一、实验题目
利用数据结构知识编写哈夫曼编/译码器的程序。
二、需求分析
[题目概述]
利用哈夫曼编码进行通信可以大大提高信道利用率,这要求在发送端通过一个编码系统对待传输预先编码,在接收端将传来的数据进行译码。对于双工通道,每端都需要一个完整的编/译码系统。
[基本要求]
试为这样的信息收发站写一个哈夫曼码的编/译码系统。
[实现提示]
构造哈夫曼树的算法实现:
假设哈夫曼树采用双亲孩子表示法存储,并增加权值域,构造哈夫曼树的叶子结点(树
木的权)有N个,合并次数为N—1次,则森林中总共有2N—1棵树,(包含合并后删除的)。
存储结构描述为:
const int n=maxn //maxn表示叶子数目
const int m=2*n-1 //m为森林中树的棵数
class tree
{
float weight; //权值
int parent; //双亲
int lch, rch; //左,右孩子
}
tree hftree[m+1]; //规定从第一个元素hftree[1]开始使用数组元素,故定义长
度为m+1而不为m
结构类型:typedef struct
{
char data;
int weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
}huffnode;
typedef struct
{
char cd[MAX];
int start;
}huffcode;
主程序
int main()
{
初始化:输入字符代码以及权值。
编制哈夫曼码:根据权值建立二叉树, 输出相应的根节点到叶结点的路径,便是哈夫曼编码。
编码:输入字符,输出哈夫曼码。
译码:输入哈夫曼,输出字符代码。
退出:结束进程,退出程序。
return 0;
}
三、概要设计
初始化界面

运行代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//5 1 29 2 7 3 8 4 14 5 23 6 3 7 11 8输入
struct node {
int element;
int num;
char mima[100];
char ch;
struct node *Lchild, *Rchild;
};
struct tree {
struct node *root;
};
tree start;
void MakeTree(tree *tr, int x, char c, tree *Lt, tree *Rt) {
node *p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->ch = c;
p->element = x;
p->Lchild = Lt->root;
p->Rchild = Rt->root;
Lt->root = Rt->root = NULL;
tr->root = p;
}
void Xunzhao(tree tree[], int *t1, int *t2, int t) {
int min1, min2, k;
if (tree[0].root->element > tree[1].root->element) {
*t1 = 0;
*t2 = 1;
min1 = tree[0].root->element;
min2 = tree[1].root->element;
} else if (tree[0].root->element < tree[1].root->element) {
*t1 = 1;
*t2 = 0;
min1 = tree[1].root->element;
min2 = tree[0].root->element;
}
for (k = 2; k < t; k++) {
if (tree[k].root->element < min1) {
*t2 = *t1;
*t1 = k;
min2 = min1;
min1 = tree[k].root->element;
} else if (tree[k].root->element < min2) {
*t2 = k;
min2 = tree[k].root->element;
}
}
}
tree MakeHaffuma(int w[], char jie[], int n) {
tree zero, ch[1000];
int i, k1, k2, k;
tree *p;
p = &zero;
p->root = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
MakeTree(&ch[i], w[i], jie[i], p, p);
for (k = n - 1; k > 0; k--) {
Xunzhao(ch, &k1, &k2, k);
MakeTree(&ch[k1], ch[k1].root->element + ch[k2].root->element, '$', &ch[k1], &ch[k2]);
ch[k2] = ch[k];
}
return ch[0];
}
void makenode(node *no) {
int i, j;
if (no == start.root) {
for (i = 0; i < 100; i++)
start.root->mima[i] = '/0';
start.root->num = 0;
}
if ((no->Lchild == NULL) && (no->Rchild == NULL)) {
cout<<no->ch;
for (j = 0; j < no->num; j++)
cout<<no->mima[j];
cout<<endl;
}
if (no->Lchild != NULL) {
for (j = 0; j < no->num; j++)
no->Lchild->mima[j] = no->mima[j];
no->Lchild->mima[no->num] = '0';
no->Lchild->num = no->num + 1;
makenode(no->Lchild);
}
if (no->Rchild != NULL) {
for (j = 0; j < no->num; j++)
no->Rchild->mima[j] = no->mima[j];
no->Rchild->mima[no->num] = '1';
no->Rchild->num = no->num + 1;
makenode(no->Rchild);
}
}
void translate(node *n, char p[]) {
char s[100];
node *q = n;
int len, i, k = 0, max;
len = strlen(p);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (p[i] == '0')
if (q->Lchild)
q = q->Lchild;
else cout<<"ERROR!";
else {
if (q->Rchild)
q = q->Rchild;
else cout<<"ERROR!";
}
if ((q->Lchild == NULL) && (q->Rchild == NULL)) {
s[k++] = q->ch;
max = i;
q = n;
}
}
if (max != len - 1) cout<<"ERROR!";
else {
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
cout<<s[i]<<":";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void Print(node *node) {
if (node) {
cout<< node->ch;
cout<<node->element;
Print(node->Lchild);
Print(node->Rchild);
}
}
int main() {
cout<<"欢迎来到哈夫曼编译系统!"<<endl;
int w[500];
char s[500];
char p[500];
char choice = '1';
int n, i;
while (choice != 3) {
cout<<"1创建 2编译 0退出\n";
cin>>choice;
switch (choice) {
case '1': {
cout<<"请输入树节点的个数:";
cin>>n;
cout<<"请输入权值及其对应的节点:"<<endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin>>w[i]>>s[i];
// cin>>s[i];
start = MakeHaffuma(w, s, n);
makenode(start.root);
break;
}
case '2': {
if (start.root == NULL)
cout<<"未构建哈夫曼树!";
else {
translate(start.root, p);
cout<<endl;
}
break;
}
case '3':
cout<<"程序退出!";
break;
}
return 0;
}
}
四、调试分析
如图所示程序编译结果无错误
五、使用说明
第一步:输入开始命令提示
第二步:输入节点个数
第三步:输入节点和对应权值
第四部:输出结果
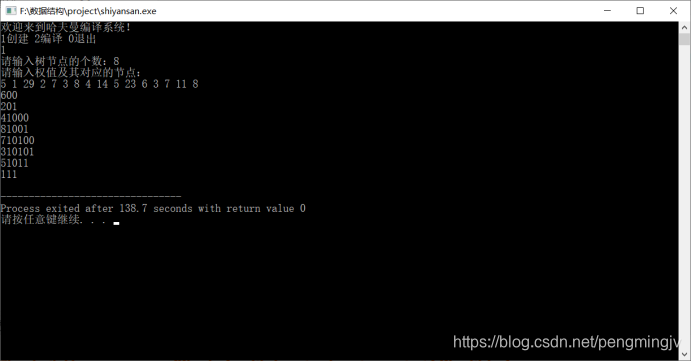
六、测试结果
七、其他数据结构实例
数据结构:编程带你了解约瑟夫环
数据结构:简易停车场管理系统
以上内容为个人学习总结,如有遗漏或者错误请在评论区中指正!!!
如果看完觉得有所收获的话,记得一键三连哦,谢谢大家!





















 2866
2866











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








