一般Salt将这种字符串'foo: bar'翻译为字典"{'foo': 'bar'}"
注解
任何包含一个换行符的行不会通过YAML解析。
扩展篇
节点组管理
节点组是使用复合目标的规范声明。复合目标的文档可以在这里找到:doc:here <compound>。
nodegroups`master配置文件参数用于定义节点组。这里有一个通过`/etc/salt/master``配置文件配置节点组的例子:
nodegroups:
group1: 'L@foo.domain.com,bar.domain.com,baz.domain.com or bl*.domain.com'
group2: 'G@os:Debian and foo.domain.com'
注解
The L within group1 is matching a list of minions, while theG ingroup2 is matching specific grains. See thecompound matchers documentation for more details.
通过 -N 参数在命令行指定运行的节点组:
salt -N group1 test.ping
To match a nodegroup in your top file, make sure to put- match:nodegroup on the line directly following the nodegroup name.
base:
group1:
- match: nodegroup
- webserver
注解
When adding or modifying nodegroups to a master configuration file, the master must be restartedfor those changes to be fully recognized.
A limited amount of functionality, such as targeting with -N from the command-line may beavailable without a restart.
分组语法
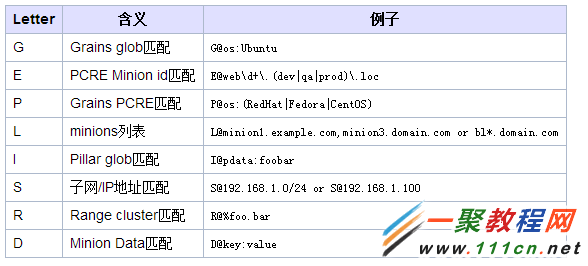
nodegroup分组时可以用到的语法关键字有G、E、P、L、I、S、R、D几个,几者的意义和用法见下表:
此外,匹配中可以使用and、or及not等boolean型操作。例:
想匹配所有minion中主机名(minion id)以webserv开头并且运行在Debian系统上或者minion的主机名(minion id)匹配正则表达式web-dc1-srv.* ,就可以用下表方式表示: www.111cn.net
| 代码如下 | 复制代码 |
| salt -C 'webserv* and G@os:Debian or E@web-dc1-srv.*' test.ping | |
当然也可以在预先分组时将这个配置写在分组规则里。在top.sls中可以如下使用:
| 代码如下 | 复制代码 |
| base: | |
Batch Size
The -b (or --batch-size) option allows commands to be executed on onlya specified number of minions at a time. Both percentages and finite numbers aresupported.
salt '*' -b 10 test.ping
salt -G 'os:RedHat' --batch-size 25% apache.signal restart
This will only run test.ping on 10 of the targeted minions at a time and thenrestart apache on 25% of the minions matchingos:RedHat at a time and workthrough them all until the task is complete. This makes jobs like rolling webserver restarts behind a load balancer or doing maintenance on BSD firewallsusing carp much easier with salt.
The batch system maintains a window of running minions, so, if there are atotal of 150 minions targeted and the batch size is 10, then the command issent to 10 minions, when one minion returns then the command is sent to oneadditional minion, so that the job is constantly running on 10 minions.
文件的传输
默认的传输根目录/srv/salt,不存在的话需要手动穿件
cp.get_file用来从master下载文件到客户端,可以外加几个参数,比如没有文件夹,创建文件夹的makedirs=True ,压缩的gzip参数。
语法如下:
|
|
salt
'*'
cp.get_file salt:
/
/
rr
/
etc
/
rr
|
get_url
cp.get_url可以从一个URL地址下载文件,URL可以是msater上的路径(salt://),也可以是http网址。
|
|
salt
'*'
cp.get_url salt:
//my/file /tmp/mine
salt
'*'
cp.get_url http:
//xiaorui.cc/good.txt /tmp/good.txt
|
通过master分发文件
[root@cbs1 salt]# cd /srv/salt/
[root@cbs1 salt]# mkdir test001
[root@cbs1 salt]# cd test001/
[root@cbs1 test001]# echo `date` > time.txt
[root@cbs1 test001]# ls
time.txt
[root@cbs1 test001]# salt -N 'group2' cp.get_file salt://test001/time.txt /tmp/time.txt
cbs2.test.com:
/tmp/time.txt
cbs3.test.com:
/tmp/time.txt
[root@cbs1 test001]# salt -N 'group2' cmd.run 'cat /tmp/time.txt'
cbs3.test.com:
Mon Apr 27 19:04:10 CST 2015
cbs2.test.com:
Mon Apr 27 19:04:10 CST 2015
[root@cbs1 test001]#
[root@cbs1 test001]# 通过minion拉去文件
[root@cbs1 test001]# cat /etc/salt/master | grep file_rec
file_recv: Ture
#file_recv_max_size: 100
[root@cbs1 test001]# /etc/init.d/salt-master restart
Stopping salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
Starting salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
[root@cbs1 test001]# salt -N 'group2' cp.push /tmp/push.txt
cbs3.test.com:
False
cbs2.test.com:
True
[root@cbs1 test001]# cat /var/cache/salt/master/minions/cbs2.test.com/files/tmp/push.txt
test push
[root@cbs1 test001]# 
























 1120
1120

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








