转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/wlwlwlwl015/article/details/43022193,上一篇blog记录了hibernate抓取策略的相关用法(http://blog.csdn.net/wlwlwlwl015/article/details/42705585),它主要是在对象导航时为我们进行HQL方面的优化。本篇blog将介绍一些通用性的优化方式,即在hibernate中使用视图和存储过程。在数据量比较大时(百万级),使用hibernate时不再推荐使用HQL,而是使用原生的SQL语句,而视图、索引、存储过程等数据库对象也都是基于底层数据库和原生的SQL派生出的优化方案,废话不多说,下面就开始通过代码介绍一下如何在hibernate中调用view、proc以及需要注意的一些关键点。
通过hibernate查询视图
数据库视图(View)的概念和优点等等就不说了,这个书上和网上都讲了很多,下面直接通过例子来看一下如何在
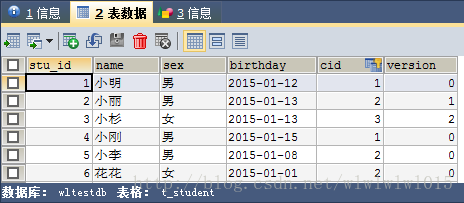
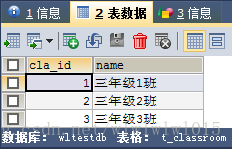
hibernate中查询视图,依旧是上一篇中的例子,一对多的典型示例:班级→学生,先看一下数据表:
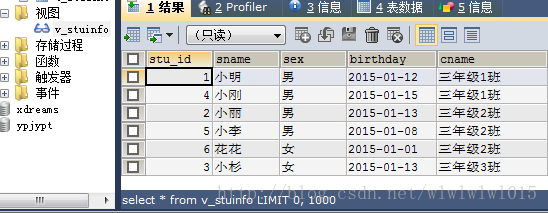
下面写一个简单的视图,例如需要查询以下几个字段:stu_id、sname、sex、birthday、cname,首先根据需求创建视图,
DELIMITER $$
USE `wltestdb`$$
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS `v_stuinfo`$$
CREATE ALGORITHM=UNDEFINED DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` SQL SECURITY DEFINER VIEW `v_stuinfo` AS (
SELECT
`t1`.`stu_id` AS `stu_id`,
`t1`.`name` AS `sname`,
`t1`.`sex` AS `sex`,
`t1`.`birthday` AS `birthday`,
`t2`.`name` AS `cname`
FROM (`t_student` `t1`
JOIN `t_classroom` `t2`
ON ((`t1`.`cid` = `t2`.`cla_id`))))$$
DELIMITER ;通过查询语句select * from v_stuinfo即可查询视图,
OK,视图没问题,接下来就是如何映射和查询了,首先是通过hibernate建立view的mapping。
1.映射视图
如果不知道如何去手写view的映射,我们可以通过MyEclipse的hibernate的反向工程来生成View的映射实体及映射配置,打开DB Browser视图,找到我们的view然后右键Hibernate Reverse Engineering,视情况选择生成annotation或者xml文件,一路next之后我们可以发现多了三个文件,2个PO类一个hbm.xml文件,
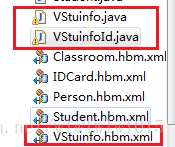
我们可以看到生成了大写V打头+视图名的一个类,还有一个是在上一个类多加了Id结尾的类,
一共视图生成2个PO类和一个hbm.xml文件,这就是hibernate为我们映射的视图,由于视图是没有主键的,所以hibernate在无法确定<id>的情况下自然也就无法通过1个实体类完成映射,hibernate的解决办法是:用两个PO来映射视图,一个PO封装查询视图返回的所有列,另一个PO将封装好的对象作为联合主键,这样就能完成映射了。下面看一下这两个类的代码和配置文件的代码,
VStuinfo:
package com.wl.entity;
/**
* VStuinfo entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools
*/
public class VStuinfo implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
private VStuinfoId id;
// Constructors
/** default constructor */
public VStuinfo() {
}
/** full constructor */
public VStuinfo(VStuinfoId id) {
this.id = id;
}
// Property accessors
public VStuinfoId getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(VStuinfoId id) {
this.id = id;
}
}package com.wl.entity;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* VStuinfoId entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools
*/
public class VStuinfoId implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
private Integer stuId;
private String sname;
private String sex;
private Date birthday;
private String cname;
// Constructors
/** default constructor */
public VStuinfoId() {
}
/** minimal constructor */
public VStuinfoId(Integer stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
/** full constructor */
public VStuinfoId(Integer stuId, String sname, String sex, Date birthday,
String cname) {
this.stuId = stuId;
this.sname = sname;
this.sex = sex;
this.birthday = birthday;
this.cname = cname;
}
// Property accessors
public Integer getStuId() {
return this.stuId;
}
public void setStuId(Integer stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public String getSname() {
return this.sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public String getSex() {
return this.sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return this.birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getCname() {
return this.cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if ((this == other))
return true;
if ((other == null))
return false;
if (!(other instanceof VStuinfoId))
return false;
VStuinfoId castOther = (VStuinfoId) other;
return ((this.getStuId() == castOther.getStuId()) || (this.getStuId() != null
&& castOther.getStuId() != null && this.getStuId().equals(
castOther.getStuId())))
&& ((this.getSname() == castOther.getSname()) || (this
.getSname() != null && castOther.getSname() != null && this
.getSname().equals(castOther.getSname())))
&& ((this.getSex() == castOther.getSex()) || (this.getSex() != null
&& castOther.getSex() != null && this.getSex().equals(
castOther.getSex())))
&& ((this.getBirthday() == castOther.getBirthday()) || (this
.getBirthday() != null
&& castOther.getBirthday() != null && this
.getBirthday().equals(castOther.getBirthday())))
&& ((this.getCname() == castOther.getCname()) || (this
.getCname() != null && castOther.getCname() != null && this
.getCname().equals(castOther.getCname())));
}
public int hashCode() {
int result = 17;
result = 37 * result
+ (getStuId() == null ? 0 : this.getStuId().hashCode());
result = 37 * result
+ (getSname() == null ? 0 : this.getSname().hashCode());
result = 37 * result
+ (getSex() == null ? 0 : this.getSex().hashCode());
result = 37 * result
+ (getBirthday() == null ? 0 : this.getBirthday().hashCode());
result = 37 * result
+ (getCname() == null ? 0 : this.getCname().hashCode());
return result;
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!--
Mapping file autogenerated by MyEclipse Persistence Tools
-->
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.wl.entity.VStuinfo" table="v_stuinfo" catalog="wltestdb">
<composite-id name="id" class="com.wl.entity.VStuinfoId">
<key-property name="stuId" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="stu_id" />
</key-property>
<key-property name="sname" type="java.lang.String">
<column name="sname" />
</key-property>
<key-property name="sex" type="java.lang.String">
<column name="sex" />
</key-property>
<key-property name="birthday" type="java.util.Date">
<column name="birthday" length="10" />
</key-property>
<key-property name="cname" type="java.lang.String">
<column name="cname" />
</key-property>
</composite-id>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
2.查询视图
查询视图很简单,既然已经映射好了,那么就当成普通对象用HQL查询就可以了,下面看一下测试代码和运行结果,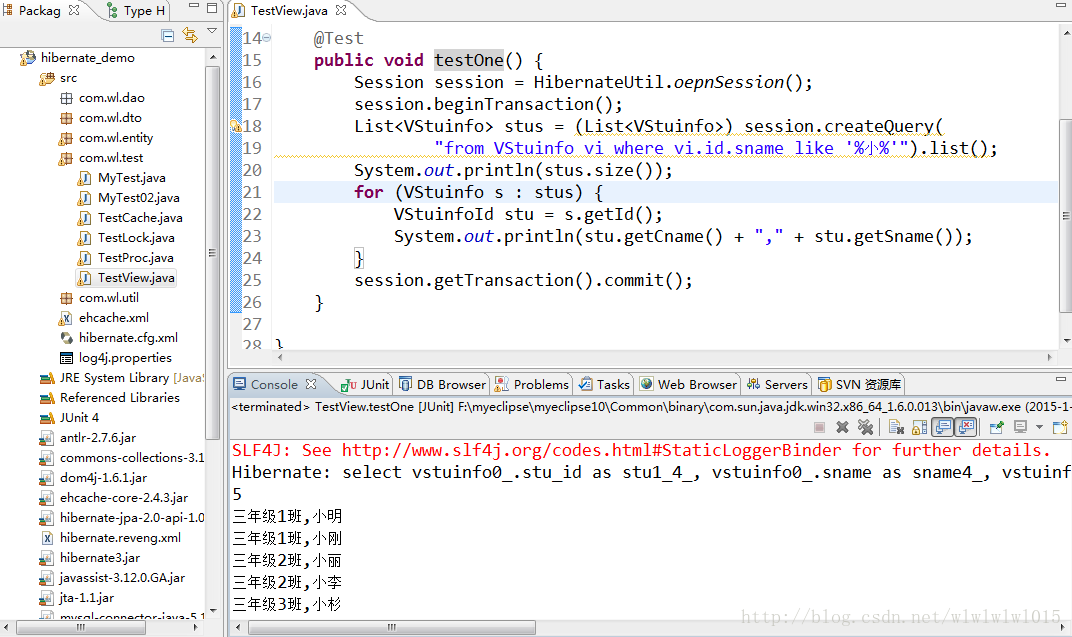
没有问题,成功打印出了视图返回的两项数据。但这样映射视图需要注意一点,就是视图返回的所有列不能有NULL值,一旦有NULL值的话,那么上图中第18行返回的List必然为NULL(之前做项目就遇到这个问题,控制台发了正确的SQL语句,可返回的List对象总是NULL)。解决办法也很简单,可以给可能为空的列添加默认值,或者是给视图指定一个主键等等,当然如果视图一定不会返回NULL值的话就可以忽略这个问题了。
通过hibernate调用存储过程
同样的存储过程的概念和优点在这里就不做介绍了,依旧是通过一个完整的例子来演示hibernate中如何调用存储过程。
1.创建存储过程
依然使用班级和学生举例说明,并且还是查询上面的那5个列,只不过是用存储过程来实现,首先是创建存储过程,
DELIMITER $$
USE `wltestdb`$$
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `proc_stuinfo`$$
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `proc_stuinfo`(
IN pstuid INT
)
BEGIN
SELECT
t1.stu_id AS stuid,t1.name AS sname,t1.sex,
t1.birthday,t2.name AS cname
FROM t_student t1 INNER JOIN t_classroom t2
ON t1.cid=t2.cla_id
WHERE t1.stu_id=pstuid;
END$$
DELIMITER ;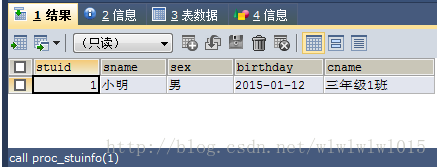
可以看到调用存储过程之后成功返回了数据,接下面就是如何通过hibernate去调用存储过程了。
2.在hibernate中调用存储过程
如何在hibernate中调用存储过程,这个问题我经常在面试中问别人,不理解的是这么常用的东西好像知道的人很少,不知道是存储过程用的少还是在jdbc的api不熟悉。其实通过hibernate调用比JDBC调用存储过程更简单,我们甚至不需要使用CallableStatement对象,直接通过creatSQLQuery("{call proc_name(param)}")就可以返回数据了。下面看一下测试代码和运行结果,
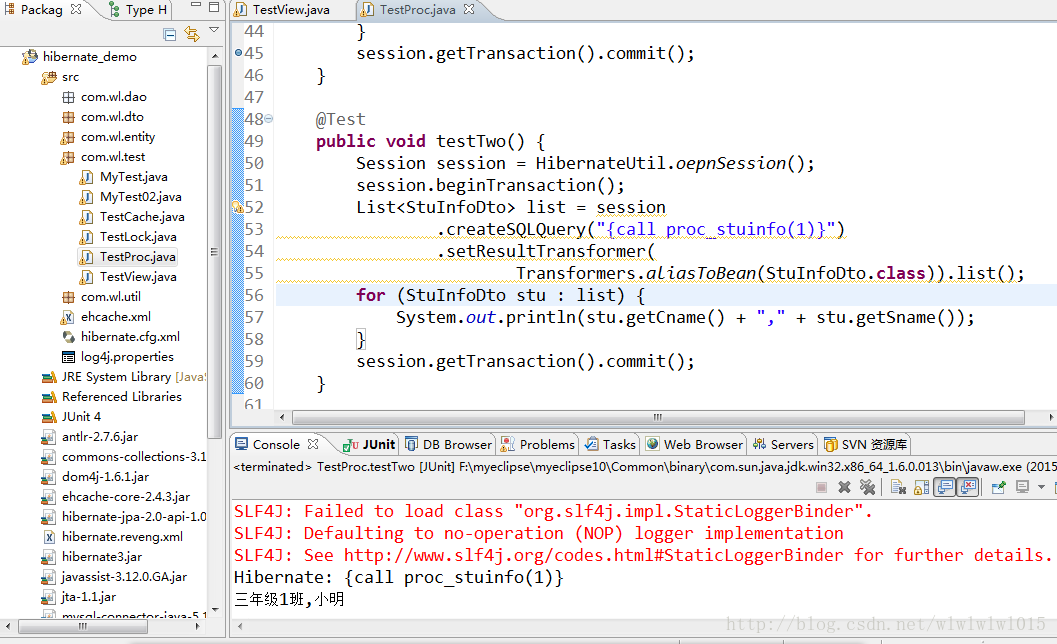
这里我封装了一个DTO对象用来保存proc返回的数据,可以看到console成功打印出了调用语句和数据结果。
我个人推荐用上面这种方式调用存储过程最简单,当然还有一些其它的方式,例如通过session得到Connection对象,再通过CallableStatement去调用存储过程,代码这样写结果也是一样的,
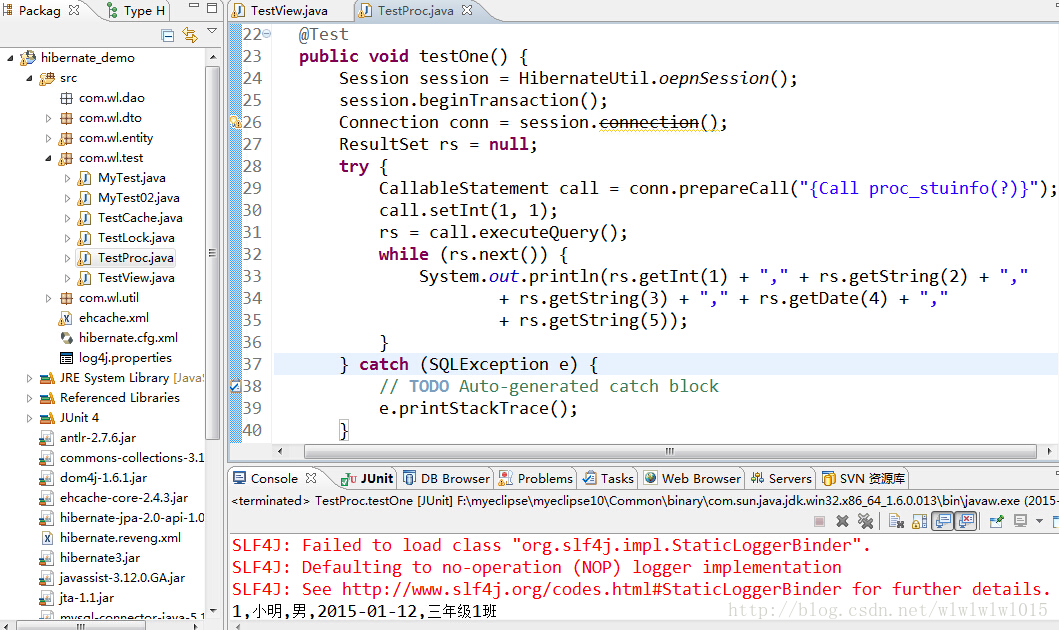
这里可以发现session.connection()方法已经过时,从hibernate3.2.2版本开始这个方法就不推荐使用了,而是通过spring提供的spring-orm包下的SessionFactoryUtils去获取Connection对象,形如:
try {
Connection connection = SessionFactoryUtils.getDataSource(
getSessionFactory()).getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}总结
本篇blog记录了持久层的另一种优化方式,就是引用视图和存储过程,当数据量很大时,比如达到百万级之后,我们用HQL语句可能就达不到我们对效率方面的要求了,所以这时应使用原生SQL,比如视图、存储过程等等,基本就可以满足我们性能方面的要求。好了,本篇blog到这里就告于段落,关于hibernate优化的总结可能会暂时放一放,准备继续学习Android和前端方面的东西,时间永远不够用,加油,Raito!






















 6669
6669

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








