一、淘宝商品详情页效果
先看一下淘宝详情页的效果

我们的效果

二、实现思路
使用两个scrollView,两个scrollView 竖直排列,通过自定义viewGroup来控制两个scrollView的竖直排列,以及滑动事件的处理。如下图
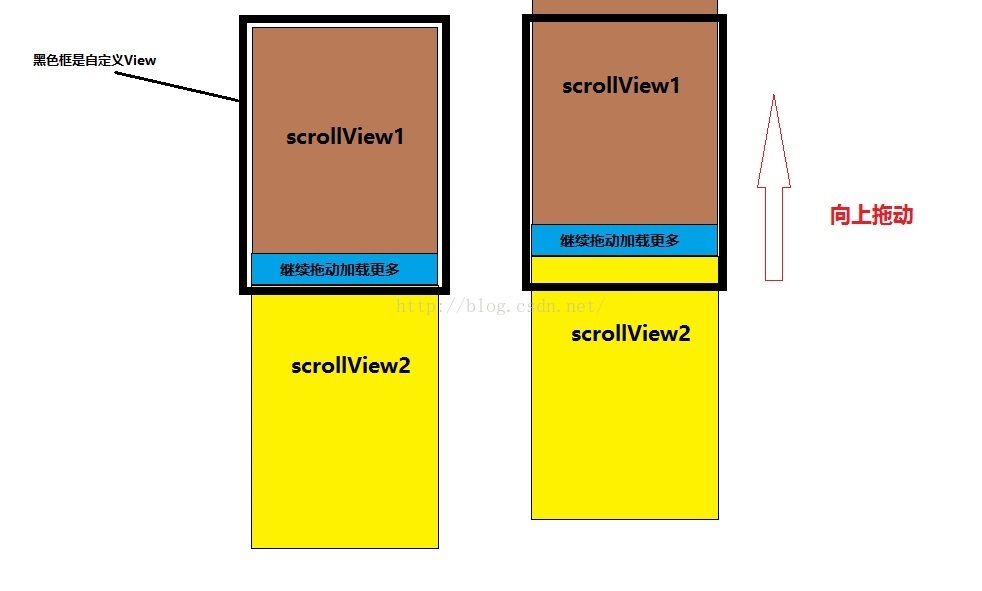
三、具体实现
1、继承viewGroup自定义布局View 重写onMeasure()和onLayout方法,在onLayout方法中完成对两个子ScrollView的竖直排列布局,代码如下:
布局文件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MainActivity">
<com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.PullUpToLoadMore
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MyScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fillViewport="true">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/a1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="180dp" />
<TextView
android:text="这里是标题"
android:textSize="18dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="子标题"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:textSize="18dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
..............
<LinearLayout
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="bottom"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:height="50dp"
android:background="#b11"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="继续拖动查看图文详情"
android:textColor="#000" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MyScrollView>
<com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MyScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fillViewport="true">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/a1" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/a3" />
.........
</LinearLayout>
</com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MyScrollView>
</com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.PullUpToLoadMore>
</RelativeLayout>
public class PullUpToLoadMore extends ViewGroup {
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int childTop = t;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
child.layout(l, childTop, r, childTop + child.getMeasuredHeight());
childTop += child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
}
2、处理滑动事件
规则如下 :
(1)、当处于第一屏时 第一个ScrollView已经滑动到底部并且滑动方向是往上滑动,这个时候滑动事件应该交给父view处理也就是拦截事件让onInterceptTouchEvent返回true.然后父view通过scrollBy()方法滚动,显示出第二个scrollView。
(2)、当处于第二屏时 第二个ScrollView已经滑动到顶部并且滑动方向是往下滑动,这个时候滑动事件交给父view处理,根据滑动事件显示出第一个ScrollView。
(3)、当手指离开屏幕时,根据滑动速度来决定是回弹到第一个ScrollView还是第二个ScrollView,通过VelocityTracker来获取滑动速度。
3、一些细节的处理
(1)、如果仔细看观察淘宝的实现效果你会发现,当你滑动到刚刚看到 “继续拖动,查看图文详情”的时候,手指抬起,然后再按下重新向上拖动你会发现,第二页并不会划出来,而是停留在了“继续拖动,查看图文详情”的底部,京东的效果也是一样。这样用户体验不太好,我们来优化一下。其实通过查看ScrollView的源码可以看出来,这是因为ScrollView类的onTouchEvent方法的默认实现,调用了parent.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true)方法 阻止了我们拦截事件,导致我们父view的onInterceptTouchEvent方法无法执行,也就拦截不到事件,拦截不到事件我们的onTouchEvent就无法执行,onTouchEvent无法执行,我们写在onTouchEvent里面的滚动逻辑就执行不到了,导致了上面我们看到的划不动的效果。解决方法就是,我们需要重写dispatchTouchEvent()方法,防止子view干扰我们,这样我们滑动的时候就可以一气呵成了。代码如下:
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//防止子View禁止父view拦截事件
this.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(false);
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
} (2)、监听ScrollView滑动事件的问题
ScrollView没有提供滚动事件的监听方法,也就没法判断是否滚动到了顶部,或者底部,这里我们继承ScrollView 自己实现滚动事件监听。
/**
* Created by baoyunlong on 16/6/8.
*/
public class MyScrollView extends ScrollView {
private static String TAG=MyScrollView.class.getName();
public void setScrollListener(ScrollListener scrollListener) {
this.mScrollListener = scrollListener;
}
private ScrollListener mScrollListener;
public MyScrollView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
switch (ev.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
if(mScrollListener!=null){
int contentHeight=getChildAt(0).getHeight();
int scrollHeight=getHeight();
int scrollY=getScrollY();
mScrollListener.onScroll(scrollY);
if(scrollY+scrollHeight>=contentHeight||contentHeight<=scrollHeight){
mScrollListener.onScrollToBottom();
}else {
mScrollListener.notBottom();
}
if(scrollY==0){
mScrollListener.onScrollToTop();
}
}
break;
}
boolean result=super.onTouchEvent(ev);
requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(false);
return result;
}
public interface ScrollListener{
void onScrollToBottom();
void onScrollToTop();
void onScroll(int scrollY);
void notBottom();
}
4、完整代码如下
/**
* Created by baoyunlong on 16/6/8.
*/
public class PullUpToLoadMore extends ViewGroup {
public static String TAG = PullUpToLoadMore.class.getName();
MyScrollView topScrollView, bottomScrollView;
VelocityTracker velocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
Scroller scroller = new Scroller(getContext());
int currPosition = 0;
int position1Y;
int lastY;
public int scaledTouchSlop;//最小滑动距离
int speed = 200;
boolean isIntercept;
public boolean bottomScrollVIewIsInTop = false;
public boolean topScrollViewIsBottom = false;
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init() {
post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
topScrollView = (MyScrollView) getChildAt(0);
bottomScrollView = (MyScrollView) getChildAt(1);
topScrollView.setScrollListener(new MyScrollView.ScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollToBottom() {
topScrollViewIsBottom = true;
}
@Override
public void onScrollToTop() {
}
@Override
public void onScroll(int scrollY) {
}
@Override
public void notBottom() {
topScrollViewIsBottom = false;
}
});
bottomScrollView.setScrollListener(new MyScrollView.ScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollToBottom() {
}
@Override
public void onScrollToTop() {
}
@Override
public void onScroll(int scrollY) {
if (scrollY == 0) {
bottomScrollVIewIsInTop = true;
} else {
bottomScrollVIewIsInTop = false;
}
}
@Override
public void notBottom() {
}
});
position1Y = topScrollView.getBottom();
scaledTouchSlop = ViewConfiguration.get(getContext()).getScaledTouchSlop();
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//防止子View禁止父view拦截事件
this.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(false);
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
int y = (int) ev.getY();
switch (ev.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//判断是否已经滚动到了底部
if (topScrollViewIsBottom) {
int dy = lastY - y;
//判断是否是向上滑动和是否在第一屏
if (dy > 0 && currPosition == 0) {
if (dy >= scaledTouchSlop) {
isIntercept = true;//拦截事件
lastY=y;
}
}
}
if (bottomScrollVIewIsInTop) {
int dy = lastY - y;
//判断是否是向下滑动和是否在第二屏
if (dy < 0 && currPosition == 1) {
if (Math.abs(dy) >= scaledTouchSlop) {
isIntercept = true;
}
}
}
break;
}
return isIntercept;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int y = (int) event.getY();
velocityTracker.addMovement(event);
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int dy = lastY - y;
if (getScrollY() + dy < 0) {
dy = getScrollY() + dy + Math.abs(getScrollY() + dy);
}
if (getScrollY() + dy + getHeight() > bottomScrollView.getBottom()) {
dy = dy - (getScrollY() + dy - (bottomScrollView.getBottom() - getHeight()));
}
scrollBy(0, dy);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
isIntercept = false;
velocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
float yVelocity = velocityTracker.getYVelocity();
if (currPosition == 0) {
if (yVelocity < 0 && yVelocity < -speed) {
smoothScroll(position1Y);
currPosition = 1;
} else {
smoothScroll(0);
}
} else {
if (yVelocity > 0 && yVelocity > speed) {
smoothScroll(0);
currPosition = 0;
} else {
smoothScroll(position1Y);
}
}
break;
}
lastY = y;
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int childTop = t;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
child.layout(l, childTop, r, childTop + child.getMeasuredHeight());
childTop += child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
//通过Scroller实现弹性滑动
private void smoothScroll(int tartY) {
int dy = tartY - getScrollY();
scroller.startScroll(getScrollX(), getScrollY(), 0, dy);
invalidate();
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (scroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
scrollTo(scroller.getCurrX(), scroller.getCurrY());
postInvalidate();
}
}
}





















 2103
2103

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








