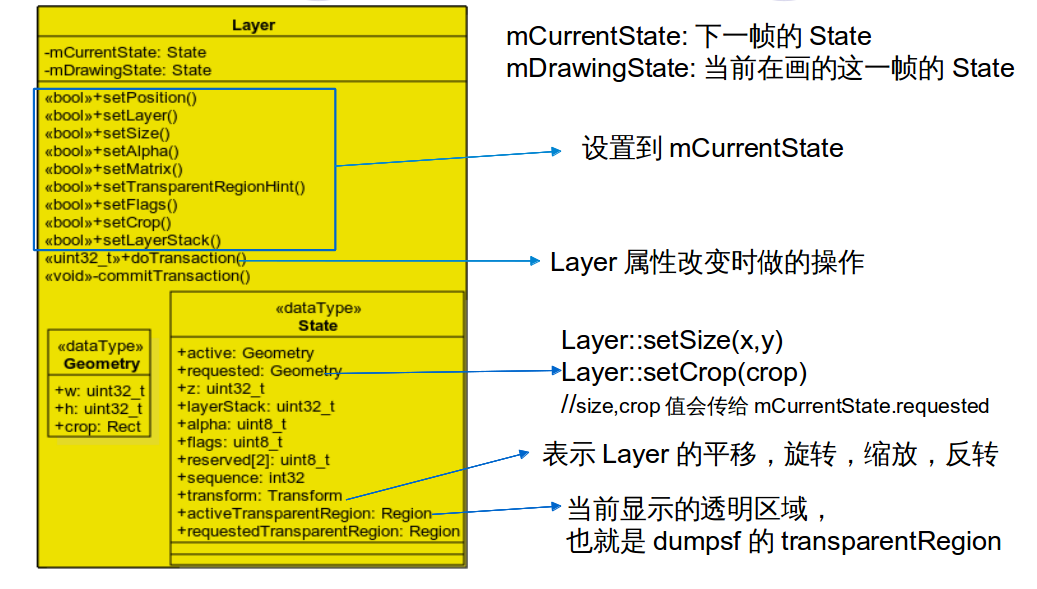
Layer::State介绍
[Layer.cpp]
//Layer::State
struct State {
Geometry active;
Geometry requested;
uint32_t z;
uint32_t layerStack;
uint8_t alpha;
uint8_t flags;
uint8_t reserved[2];
int32_t sequence; // changes when visible regions can change
Transform transform; //表示Layer的旋转,平移,缩放
// the transparentRegion hint is a bit special, it's latched only
// when we receive a buffer -- this is because it's "content"
// dependent.
Region activeTransparentRegion;//当前显示的transparentRegion,也就是dumpsf的transparentRegion
Region requestedTransparentRegion;
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
[Layer.cpp]
struct Geometry {
uint32_t w; //size的宽高
uint32_t h;
Rect crop; //crop
inline bool operator ==(const Geometry& rhs) const {
return (w == rhs.w && h == rhs.h && crop == rhs.crop);
}
inline bool operator !=(const Geometry& rhs) const {
return !operator ==(rhs);
}
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Layer::State设置流程
java层的就不看了,直接看Native层的例子 resize
60 SurfaceComposerClient::openGlobalTransaction();
61 surfaceControl->setSize(320, 240);
62 SurfaceComposerClient::closeGlobalTransaction();
- 1
- 2
- 3
http://androidxref.com/6.0.1_r10/xref/frameworks/native/libs/gui/SurfaceControl.cpp#110
107status_t SurfaceControl::setSize(uint32_t w, uint32_t h) {
108 status_t err = validate();
109 if (err < 0) return err;
110 return mClient->setSize(mHandle, w, h);//这个mClinet就是SurfaceCompserClient强引用对象
111}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
http://androidxref.com/6.0.1_r10/xref/frameworks/native/libs/gui/SurfaceComposerClient.cpp#570
569status_t SurfaceComposerClient::setSize(const sp<IBinder>& id, uint32_t w, uint32_t h) {
570 return getComposer().setSize(this, id, w, h);//Composer是个单例
571}
- 1
- 2
- 3
http://androidxref.com/6.0.1_r10/xref/frameworks/native/libs/gui/SurfaceComposerClient.cpp#282
279status_t Composer::setSize(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client,
280 const sp<IBinder>& id, uint32_t w, uint32_t h) {
281 Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
282 layer_state_t* s = getLayerStateLocked(client, id);
283 if (!s)
284 return BAD_INDEX;
//每层Layer的属性暂存到Layer_state_t Struct
285 s->what |= layer_state_t::eSizeChanged;
286 s->w = w;
287 s->h = h;
288
289 // Resizing a surface makes the transaction synchronous.
290 mForceSynchronous = true;
291
292 return NO_ERROR;
293}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
每层Layer的属性暂存到SurfaceomposerClient对象Client,一起包装为ComposerState
250layer_state_t* Composer::getLayerStateLocked(
251 const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, const sp<IBinder>& id) {
252
253 ComposerState s;
254 s.client = client->mClient;
255 s.state.surface = id;
256
257 ssize_t index = mComposerStates.indexOf(s);
258 if (index < 0) {
259 // we don't have it, add an initialized layer_state to our list
260 index = mComposerStates.add(s);
261 }
262
263 ComposerState* const out = mComposerStates.editArray();
264 return &(out[index].state);
265}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
closeTransaction这边流程就不具体看了,直接看函数 SurfaceFlinger::setTransactionState
http://androidxref.com/6.0.1_r10/xref/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
2093void SurfaceFlinger::setTransactionState(
2094 const Vector<ComposerState>& state,
2095 const Vector<DisplayState>& displays,
2096 uint32_t flags)
2097{
2098 ATRACE_CALL();
2099 Mutex::Autolock _l(mStateLock);
2100 uint32_t transactionFlags = 0;
...
2124 count = state.size();
2125 for (size_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) { //遍历每层Layer
2126 const ComposerState& s(state[i]);
...
2134 if (s.client != NULL) {
2135 sp<IBinder> binder = IInterface::asBinder(s.client);
2136 if (binder != NULL) {
2137 String16 desc(binder->getInterfaceDescriptor());
2138 if (desc == ISurfaceComposerClient::descriptor) {
2139 sp<Client> client( static_cast<Client *>(s.client.get()) );
//设置Layer属性,返回flags(表示Layer属性是否有变化)
2140 transactionFlags |= setClientStateLocked(client, s.state);
2141 }
2142 }
2143 }
2144 }
2145
2146 if (transactionFlags) {
2147 // this triggers the transaction
2148 setTransactionFlags(transactionFlags);
2149 ...
2168 }
2169}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
2221uint32_t SurfaceFlinger::setClientStateLocked(
2222 const sp<Client>& client,
2223 const layer_state_t& s)
2224{
2225 uint32_t flags = 0;
2226 sp<Layer> layer(client->getLayerUser(s.surface));
2227 if (layer != 0) {
...
2244 if (what & layer_state_t::eSizeChanged) {
2245 if (layer->setSize(s.w, s.h)) {
2246 flags |= eTraversalNeeded; //设置eTraversalNeeded flags
2247 }
2248 }
...
2281 return flags;
2282}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
[frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/Layer.cpp]
1137bool Layer::setSize(uint32_t w, uint32_t h) {
1138 if (mCurrentState.requested.w == w && mCurrentState.requested.h == h)
1139 return false;
// size,crop传给mCurrentState.requested
1140 mCurrentState.requested.w = w;
1141 mCurrentState.requested.h = h;
1142 setTransactionFlags(eTransactionNeeded);
1143 return true;
1144}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
2085uint32_t SurfaceFlinger::setTransactionFlags(uint32_t flags) {
2086 uint32_t old = android_atomic_or(flags, &mTransactionFlags);
2087 if ((old & flags)==0) { // wake the server up, Layer属性发生变化
2088 signalTransaction();
2089 }
2090 return old;
2091}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
760void SurfaceFlinger::signalTransaction() {
761 mEventQueue.invalidate();
762}
- 1
- 2
- 3
Vsync信号到来时
Layer 属性发生变化做的操作
SurfaceFlinger::handleTransactionLocked
->Layer::doTransaction()
- 根据Layer的size是否变化,改变buffer大小
- mCurrentSate.active=mCurrentSate.requested(一般情况下都会赋值,除非flags设置了eDontUpdateGeometryState),
- 修改flags(使之重新计算visibelRegion的值)
–>Layer::commitTransaction() : 赋值 mDrawingState = mCurrentState;
uint32_t Layer::doTransaction(uint32_t flags) {
ATRACE_CALL();
const Layer::State& s(getDrawingState());
const Layer::State& c(getCurrentState());
const bool sizeChanged = (c.requested.w != s.requested.w) ||
(c.requested.h != s.requested.h);
if (sizeChanged) {//根据Layer的size是否变化,改变buffer大小
// the size changed, we need to ask our client to request a new buffer
ALOGE("...");
// record the new size, form this point on, when the client request
// a buffer, it'll get the new size.
mSurfaceFlingerConsumer->setDefaultBufferSize(
c.requested.w, c.requested.h);
}
if (!isFixedSize()) {
const bool resizePending = (c.requested.w != c.active.w) ||
(c.requested.h != c.active.h);
if (resizePending && mSidebandStream == NULL) {
// don't let Layer::doTransaction update the drawing state
// if we have a pending resize, unless we are in fixed-size mode.
// the drawing state will be updated only once we receive a buffer
// with the correct size.
//
// in particular, we want to make sure the clip (which is part
// of the geometry state) is latched together with the size but is
// latched immediately when no resizing is involved.
//
// If a sideband stream is attached, however, we want to skip this
// optimization so that transactions aren't missed when a buffer
// never arrives
flags |= eDontUpdateGeometryState; //设置了这个flag就不会用requested的值
}
}
// always set active to requested, unless we're asked not to
// this is used by Layer, which special cases resizes.
if (flags & eDontUpdateGeometryState) {
} else {
Layer::State& editCurrentState(getCurrentState());
editCurrentState.active = c.requested; //mCurrentSate.active=mCurrentSate.requested
}
if (s.active != c.active) {
// invalidate and recompute the visible regions if needed
flags |= Layer::eVisibleRegion; //修改flags(使之重新计算visibelRegion的值)
}
if (c.sequence != s.sequence) {
// invalidate and recompute the visible regions if needed
flags |= eVisibleRegion;
this->contentDirty = true;
// we may use linear filtering, if the matrix scales us
const uint8_t type = c.transform.getType();
mNeedsFiltering = (!c.transform.preserveRects() ||
(type >= Transform::SCALE));
}
// Commit the transaction
commitTransaction();
return flags;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
void Layer::commitTransaction() {
mDrawingState = mCurrentState;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
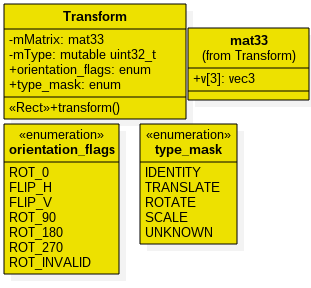
重点介绍一下 transform的值
1.先介绍一下Transform类
[frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/Transform.h]
成员变量:
Mmatrix: mat33类型,就是一个3X3矩阵
mType: uint32_t类型,最低位为1表示需要translate(还有其他位表示ROT_90…)
成员函数:
transform(): 执行变换的函数
1.1 Transform.mat33的赋值
右边的矩阵是mat33,每个变量的分别表示:
scaleX: x轴的缩放因子
skewX: x轴的斜交因子(错切因子)
translateX: x轴的平移向量
scaleY: y轴的缩放因子
skewY: y轴的斜交因子
translateX: y轴的平移向量
最后一排: 3D效果,透视变换
Transform.mat33 的值由position和 matrix组成,由setMatirx和setPosition赋值
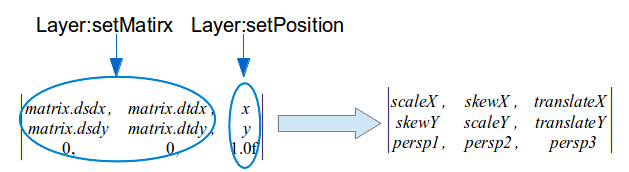
bool Layer::setMatrix(const layer_state_t::matrix22_t& matrix) {
mCurrentState.sequence++;
mCurrentState.transform.set(
matrix.dsdx, matrix.dsdy, matrix.dtdx, matrix.dtdy);
setTransactionFlags(eTransactionNeeded);
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
bool Layer::setPosition(float x, float y) {
if (mCurrentState.transform.tx() == x && mCurrentState.transform.ty() == y)
return false;
mCurrentState.sequence++;
mCurrentState.transform.set(x, y);
setTransactionFlags(eTransactionNeeded);
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
1.2 Transfrom.transform() 函数
203Rect Transform::transform(const Rect& bounds) const
204{
205 Rect r;
206 vec2 lt( bounds.left, bounds.top );//四个顶点的坐标
...
211 lt = transform(lt);//每个顶点根据mat33的值重新计算(平移,缩放)
...
216 r.left = floorf(min(lt[0], rt[0], lb[0], rb[0]) + 0.5f);//left的值是最小的x值
...
221 return r;
222}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
//根据mat33重新计算顶点坐标
176vec2 Transform::transform(const vec2& v) const {
177 vec2 r;
178 const mat33& M(mMatrix);
179 r[0] = M[0][0]*v[0] + M[1][0]*v[1] + M[2][0];//x=scaleX*x+skewY*y+translateX
180 r[1] = M[0][1]*v[0] + M[1][1]*v[1] + M[2][1];//y=scaleY*Y+skewX*x+translateY
181 return r;
182}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
SurfaceFlinger层对visibelRegion的计算过程
Layer的visibleRegion值和 position, transform.mMatrix, size, transparentRegion 有关。
Layer的position, transform.mMatrix, size,都是由SurfaceControl.java设置的。
SurfaceFlinger::handleMessageRefresh()
->SurfaceFlinger::rebuildLayerStacks()
–>SurfaceFlinger::computeVisibleRegions
—> Layer::setVisibleRegion
void SurfaceFlinger::computeVisibleRegions(size_t dpy,
const LayerVector& currentLayers, uint32_t layerStack,
Region& outDirtyRegion, Region& outOpaqueRegion)
{
...
while (i--) {
const sp<Layer>& layer = currentLayers[i];
// start with the whole surface at its current location
const Layer::State& s(layer->getDrawingState()); //得到mDrawingState
...
// handle hidden surfaces by setting the visible region to empty
if (CC_LIKELY(layer->isVisible())) {
Rect bounds(s.transform.transform(layer->computeBounds())); //计算visibleRegion
visibleRegion.set(bounds);
...
}
// Store the visible region in screen space
layer->setVisibleRegion(visibleRegion); //设置到visibleRegion
}
...
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- layer->computeBounds()
Rect Layer::computeBounds() const {
const Layer::State& s(getDrawingState());
return computeBounds(s.activeTransparentRegion);
}
Rect Layer::computeBounds(const Region& activeTransparentRegion) const {
const Layer::State& s(getDrawingState());
//这个w,h值是size值,由setSize()赋值
Rect win(s.active.w, s.active.h);
if (!s.active.crop.isEmpty()) {
//和crop值相交,setCrop()
win.intersect(s.active.crop, &win);
}
// subtract the transparent region and snap to the bounds
//去掉TransparentRegion透明区域的值
return reduce(win, activeTransparentRegion);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- s.transform.transform()
根据mDrawingState.transform 进行 transfrom操作
Framewrok层
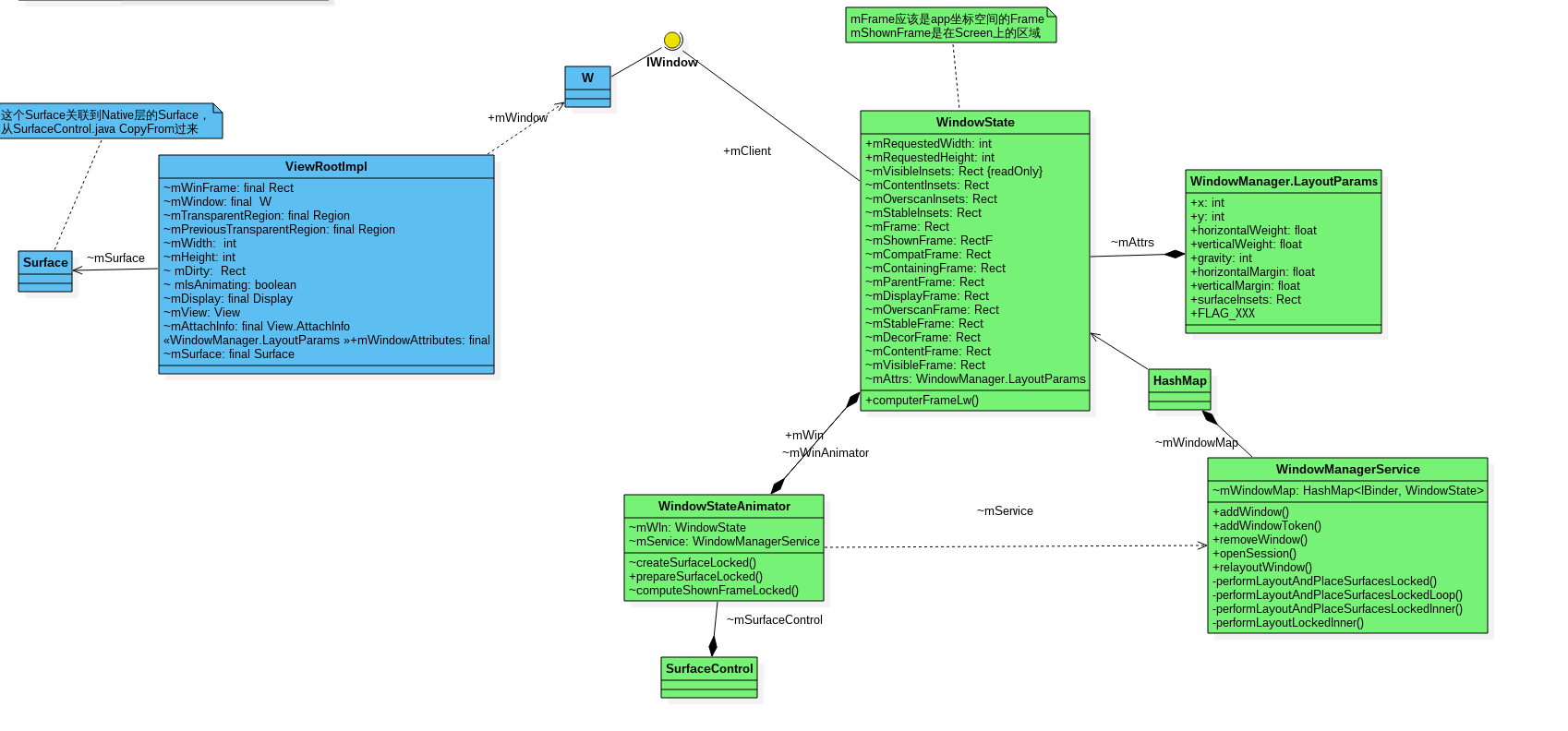
Android窗口管理系统类图(部分)
几个概念
Window和Surface一一对应 (SurfaceView是个window)
(Window指的是WMS管理的WindowState们)
Surface和Layer一一对应
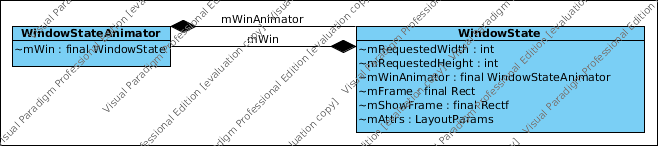
WindowState介绍
顾名思义表示window的状态,主要指宽高,位置,动画等信息
TODO 图 mContentFramee mVisibelFrame
WindowManager.LayoutParams
java.lang.Object
↳ android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams
↳ android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/ViewGroup.LayoutParams.html
LayoutParams are used by views to tell their parents how they want to be laid out. See ViewGroup Layout Attributes for a list of all child view attributes that this class supports.
The base LayoutParams class just describes how big the view wants to be for both width and height. For each dimension, it can specify one of:
FILL_PARENT (renamed MATCH_PARENT in API Level 8 and higher), which means that the view wants to be as big as its parent (minus padding)
WRAP_CONTENT, which means that the view wants to be just big enough to enclose its content (plus padding)
an exact number
There are subclasses of LayoutParams for different subclasses of ViewGroup. For example, AbsoluteLayout has its own subclass of LayoutParams which adds an X and Y value.
以上是谷歌的解释
WindowManager.LayoutParams 是 WindowManager 接口的嵌套类;它继承于 ViewGroup.LayoutParams; 设置Windows 的Layout属性
WindowManager.LayoutParams
1368 * Positive insets between the drawing surface and window content.
1372 public final Rect surfaceInsets = new Rect();
- 1
- 2
APP可以调用setLayouParams 进行设置
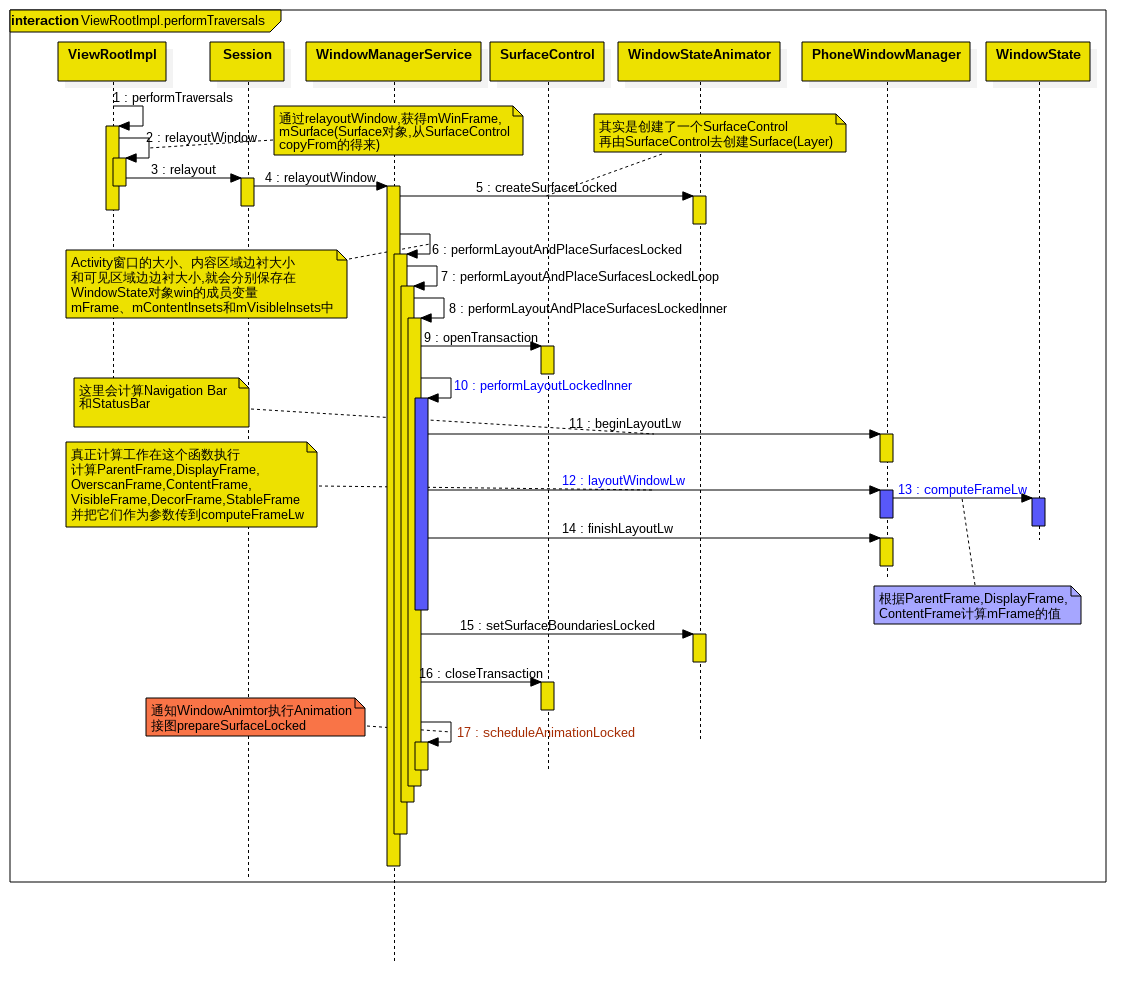
紫色的是主要进行计算的地方
ViewRootImpl那边就不看了,直接从SystemServer这边开始
3087 public int relayoutWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq,
3088 WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, int requestedWidth,
3089 int requestedHeight, int viewVisibility, int flags,
3090 Rect outFrame, Rect outOverscanInsets, Rect outContentInsets,
3091 Rect outVisibleInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets, Configuration outConfig,
3092 Surface outSurface) {
...
3104 synchronized(mWindowMap) {
3105 WindowState win = windowForClientLocked(session, client, false);
...
3164 final boolean scaledWindow =
3165 ((win.mAttrs.flags & WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SCALED) != 0);
3166
3167 if (scaledWindow) {
3168 // requested{Width|Height} Surface's physical size
3169 // attrs.{width|height} Size on screen
//需要缩放时,真正的显示在屏幕的size是attrs.{width|height}会在后面解释
3170 win.mHScale = (attrs.width != requestedWidth) ?
3171 (attrs.width / (float)requestedWidth) : 1.0f;
3172 win.mVScale = (attrs.height != requestedHeight) ?
3173 (attrs.height / (float)requestedHeight) : 1.0f;
3174 } else {
3175 win.mHScale = win.mVScale = 1;
3176 }
...
3201 if (viewVisibility == View.VISIBLE &&
3202 (win.mAppToken == null || !win.mAppToken.clientHidden)) {
...
3245 try {
3246 if (!win.mHasSurface) {
3247 surfaceChanged = true;
3248 }
3249 SurfaceControl surfaceControl = winAnimator.createSurfaceLocked();
3250 if (surfaceControl != null) {
3251 outSurface.copyFrom(surfaceControl);
3254 }
...
3259 }
...
3289 } else {
...
3335 }
//计算WindowState的其他变量,下面这些传出去的变量都在这里计算
3368 performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked();
...
3377 outFrame.set(win.mCompatFrame);
3378 outOverscanInsets.set(win.mOverscanInsets);
3379 outContentInsets.set(win.mContentInsets);
3380 outVisibleInsets.set(win.mVisibleInsets);
3381 outStableInsets.set(win.mStableInsets);
3382 outOutsets.set(win.mOutsets);
...
3401 }
...
3409 return (inTouchMode ? WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_IN_TOUCH_MODE : 0)
3410 | (toBeDisplayed ? WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_FIRST_TIME : 0)
3411 | (surfaceChanged ? WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_SURFACE_CHANGED : 0);
3412 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked:
主要功能:刷新系统的UI,顺便计算一下window大小。
Activity窗口在其属性发生了变化,例如,可见性、大小发生了变化,又或者它新增、删除了子视图,都需要重新计算大小,而这些变化都是要求WindowManagerService服务重新刷新系统的UI的。事实上,刷新系统的UI是WindowManagerService服务的主要任务,在新增和删除了窗口、窗口动画显示过程、窗口切换过程中,WindowManagerService服务都需要不断地刷新系统的UI。
WindowManagerService类的成员函数performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked主要是通过调用另外一个成员函数performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner来刷新系统的UI的,而在刷新的过程中,就会对系统中的各个窗口的大小进行计算。
8926 private final void performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked() {
8927 int loopCount = 6;
8928 do {
8929 mTraversalScheduled = false;
8930 performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedLoop();
8931 mH.removeMessages(H.DO_TRAVERSAL);
8932 loopCount--;
8933 } while (mTraversalScheduled && loopCount > 0);
8934 mInnerFields.mWallpaperActionPending = false;
8935 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
//标志是否在刷新UI,防止performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner被多次调用
8937 private boolean mInLayout = false;
8938 private final void performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedLoop() {
8939 if (mInLayout) {
8940 if (DEBUG) {
8941 throw new RuntimeException("Recursive call!");
8942 }
8943 Slog.w(TAG, "performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked called while in layout. Callers="
8944 + Debug.getCallers(3));
8945 return;
8946 }
8961 mInLayout = true;
8962
8963 boolean recoveringMemory = false;
8964 if (!mForceRemoves.isEmpty()) {//Memory不足时,把可强制移除的windows移除以便回收内存
8965 recoveringMemory = true;
8966 // Wait a little bit for things to settle down, and off we go.
8967 while (!mForceRemoves.isEmpty()) {
8968 WindowState ws = mForceRemoves.remove(0);
8969 Slog.i(TAG, "Force removing: " + ws);
8970 removeWindowInnerLocked(ws);
8971 }
8972 Slog.w(TAG, "Due to memory failure, waiting a bit for next layout");
8973 Object tmp = new Object();
8974 synchronized (tmp) {
8975 try {
8976 tmp.wait(250);
8977 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
8978 }
8979 }
8980 }
8981
8982 try {
//调用performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner
8983 performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner(recoveringMemory);
8984
8985 mInLayout = false;
8986
8987 if (needsLayout()) {
8988 if (++mLayoutRepeatCount < 6) {
8989 requestTraversalLocked();
8990 } else {
8991 Slog.e(TAG, "Performed 6 layouts in a row. Skipping");
8992 mLayoutRepeatCount = 0;
8993 }
8994 } else {
8995 mLayoutRepeatCount = 0;
8996 }
8997
8998 if (mWindowsChanged && !mWindowChangeListeners.isEmpty()) {
8999 mH.removeMessages(H.REPORT_WINDOWS_CHANGE);
9000 mH.sendEmptyMessage(H.REPORT_WINDOWS_CHANGE);
9001 }
9002 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
9003 mInLayout = false;
9004 Slog.wtf(TAG, "Unhandled exception while laying out windows", e);
9005 }
9006
9007 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
9008 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner
是WindowManagerService的核心函数。(所以它非常……长,大概600行,不仅仅是计算windows大小,实际上是完成了一次UI的刷新)
主要步骤:
1. 调用performLayoutLockedInner 计算各个windows大小。
2. 执行windows Animation。
3. step1,2 是打包成一个Transaction的,通过closeTransaction函数
去设置Layer的属性。
经过step1,2,3的操作之后,一次系统UI的刷新过程就完成了
- 1
- 2
- 销毁系统中的不会再显示的windows的drawing surface;
移除已经完成Exiting的window token;
移除已经退出了的Activity 的AppWindowToken.
9875 private final void performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner(boolean recoveringMemory) {
...
9923 SurfaceControl.openTransaction();
...
9941 for (int displayNdx = 0; displayNdx < numDisplays; ++displayNdx) {
...
9944 WindowList windows = displayContent.getWindowList();
...
9958 int repeats = 0;
9959 do {
9960 repeats++;
...
9991 // FIRST LOOP: Perform a layout, if needed.
9992 if (repeats < 4) {
9993 performLayoutLockedInner(displayContent, repeats == 1,
9994 false /*updateInputWindows*/); //计算各个windows的大小
9995 } else {
9996 Slog.w(TAG, "Layout repeat skipped after too many iterations");
9997 }
9999 // FIRST AND ONE HALF LOOP: Make WindowManagerPolicy think
10000 // it is animating.
. . .
10015 } while (displayContent.pendingLayoutChanges != 0);
...
10024 final int N = windows.size();
10025 for (i=N-1; i>=0; i--) {
10026 WindowState w = windows.get(i);
...
10086 // Moved from updateWindowsAndWallpaperLocked().
10087 if (w.mHasSurface) {
...
10119 winAnimator.setSurfaceBoundariesLocked(recoveringMemory);
10120 }
10199 } finally {
10200 SurfaceControl.closeTransaction();
}
10287 // Destroy the surface of any windows that are no longer visible.
...
10306 // Time to remove any exiting tokens?
...
10321 // Time to remove any exiting applications?
...
10355 // Finally update all input windows now that the window changes have stabilized.
...
10440 scheduleAnimationLocked(); //通知WindowAnimator执行动画
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
performLayoutLockedInner的执行过程,主要是分三个阶段:
1. 准备阶段:调用PhoneWindowManager类的成员函数beginLayoutLw来设置屏幕的大小。屏幕的大小可以通过调用WindowManagerService类的成员变量mDisplay所描述的一个Display对象的成员函数getWidth和getHeight来获得。
2. 计算阶段:调用PhoneWindowManager类的成员函数layoutWindowLw来计算各个窗口的大小、内容区域边衬大小以及可见区域边衬大小。
3. 结束阶段:调用PhoneWindowManager类的成员函数finishLayoutLw来执行一些清理工作。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
9048 private final void performLayoutLockedInner(final DisplayContent displayContent,
9049 boolean initial, boolean updateInputWindows) {
9054 WindowList windows = displayContent.getWindowList();
9074 mPolicy.beginLayoutLw(isDefaultDisplay, dw, dh, mRotation);
9090 // First perform layout of any root windows (not attached
9091 // to another window).
9092 int topAttached = -1;
9093 for (i = N-1; i >= 0; i--) {
9094 final WindowState win = windows.get(i);
9096 // Don't do layout of a window if it is not visible, or
9097 // soon won't be visible, to avoid wasting time and funky
9098 // changes while a window is animating away.
9099 final boolean gone = (behindDream && mPolicy.canBeForceHidden(win, win.mAttrs))
9100 || win.isGoneForLayoutLw();
9122 // If this view is GONE, then skip it -- keep the current
9123 // frame, and let the caller know so they can ignore it
9124 // if they want. (We do the normal layout for INVISIBLE
9125 // windows, since that means "perform layout as normal,
9126 // just don't display").
9127 if (!gone || !win.mHaveFrame || win.mLayoutNeeded
9128 || ((win.isConfigChanged() || win.setInsetsChanged()) &&
9129 ((win.mAttrs.privateFlags & PRIVATE_FLAG_KEYGUARD) != 0 ||
9130 (win.mHasSurface && win.mAppToken != null &&
9131 win.mAppToken.layoutConfigChanges)))) {
9132 if (!win.mLayoutAttached) { //通过mLayoutAttached这个flag判断是否是父window
9145 mPolicy.layoutWindowLw(win, null);//计算父window,真正计算工作在这个函数执行
}
}
}
9159 // Now perform layout of attached windows, which usually
9160 // depend on the position of the window they are attached to.
9161 // XXX does not deal with windows that are attached to windows
9162 // that are themselves attached.
9163 for (i = topAttached; i >= 0; i--) {
9164 final WindowState win = windows.get(i);
9171 // If this view is GONE, then skip it -- keep the current
9172 // frame, and let the caller know so they can ignore it
9173 // if they want. (We do the normal layout for INVISIBLE
9174 // windows, since that means "perform layout as normal,
9175 // just don't display").
9176 if (attachedBehindDream && mPolicy.canBeForceHidden(win, win.mAttrs)) {
9177 continue;
9178 }
9179 if ((win.mViewVisibility != View.GONE && win.mRelayoutCalled)
9180 || !win.mHaveFrame || win.mLayoutNeeded) {
9187 mPolicy.layoutWindowLw(win, win.mAttachedWindow);//计算子窗口,会把父窗口的WindowState也传进去
...
9208 mPolicy.finishLayoutLw(); //这个函数直接return,啥都没做
9209 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
-
PhoneWindowManager
layoutWindowLw
主要功能:根据LayoutParams 计算
ParentFrame,DisplayFrame,OverscanFrame,ContentFrame,VisibleFrame,DecorFrame,StableFrame
把这些作为参数传到computeFrameLw中 -
WindowState
computeFrameLw
主要功能:计算WindowState.mFrame以及WindowState其他参数
(eg. mContentFrame, mContentInsets …)
534 public void computeFrameLw(Rect pf, Rect df, Rect of, Rect cf, Rect vf, Rect dcf, Rect sf,
535 Rect osf) {
559 final int pw = mContainingFrame.width(); //父窗口的宽高
560 final int ph = mContainingFrame.height();
561
562 int w,h; //初步计算窗口宽高
563 if ((mAttrs.flags & WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SCALED) != 0) {
564 if (mAttrs.width < 0) {
565 w = pw;
566 } else if (mEnforceSizeCompat) {
567 w = (int)(mAttrs.width * mGlobalScale + .5f);
568 } else {
569 w = mAttrs.width;
570 }
571 if (mAttrs.height < 0)
...
578 } else {
...
593 }
607 mOverscanFrame.set(of); //给WindowState的其他属性赋值
608 mContentFrame.set(cf);
609 mVisibleFrame.set(vf);
610 mDecorFrame.set(dcf);
611 mStableFrame.set(sf);
620 float x, y; //左上角
621 if (mEnforceSizeCompat) {
622 x = mAttrs.x * mGlobalScale;
623 y = mAttrs.y * mGlobalScale;
624 } else {
625 x = mAttrs.x;
626 y = mAttrs.y;
627 }
//计算mFrame (根据父窗口区域mContainingFrame和gravity[gravity简单的说是参考布局(左对齐,居中...)])
636 Gravity.apply(mAttrs.gravity, w, h, mContainingFrame,
637 (int) (x + mAttrs.horizontalMargin * pw),
638 (int) (y + mAttrs.verticalMargin * ph), mFrame);
639
640 // Now make sure the window fits in the overall display frame.
// 计算mFrame (根据显示屏区域mDisplayFrame和gravity)
641 Gravity.applyDisplay(mAttrs.gravity, mDisplayFrame, mFrame);
653 // Make sure the content and visible frames are inside of the
654 // final window frame. mContentFrame必须包含在mFrame中
655 mContentFrame.set(Math.max(mContentFrame.left, mFrame.left),
656 Math.max(mContentFrame.top, mFrame.top),
657 Math.min(mContentFrame.right, mFrame.right),
658 Math.min(mContentFrame.bottom, mFrame.bottom));
. . .
//mContentInsets = mFrame - mContentFrame
675 mContentInsets.set(mContentFrame.left - mFrame.left,
676 mContentFrame.top - mFrame.top,
677 mFrame.right - mContentFrame.right,
678 mFrame.bottom – mContentFrame.bottom);
...
690 mCompatFrame.set(mFrame);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
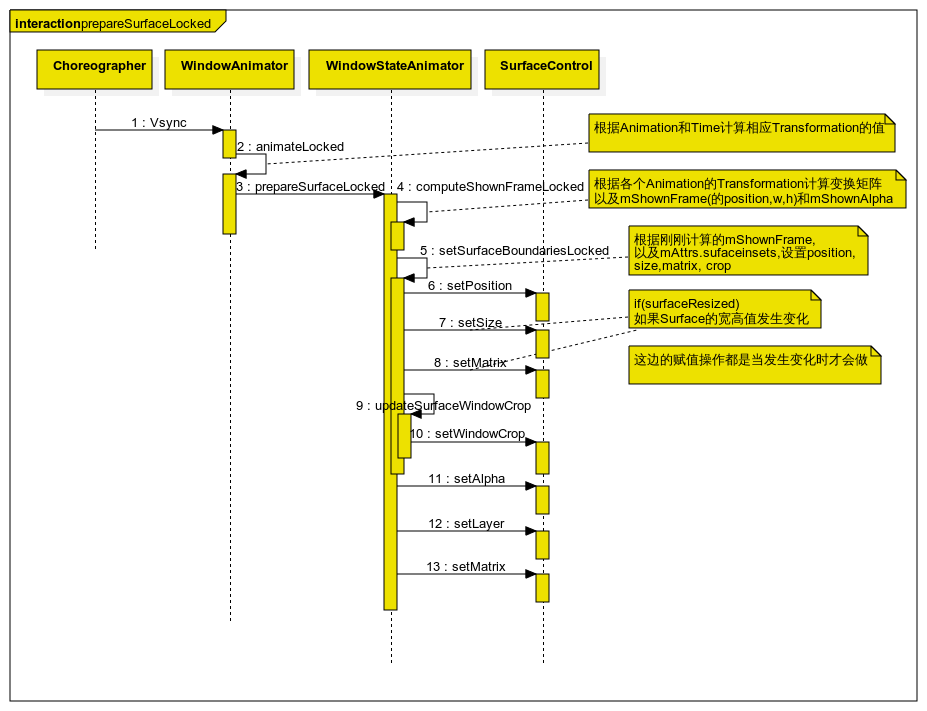
- WindowStateAnimator
- 官方说明:
Keep track of animations and surface operations for a single WindowState.
- 官方说明:
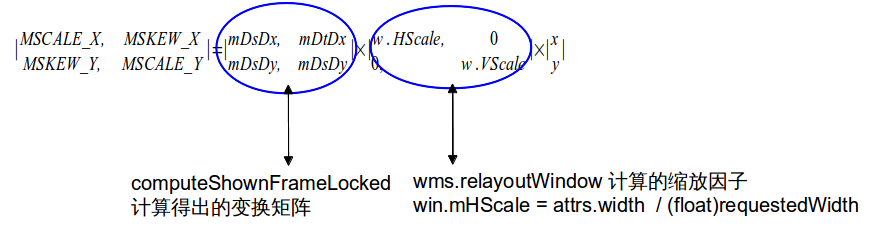
- computeShownFrameLocked()
1.根据Animation的Transformation,通过矩阵运算得出变换矩阵;
2.计算Rectf WindowState::mShownFrame(x,y=平移向量的值; w,h值=WindowState.mFrame width,height值) 和mShownAlpha。
1036 void computeShownFrameLocked() {
...
1076 if (selfTransformation || attachedTransformation != null
1077 || appTransformation != null || screenAnimation) {
1078 // cache often used attributes locally
1079 final Rect frame = mWin.mFrame;
1080 final float tmpFloats[] = mService.mTmpFloats;
1081 final Matrix tmpMatrix = mWin.mTmpMatrix;
1082
1083 // Compute the desired transformation. 根据Animation的transformation计算变换矩阵的值
1084 if (screenAnimation && screenRotationAnimation.isRotating()) { //显示屏是否有旋转动画
...
1099 } else {
1100 tmpMatrix.reset();
1101 }
1102 tmpMatrix.postScale(mWin.mGlobalScale, mWin.mGlobalScale);
1103 if (selfTransformation) { //当前窗口是否有动画
1104 tmpMatrix.postConcat(mTransformation.getMatrix());
1105 }
1106 tmpMatrix.postTranslate(frame.left + mWin.mXOffset, frame.top + mWin.mYOffset);
1107 if (attachedTransformation != null) { //父窗口是否有动画
1108 tmpMatrix.postConcat(attachedTransformation.getMatrix());
1109 }
1110 if (appTransformation != null) { //Activity切换动画
1111 tmpMatrix.postConcat(appTransformation.getMatrix());
1112 }
1113 if (screenAnimation) { //显示屏是否有动画
1114 tmpMatrix.postConcat(screenRotationAnimation.getEnterTransformation().getMatrix());
1115 }
1116
...
1133 mHaveMatrix = true;
1134 tmpMatrix.getValues(tmpFloats);
1135 mDsDx = tmpFloats[Matrix.MSCALE_X]; //变换矩阵的赋值
1136 mDtDx = tmpFloats[Matrix.MSKEW_Y];
1137 mDsDy = tmpFloats[Matrix.MSKEW_X];
1138 mDtDy = tmpFloats[Matrix.MSCALE_Y];
1139 float x = tmpFloats[Matrix.MTRANS_X]; //mShowFrame的左上角
1140 float y = tmpFloats[Matrix.MTRANS_Y];
1141 int w = frame.width();
1142 int h = frame.height();
1143 mWin.mShownFrame.set(x, y, x+w, y+h);
...
1150 mShownAlpha = mAlpha; //这个alpha变化效果因为硬件不支持被关闭了,这个值现在是木有效果的
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- setSurfaceBoundariesLocked()
根据WindowState::mShownFrame, mAttrs.sufaceinsets,设置position, size,matrix, crop
1356 void setSurfaceBoundariesLocked(final boolean recoveringMemory) {
1357 final WindowState w = mWin;
1358
1359 int width;
1360 int height;
1361 if ((w.mAttrs.flags & LayoutParams.FLAG_SCALED) != 0) {
1362 // for a scaled surface, we always want the requested size.
1364 width = w.mRequestedWidth;
1365 height = w.mRequestedHeight;
1366 } else {
1367 width = w.mCompatFrame.width();
1368 height = w.mCompatFrame.height();
1369 }
1370 ...
1380 float left = w.mShownFrame.left;
1381 float top = w.mShownFrame.top;
1382
1383 // Adjust for surface insets.
1384 final LayoutParams attrs = w.getAttrs();
1385 final int displayId = w.getDisplayId();
1386 float scale = 1.0f;
. . .
1396 width += scale * (attrs.surfaceInsets.left + attrs.surfaceInsets.right); //后面会调用setSize(width,height)
1397 height += scale * (attrs.surfaceInsets.top + attrs.surfaceInsets.bottom);
1398 left -= scale * attrs.surfaceInsets.left; //后面会调用 setPosition(l,r)
1399 top -= scale * attrs.surfaceInsets.top;
1409 mSurfaceControl.setPosition(left, top);
1428 mSurfaceControl.setSize(width, height);
1429 mSurfaceControl.setMatrix(
1430 mDsDx * w.mHScale, mDtDx * w.mVScale,
1431 mDsDy * w.mHScale, mDtDy * w.mVScale);
1452 updateSurfaceWindowCrop(recoveringMemory);
1453 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
-
setMatrix的值
-
setSize的值
如果有缩放width = WindowState.mRequestWidth+scale * (attrs.surfaceInsets.left + attrs.surfaceInsets.right);
height = WindowState.mRequestWidth+scale * (attrs.surfaceInsets.top + attrs.surfaceInsets.bottom);
根据上面两项,缩放之后,宽高值是attrs.{width|height},这下wms.relayoutWindow计算的缩放因子的注释就清楚了( requested{Width|Height} Surface’s physical size. attrs.{width|height} Size on screen)
2. WindowState 和 WindowStateAnimator
–>WindowState mWin是在WindowStateAnimator构造函数赋值
195 WindowStateAnimator(final WindowState win) {
…
212 mWin = win;
—>WindowStateAnimator 是在 WindowState 构造函数里面创建
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowState.java#501
mWinAnimator = new WindowStateAnimator(this); //把 WindowState 本身传进去
WindowState
mRequestedWidth,mRequestedHeight :APP申请的宽高
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs的值是由ViewRootImpl.java这边传下去的
(CALL performTraversals() relayoutResult = relayoutWindow(params, viewVisibility, insetsPending); //params 是WindowManager.LayoutParams, 由mWindowAttributes赋值给它 )
mWindowAttributes的值在这两处获得(mWindowAttributes.copyFrom(attrs);)
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java#461 setView()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java#797 setLayoutParams()
Cmd:
adb shell dumpsys window
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
static final boolean DEBUG_SURFACE_TRACE = false; -> true
[frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowStateAnimator.java]
dumpAllSurfaces() 会执行
adb shell dumpsys window surfaces
Surface #3: #544e0ff SurfaceView
mLayerStack=0 mLayer=21025
mShown=true mAlpha=1.0 mIsOpaque=false
mPosition=0.0,0.0 mSize=1920x1080
mCrop=[0,0][1920,1080]
Transform: (0.5625, 0.0, 0.0, 1.7777778)
参考(图片来源):
Android窗口管理服务WindowManagerService计算Activity窗口大小的过程分析










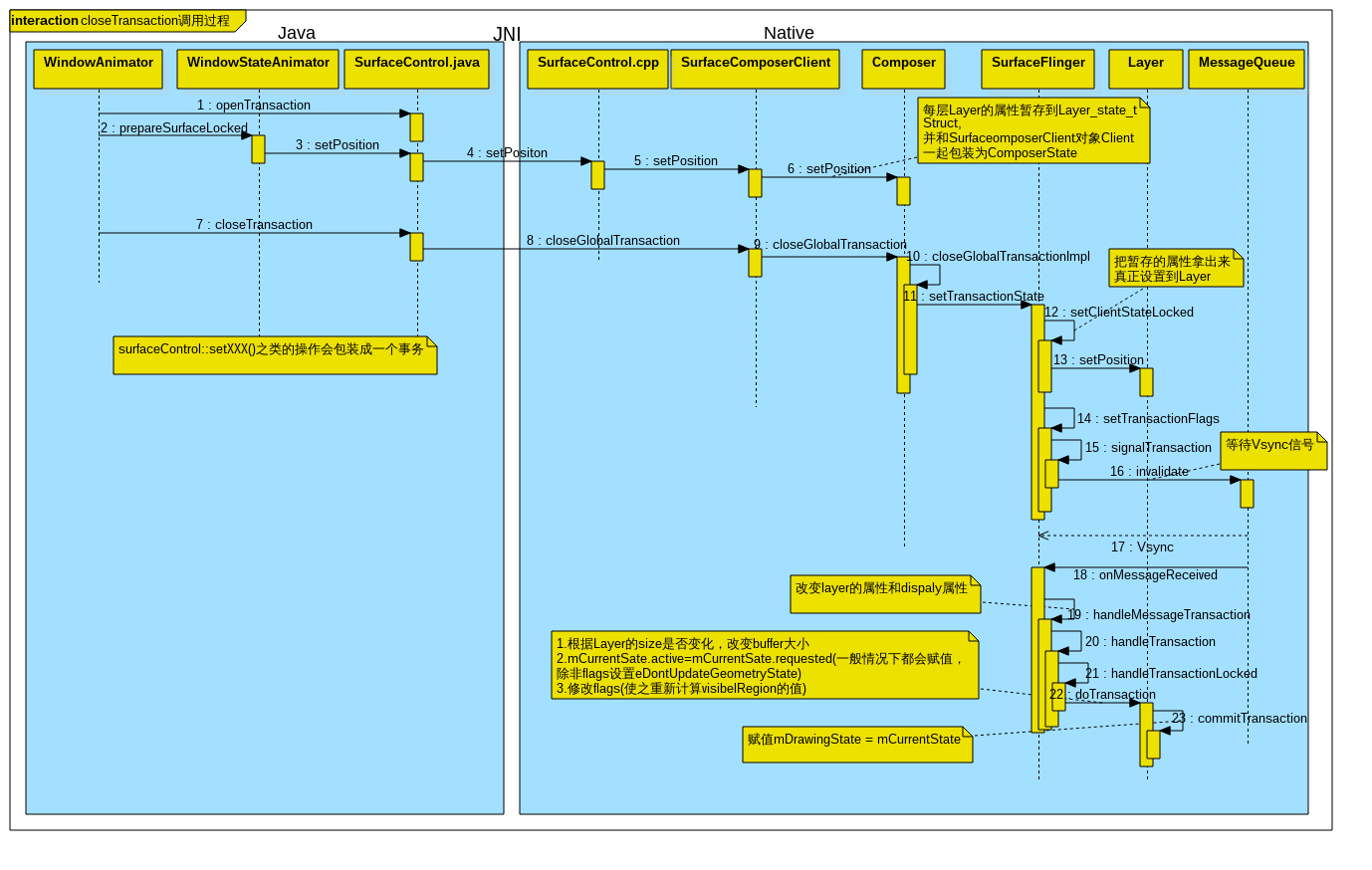
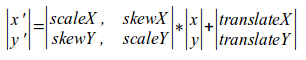
















 2533
2533

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








