转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/beiyeqingteng/article/category/859395
1. 找出二叉查找树中第n大的值
问题:
给一个二叉查找树(BST),找出第 k 大的值。比如:
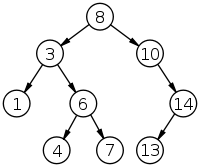
该图中,第3大的值是10.
分析:
我们可以通过类似中序遍历的方法把BST从大到小排序,然后,就可以得到第 k 大的值了。代码如下
public class NthLeaf {
static int k = 0;
// get the nth leaf by using preorder traversal
public void getNthleve(Node root, int n) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (root.rightChild != null)
getNthleve(root.rightChild, n);
k++;
if (k == n) {
System.out.println(root.toString());
}
else
getNthleve(root.leftChild, n);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node a = new Node(8);
Node b = new Node(3);
Node c = new Node(10);
Node d = new Node(14);
Node e = new Node(13);
Node f = new Node(1);
Node g = new Node(6);
Node h = new Node(4);
Node i = new Node(7);
a.leftChild = b;
a.rightChild = c;
c.rightChild = d;
d.leftChild = e;
b.leftChild = f;
b.rightChild = g;
g.leftChild = h;
g.rightChild = i;
System.out.println("begin!");
new NthLeaf().getNthleve(a, 3);
}
}
class Node {
Node leftChild = null;
Node rightChild = null;
int value;
Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return value + "";
}
}2.问题:
给定一个二叉树,从左到右,找出第 k 个叶子节点。
比如
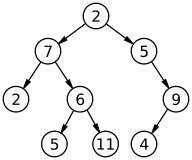
图中二叉树的第 3 个叶子节点(从左到右)是 11.
分析:
因为顺序是从左往右数,所以,对于一个节点下的两个叶子节点来讲(比如 6 下面有两个叶子节点 5 和 11),我们要确保先遍历最左边一个,然后再遍历右边一个。这样,其实,在中序遍历,前序遍历和后序遍历中,都能保证左边叶子节点比右边叶子节点先被遍历。我们只需要对每一个遍历的节点进行检查,看是否是叶子节点,是,则把个数+1. 代码如下:
public class NthLeaf {
static int k = 0;
// get the nth leaf by using preorder traversal
public void getNthleve(Node root, int n) {
if (root == null) return;
if (root.rightChild == null && root.leftChild == null) {
k++;
if (k == n) {
System.out.print(root.toString());
}
}
getNthleve(root.leftChild, n);
getNthleve(root.rightChild, n);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node a = new Node(2);
Node b = new Node(7);
Node c = new Node(5);
Node d = new Node(2);
Node e = new Node(6);
Node f = new Node(9);
Node g = new Node(5);
Node h = new Node(11);
Node i = new Node(4);
a.leftChild = b;
a.rightChild = c;
b.leftChild = d;
b.rightChild = e;
c.rightChild = f;
e.leftChild = g;
e.rightChild = h;
f.rightChild = i;
new NthLeaf().getNthleve(a, 3);
}
}
class Node {
Node leftChild = null;
Node rightChild = null;
int value;
Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return value + "";
}
}3.问题:
给你一个complete 二叉树,逆时针打印所有边缘节点, 比如:

那么,逆时针打印边缘节点后,输出:1 , 3, 5, 9, 8, 6 .
分析:
如果想写一个方法实现这个要求是很难的,但是,我们可以考虑分步实现。
第一步:打印左边的边缘节点;
第二步:打印底部所有节点;
第三步:打印右边所有边缘节点。
public static void printLeft(Node root) {
if (root.leftChild != null || root.rightChild != null) {
print(root);
printLeft(root.leftChild);
}
}
public static void printButtom(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
if (root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null) {
print(root);
}
printButtom(root.leftChild);
printButtom(root.rightChild);
}
}
public static void printRight(Node root, Node node) {
if (root.leftChild != null || root.rightChild != null) {
printRight(root.rightChild, node);
// do not print the root again
if (root != node) {
print(root);
}
}
}4. check whether two binary trees are identical
Question:
Given two binary trees, check whether they are identical or not.
Analyze:
we first compare the roots of these two trees, if they are the same, we continue to compare the root of their left and right subtrees.
Code:
boolean sameTree(Node a, Node b) {
// 1. both empty -> true
if (a == null && b == null) return(true);
// 2. both non-empty -> compare them
else if (a!=null && b!=null) {
return (a.data == b.data &&
sameTree(a.leftChild, b.leftChild) &&
sameTree(a.rightChild, b.rightChild)
);
}
// 3. one empty, one not -> false
else return false;
} 问题:
给一个数组,检查它是否可能是一棵二叉查询树后序遍历的结果。换句话说,是否存在一棵二叉查询树,对它进行后序遍历后,得到的数组和给定的数组完全一样。
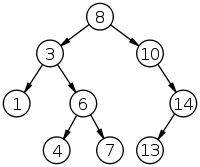
比如,对上面这个二叉查询树后序遍历后,得到的数组是:[1, 4, 7, 6, 3, 13, 14, 10, 8]。
思路:
因为二叉树后序遍历的时候,先左后右然后中间。所以,数组的最后一个一定是整个二叉查询树的根(比如 8),而且,数组前一部分比数组最后一个值(也就是二叉查询树的根)小,因为它们是根的左子树部分。数组剩余部分,是根的右子树部分。而且,在剩余部分里,所有的值都必须比根要大。这样,我们可以把原来的数组分成两个部分,然后每一个部分可以进行递归判断,直到数组的长度小于等于2。(因为当长度小于等于2时,什么样的情况都是可以的)。
我们先把给定的数组分成两个部分,即我们需要先找到数组的分界点。代码如下:
- /**
- *
- * @param array the input array
- * @param begin the starting index of the array
- * @param end the ending index of the array
- * @return the turning point of the array, where the left part of turning point is smaller than array[end], the right
- * part of the turning point is larger than array[end].
- */
- public int turningPoint(int[] array, int begin, int end) {
- int tp = -1;
- for (int i = begin; i < end; i++) {
- if (array[i] > array[end]) {
- tp = i;
- break;
- }
- }
- return tp;
- }
找到分界点后,我们还要判断从分界点开始,到数组末,是否所有的值都比数组的最后一个值(也就是根)大,否则,这样的数组不是一个二叉查询树的后序遍历。代码如下:
- //check whether all the elements from strat are larger than array[end]
- public boolean checkValid(int[] array, int start, int end) {
- for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
- if (array[i] < array[end]) return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
有了上面两个方法,我们就可以把递归写出来了,代码如下:
- // the main method to check whether the array is identical to a BST's post order array
- public boolean isPostOrder(int[] array, int begin, int end) {
- // the exit
- if ((end - begin + 1) <= 2) return true;
- //get the turning point
- int turningPoint = turningPoint(array, begin, end);
- boolean result = checkValid(array, turningPoint, end); //check whether the right part of the array is valid
- if (result == false) {
- return false;
- }
- // recursion
- return isPostOrder(array, begin, turningPoint - 1) && isPostOrder(array, turningPoint, end - 1);
- }
























 442
442











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








