1.背景
1.1. 项目介绍
golang/sync库拓展了官方自带的sync库,提供了errgroup、semaphore、singleflight及syncmap四个包,本次先分析第一个包errgroup的源代码。
errgroup提供了类似于WaitGroup的组织子任务运行的能力,但是提供了错误处理和通过ctx取消子任务的能力。
1.2.使用方法
go get -u golang.org/x/sync
- 核心API:Go、Wait、TryGo、SetLimit
- Go和Wait:Go开启协程执行任务,Wait注释当前协程直到所有任务完成,使用上与WaitGroup几乎一致
var (
Web = fakeSearch("web")
Image = fakeSearch("image")
Video = fakeSearch("video")
)
type Result string
type Search func(ctx context.Context, query string) (Result, error)
// 一个并发启动多个协程执行任务的例子
func ExampleGroup_parallel() {
Google := func(ctx context.Context, query string) ([]Result, error) {
g, ctx := errgroup.WithContext(ctx)
searches := []Search{Web, Image, Video}
results := make([]Result, len(searches))
for i, search := range searches {
i, search := i, search // https://golang.org/doc/faq#closures_and_goroutines
g.Go(func() error {
result, err := search(ctx, query)
if err == nil {
results[i] = result
}
return err
})
}
if err := g.Wait(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return results, nil
}
results, err := Google(context.Background(), "golang")
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, err)
return
}
for _, result := range results {
fmt.Println(result)
}
// Output:
// web result for "golang"
// image result for "golang"
// video result for "golang"
}
- SetLimit和TryGo:设置协程上限,当当前无空闲协程时,调用TryGo会返回错误,如果存在可用协程则启动任务
func testSetLimitTryGo() {
var group errgroup.Group
// 设置10个协程
group.SetLimit(10)
// 启动11个任务
for i := 1; i <= 11; i++ {
i := i
fn := func() error {
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
return nil
}
if ok := group.TryGo(fn); !ok {
log.Printf("tryGo false, goroutine no = %v", i)
} else {
log.Printf("tryGo true, goroutine no = %v", i)
}
}
group.Wait()
log.Printf("group task finished")
}
// 输出
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 1
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 2
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 3
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 4
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 5
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 6
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 7
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 8
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 9
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo true, goroutine no = 10
2022/10/30 11:44:28 tryGo false, goroutine no = 11
2022/10/30 11:44:28 group task finished
- WithContext:绑定一个ctx,通过ctx可以控制在某个任务出错时,其余暂未运行的任务取消执行
func testWithContextCancel() {
group, ctx := errgroup.WithContext(context.Background())
// 设置10个协程
group.SetLimit(10)
// 启动10个任务,在第5个任务生成错误
for i := 1; i <= 10; i++ {
i := i
fn := func() error {
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
if i == 5 {
return errors.New("task 5 is fail")
}
// 当某个任务错误时,终止当前任务
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
if errors.Is(ctx.Err(), context.Canceled) {
log.Printf("ctx Cancel, all task cancel, goroutine no = %v", i)
} else {
log.Printf("ctx Done, all task done, goroutine no = %v", i)
}
default:
log.Printf("task Done, goroutine no = %v", i)
}
return nil
}
if ok := group.TryGo(fn); !ok {
log.Printf("tryGo false, goroutine no = %v", i)
} else {
log.Printf("tryGo true, goroutine no = %v", i)
}
}
if err := group.Wait(); err != nil {
log.Printf("group.Wait err = %v", err)
return
}
log.Printf("group task finished")
}
// 输出
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 1
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 2
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 3
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 4
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 5
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 6
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 7
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 8
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 9
2022/10/30 17:11:23 tryGo true, goroutine no = 10
2022/10/30 17:11:23 task Done, goroutine no = 9
2022/10/30 17:11:23 task Done, goroutine no = 1
2022/10/30 17:11:23 task Done, goroutine no = 4
2022/10/30 17:11:23 task Done, goroutine no = 3
2022/10/30 17:11:23 task Done, goroutine no = 7
2022/10/30 17:11:23 ctx Cancel, all task cancel, goroutine no = 6
2022/10/30 17:11:23 task Done, goroutine no = 10
2022/10/30 17:11:23 ctx Cancel, all task cancel, goroutine no = 8
2022/10/30 17:11:23 ctx Cancel, all task cancel, goroutine no = 2
2022/10/30 17:11:23 group.Wait err = task 5 is fail
2.源码分析
2.1.项目结构
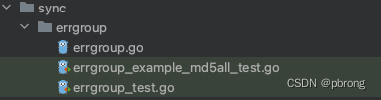
- errgroup.go:核心实现,提供相关API
- errgroup_test.go:相关API单元测试
2.2.数据结构
- errgroup.go
// 空Group结构体也使用,但是不能通过ctx来判断是否有其他子任务出错
type Group struct {
// 子任务出错时进行调用
cancel func()
// wg,实际完成子任务编排
wg sync.WaitGroup
// 信号量,在setLimit时才进行初始化
sem chan token
// once保证err只会被赋值一次
errOnce sync.Once
// 子任务报错
err error
}
2.3.API代码流程
- func (g *Group) Go(f func() error)
// Go方法创建一个协程来执行f函数(协程不足则阻塞)
func (g *Group) Go(f func() error) {
if g.sem != nil {
// 如果存在信号量,则说明存在协程限制,每启动一次任务则写入一次信号量
// 如果在这里阻塞,说明协程已经被使用完,需要等到其他任务完成时释放
g.sem <- token{}
}
// 基于wg添加1次任务,启动协程执行
g.wg.Add(1)
go func() {
// 释放信号量并调用wg.Done
defer g.done()
// 执行任务时若出现err,则写入g.err
if err := f(); err != nil {
// errOnce保证只会写入一次err
g.errOnce.Do(func() {
g.err = err
// 如果存在cancel方法,则调用一次
if g.cancel != nil {
g.cancel()
}
})
}
}()
}
func (g *Group) done() {
if g.sem != nil {
<-g.sem
}
g.wg.Done()
}
- func (g *Group) Wait() error
// Wait方法会阻塞到所有协程完成任务,并且当存在cancel方法时进行调用,返回第一个出现的错误
func (g *Group) Wait() error {
g.wg.Wait()
if g.cancel != nil {
g.cancel()
}
return g.err
}
- func WithContext(ctx context.Context) (*Group, context.Context)
// WithContext函数初始化一个携带有cancelCtx的errGroup
// 当第一个任务出现err时会调用ctx的cancel方法,此时ctx.Done通道被写入,ctx.Err返回ctx cancel错误
func WithContext(ctx context.Context) (*Group, context.Context) {
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
return &Group{cancel: cancel}, ctx
}
- func (g *Group) SetLimit(n int)
// SetLimit方法为errGroup设置协程上限
func (g *Group) SetLimit(n int) {
if n < 0 {
g.sem = nil
return
}
// 不可重复调用SetLimit方法
if len(g.sem) != 0 {
panic(fmt.Errorf("errgroup: modify limit while %v goroutines in the group are still active", len(g.sem)))
}
// 设置一个容量为n的信号量通道
g.sem = make(chan token, n)
}
- func (g *Group) TryGo(f func() error) bool
// TryGo方法尝试创建新的任务,当协程不足时则不会阻塞,而是直接返回false,协程充足时启动任务并返回true
func (g *Group) TryGo(f func() error) bool {
// 如果存在信号量,则尝试写入
if g.sem != nil {
select {
case g.sem <- token{}:
// 写入成功,继续执行任务
default:
// 写入失败,返回false
return false
}
}
// 添加wg
g.wg.Add(1)
go func() {
// 释放信号量,调用wg.Done
defer g.done()
// 执行任务并把第一次出错的err写入,调用cancel方法
if err := f(); err != nil {
g.errOnce.Do(func() {
g.err = err
if g.cancel != nil {
g.cancel()
}
})
}
}()
// 任务已提交执行,返回true(不代表已经执行完成了)
return true
}
3.总结
- errgroup的实现精简,基于WaitGroup实现了底层的协程控制能力,并支持了context的cancel通知机制,提供了任意子任务报错就终止其他子任务的能力,并且可以通过Wait方法获取第一次出现错误的err
- go的context不光可以实现请求数值的传递,也可以协调各个子协程间的动作,比如某一协程出现报错后主动调用ctx.cancel()方法,那么其他子协程在执行任务前可以先通过ctx.Done及ctx.Err来判断是否需要终止掉当前任务:
fn := func() error {
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
if i == 5 {
return errors.New("task 5 is fail")
}
// 当某个任务错误时,终止当前任务
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
if errors.Is(ctx.Err(), context.Canceled) {
log.Printf("ctx Cancel, all task cancel, goroutine no = %v", i)
} else {
log.Printf("ctx Done, all task done, goroutine no = %v", i)
}
default:
log.Printf("task Done, goroutine no = %v", i)
}
return nil
}
- 对于协程池相关的场景,可以通过通道来实现信号量,因为通道自身的特性是线程安全的、FIFO的,可以很好地实现抢占和阻塞的场景:
type token struct{}
// 简单的协程池
type Pool struct {
sem chan token
}
func NewPoolWithLimit(limit int) Pool {
if limit <= 0 {
return Pool{}
}
return Pool{
sem: make(chan token, limit),
}
}
func (p *Pool) RunFunc(f func()) {
if p.sem != nil {
p.sem <- token{}
}
go func() {
defer func() {
<-p.sem
}()
f()
}()
}







 本文围绕golang/sync库中的errgroup包展开。介绍了errgroup提供组织子任务运行、错误处理和通过ctx取消子任务的能力及使用方法。对其源码进行分析,包括项目结构、数据结构和API代码流程。总结指出其基于WaitGroup实现协程控制,支持context机制。
本文围绕golang/sync库中的errgroup包展开。介绍了errgroup提供组织子任务运行、错误处理和通过ctx取消子任务的能力及使用方法。对其源码进行分析,包括项目结构、数据结构和API代码流程。总结指出其基于WaitGroup实现协程控制,支持context机制。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










