513. 找树左下角的值
1. LeeCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
2. 题目描述


3. 解法
1. 迭代法
很简单,层序遍历,找最底层最左边的那个。
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> qu;
qu.push(root);
int result;
while (!qu.empty()) {
int size = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* cur = qu.front();
qu.pop();
if (i == 0) result = cur->val;
if (cur->left) qu.push(cur->left);
if (cur->right) qu.push(cur->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};2. 递归法
最终答案满足条件:深度最大的最左叶子节点
因此,1. 从右向左递归,最终值一定被最左叶子节点覆盖;2. 记录叶子节点深度,只选深度最大。
class Solution {
public:
int result;
int max_depth = 0;
void order(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root == NULL) return;
depth++;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && depth >= max_depth) {
max_depth = depth;
result = root->val;
}
order(root->right, depth);
order(root->left, depth);
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
order(root, 0);
return result;
}
};112. 路径总和
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
2. 题目描述


3. 解法
用深度递归,当判断为叶子节点,且路径总和等于target时,返回真实路径总和,否则返回不可能是target的值。
class Solution {
public:
int waySum(TreeNode* root, int sum, int targetSum) {
if (root == NULL) return 2000;
sum += root->val;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
if (sum == targetSum) return targetSum;
}
if (root->left) {
int left = waySum(root->left, sum, targetSum);
if (left == targetSum) return left;
}
if (root->right) {
int right = waySum(root->right, sum, targetSum);
if (right == targetSum) return right;
}
return 2000;
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
return targetSum == waySum(root, 0, targetSum) ? true : false;
}
};用深度递归,参数量更少的办法是,target可以自顶向下减,而且返回值可以直接是bool型。
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == NULL) return false;
targetSum -= root->val;
if (!root->left && !root->right && targetSum == 0) return true;
return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum);
}
};4. 扩展
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台

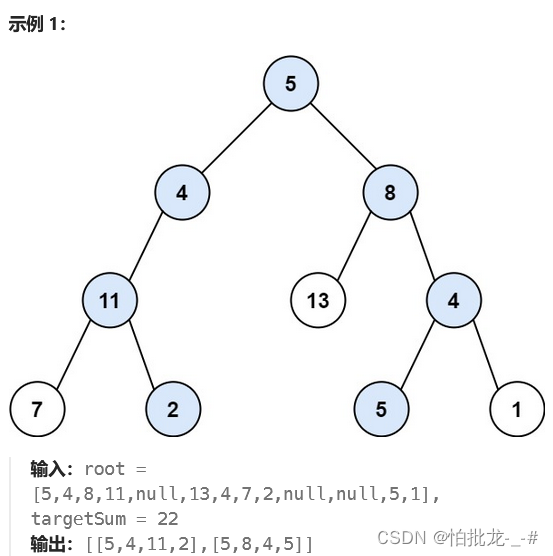
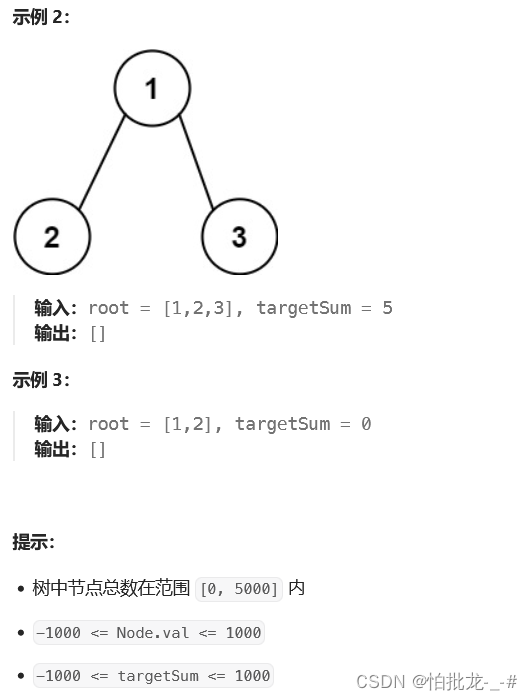
与之前的路径字符串输出一样,也与上题一样,深度递归,新添一个一维vector<int>,如果符合题目,则加入到二维vector<vector<int>>。
class Solution {
public:
void order(TreeNode* root, int targetSum, vector<int> result, vector<vector<int>>& results) {
if (root == NULL) return;
result.push_back(root->val);
targetSum -= root->val;
if (!root->left && !root->right && targetSum == 0) results.push_back(result);
order(root->left, targetSum, result, results);
order(root->right, targetSum, result, results);
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> results;
vector<int> result;
order(root, targetSum, result, results);
return results;
}
};用回溯更快,更省空间。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> results;
vector<int> result;
void order(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == NULL) return;
result.push_back(root->val);
targetSum -= root->val;
if (!root->left && !root->right && targetSum == 0) results.push_back(result);
if (root->left) {
order(root->left, targetSum);
result.pop_back();
}
if (root->right) {
order(root->right, targetSum);
result.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
order(root, targetSum);
return results;
}
};106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
2. 题目描述


3. 解法
简简单单递归,每次只找当前根节点,而根节点总是在postorder最后一个。然后因为数字不重复,在inorder中找到该根节点后,就可以划分出左右子树的中序遍历和后序遍历。然后继续递归。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
if (inorder.size() == 0) return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder.back());
int i = 0;
for (; i < inorder.size(); i++) {
if (inorder[i] == postorder.back()) break;
}
vector<int> left_in(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + i);
vector<int> right_in(inorder.begin() + i + 1, inorder.end());
vector<int> left_post(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + i);
vector<int> right_post(postorder.begin() + i, postorder.end() - 1);
root->left = buildTree(left_in, left_post);
root->right = buildTree(right_in, right_post);
return root;
}
};4. 扩展
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
前序与中序遍历序列,逻辑跟上面一样,注意切片不要超了。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
if (inorder.size() == 0) return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
int i = 0;
for (; i < inorder.size(); i++) {
if (inorder[i] == preorder[0]) break;
}
vector<int> left_in(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + i);
vector<int> right_in(inorder.begin() + i + 1, inorder.end());
vector<int> left_pre(preorder.begin() + 1, preorder.begin() + i + 1);
vector<int> right_pre(preorder.end() - right_in.size(), preorder.end());
root->left = buildTree(left_pre, left_in);
root->right = buildTree(right_pre, right_in);
return root;
}
};




















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








