一、简介
受朋友之邀,写篇关于CoreData 入门级教程,Core Data是iOS5之后才出现的一个框架,它提供了对象-关系映射(ORM)的功能,即能够将OC对象转化成数据,保存在SQLite数据库文件中,也能够将保存在数据库中的数据还原成OC对象。在此数据操作期间,我们不需要编写任何SQL语句。
二、开始创建
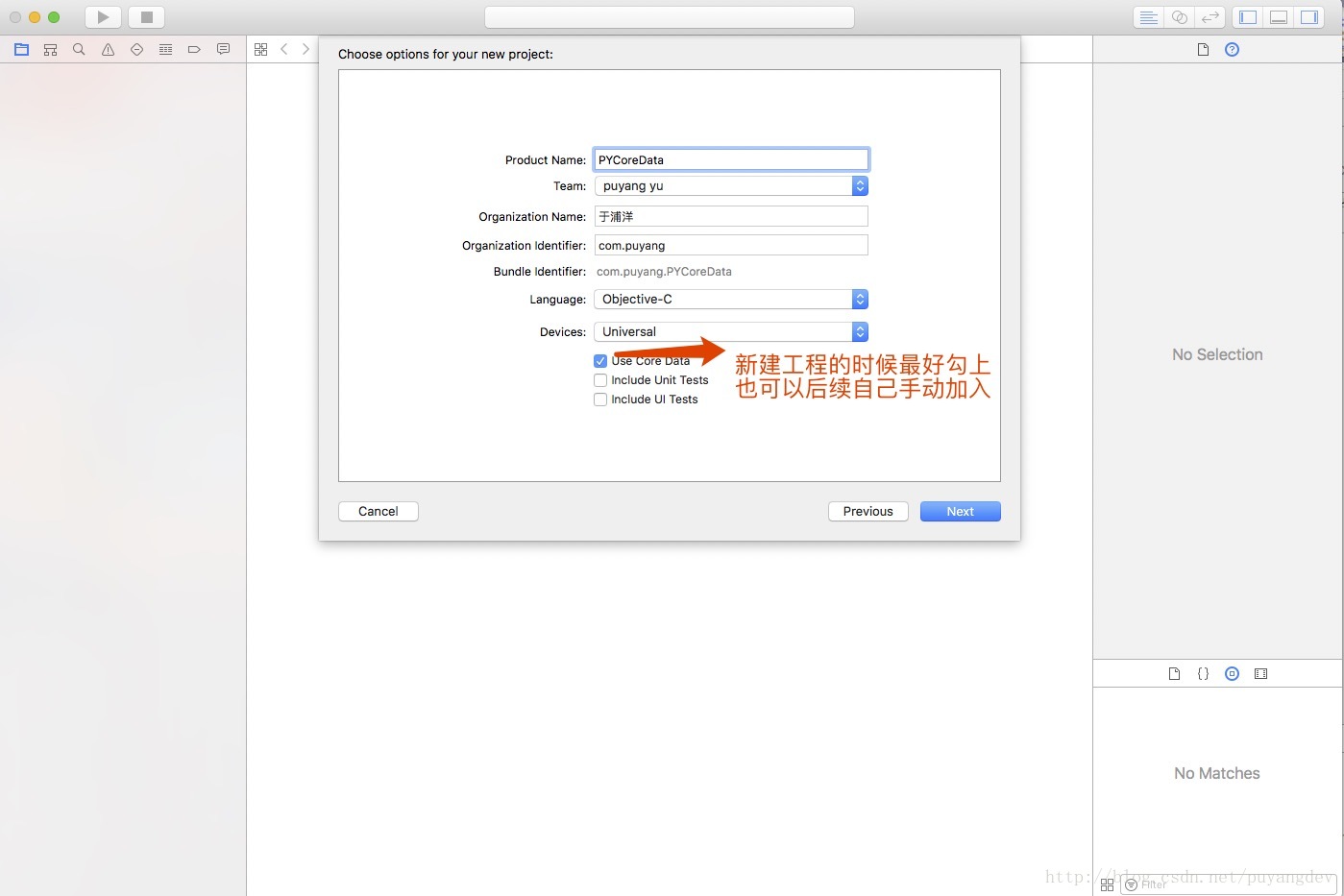
2.1、创建工程
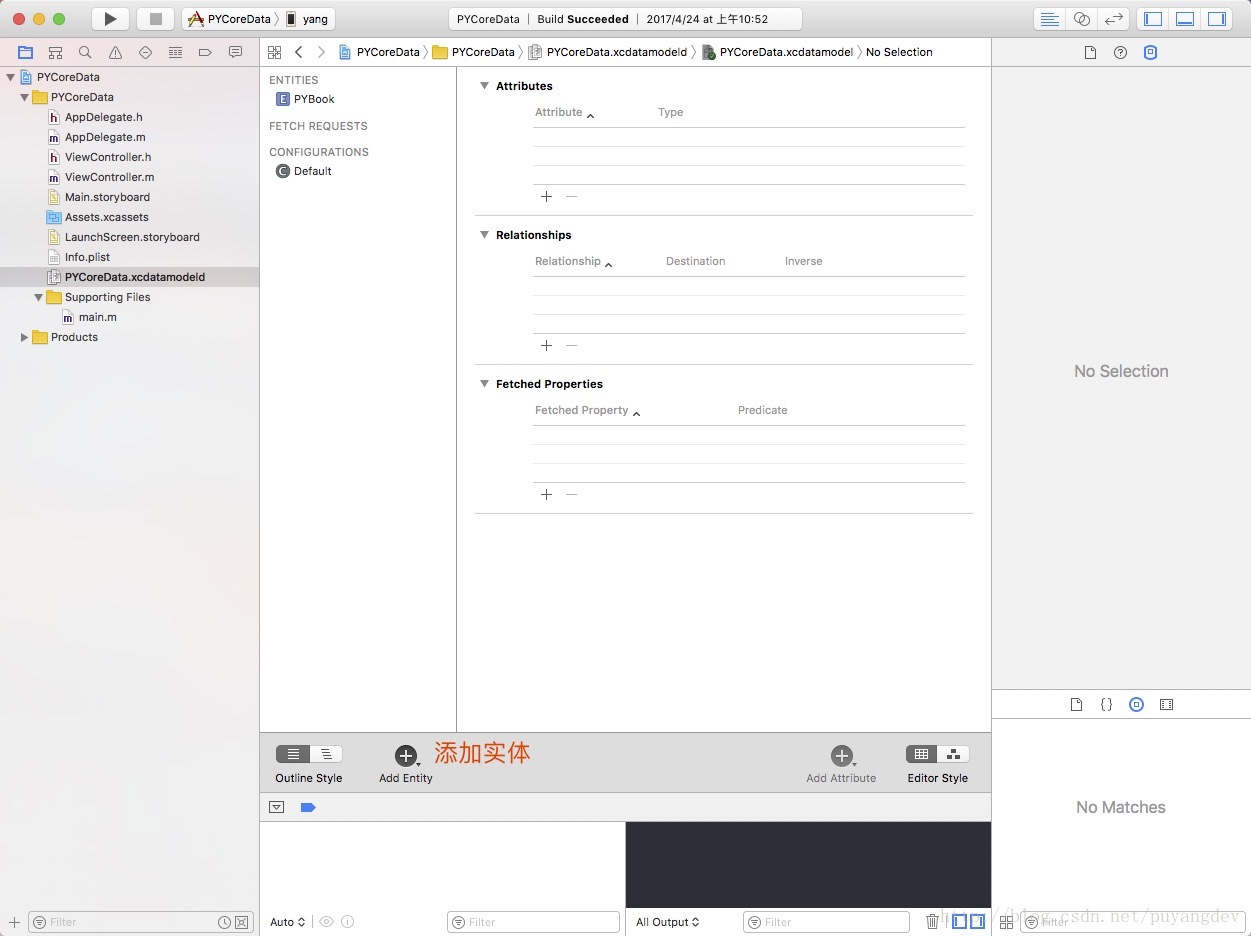
2.2 添加实体
2.3 添加属性
2.4创建 PYBook类
记得在xcode 4.6的时候,PYBook类 是可以自动生成的(File->New->CoreData->NSManageredObjectSubClass->选择PYBook),由于用这里使用的是Xcode 8.3 ,和xcode老版本略有区别,如下图
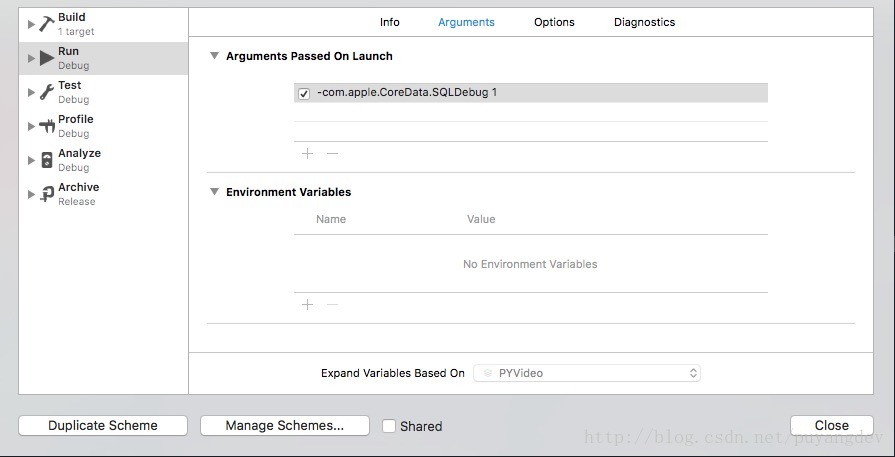
三、打开CoreData的SQL语句输出开关
1.打开Product,点击EditScheme...2.点击Arguments,在ArgumentsPassed On Launch中添加2项
1> -com.apple.CoreData.SQLDebug
2> 1
如下图所示
四、解决CoreData 数据结构后,更新安装会闪退的问题
使用IOS的CoreData进行存储很方便,CoreData已经帮我们做了很多基础的工作,一般情况下没必要自己操作数据库了。在开发中修改了实体模型,可能会遇到schema incompatibility的错误,这是因为修改了数据结构,要进行数据迁移。其实很多简单的情况,不用这么麻烦,Coredata提供了轻量级的自动数据迁移,比如以下三个情况会自动进行:
1.简单的增加一个字段
2.把一个必填字段改为可选字段
3.把可选字段改为必填字段(但一定要定义默认值)
如果iOS App 使用到CoreData,并且在上一个版本上有数据库更新(新增表、字段等操作),那在覆盖安装程序时就要进行CoreData数据库的迁移,具体操作如下:
4.1.创建新的版本
选中你的PYCoreData.xcdatamodel 文件,选择菜单editor->Add Model Version 比如取名:PYCoreData2.xcdatamodel
4.2.设置当前版本
选择上级PYCoreData.xcdatamodel ,在inspector中的Versioned Core Data Model选择Current模版为 PYCoreData2
4.3.修改数据库表结构
修改新数据模型PYCoreData,在新的文件上添加字段及表
4.4 类重建
如果设置的是手动创建类,则删除原来的类文件,重新生成下类
4.5 在App delegate类里修改persistentStoreCoordinator方法
- (NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *)persistentStoreCoordinator {
// The persistent store coordinator for the application. This implementation creates and returns a coordinator, having added the store for the application to it.
if (_persistentStoreCoordinator != nil) {
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
// Create the coordinator and store
_persistentStoreCoordinator = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:[self managedObjectModel]];
NSURL *storeURL = [[self applicationDocumentsDirectory] URLByAppendingPathComponent:@"PYCoreData.sqlite"];
NSError *error = nil;
NSDictionary *options = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:
[NSNumber numberWithBool:YES], NSMigratePersistentStoresAutomaticallyOption,
[NSNumber numberWithBool:YES], NSInferMappingModelAutomaticallyOption, nil];
NSString *failureReason = @"There was an error creating or loading the application's saved data.";
if (![_persistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:storeURL options:options error:&error]) {
// Report any error we got.
NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[NSLocalizedDescriptionKey] = @"Failed to initialize the application's saved data";
dict[NSLocalizedFailureReasonErrorKey] = failureReason;
dict[NSUnderlyingErrorKey] = error;
error = [NSError errorWithDomain:@"YOUR_ERROR_DOMAIN" code:9999 userInfo:dict];
// Replace this with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}4.6 在App delegate中指定momd资源
- (NSManagedObjectModel *)managedObjectModel {
// The managed object model for the application. It is a fatal error for the application not to be able to find and load its model.
if (_managedObjectModel != nil) {
return _managedObjectModel;
}
NSURL *modelURL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"PYCoreData" withExtension:@"momd"];
_managedObjectModel = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:modelURL];
return _managedObjectModel;
}




























 3273
3273

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








