【题目描述】
数组中有一个数出现的次数超过了数组长度的一半,找出这个数【解题方法】
1、若数组有序:
方法:可直接输出数组n/2位置上的元素即可
2、若数组无序
方法一:排序
采用快速排序,将无序数组变成有序数组,再输出n/2位置上的元素即可,复杂度为O(nlogn);方法二:哈希表
1)根据题目需求,可设计出哈希表的数据结构(两个int,其中一个存储数组中的数data,另一个存储数出现的次数count)2)冲突解决:根据题目需求,若出现冲突,则对应data的count++
3)哈希函数构造:采用取余法
哈希表的查找时间复杂度:O(1),空间复杂度为O(n)
代码实现
/**********************************
Author:tmw
date:2018-2-25
**********************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//这里定义哈希表的大小,题给测试例数组长度为5,因此设5,根据题目情境,HASHSIZE的设定值最好为给定数组长度
#define HASHSIZE 10
#define init_data -65534
/**数据结构定义**/
typedef struct hash_node
{
int data;
int count;
}hash_node;
/**定义哈希表**/
struct hash_node HashTable[HASHSIZE];
/**哈希表初始化**/
void init_hash_table()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<HASHSIZE;i++)
{
HashTable[i].data = init_data;
HashTable[i].count = 0;
}
}
/**哈希函数的定义**/
int hash_func(int key)
{
return key%HASHSIZE;
}
/**哈希表的建立**/
void create_hash_table(int key)
{
int hash_index = hash_func(key);
//当哈希表中没有key时,则将key插入表中
if(HashTable[hash_index].data==init_data)
HashTable[hash_index].data = key;
//当哈希表存在key时,不需要将key插入,直接让记录key值个数的count++即可
else
HashTable[hash_index].count++;
}
/**在hash表中查找最大的count数,并返回对应值**/
int hash_find()
{
hash_node p; //p的count记录最大的count值,p的data用于返回找到的值
p = HashTable[0];
int i;
for(i=1;i<HASHSIZE;i++)
{
if(HashTable[i].count > p.count )
p = HashTable[i];
}
return p.data;
}方法三:记录两个值--依据题目特殊性的特殊解法
设两个值:candidate和ctimes:其中candidate用来存储遍历数组过程中的某个数;ctimes用于记录当前数出现的次数,初始值为11)如果下一个数与当前candidate数相同,则ctime++
2)如果下一个数与当前candidate数不同,则ctimes--
3)当ctimes为0时,则candidate数换成下一个数,同时将ctimes置1
数组遍历完后,返回candidate数
时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1)
代码实现
/********************************
Author:tmw
date:2018-2-25
*********************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Remark2number_find_key(int array[],int array_length)
{
//初始化camdidate值为数组首元素
int candidate = array[0];
//初始化ctimes值为1
int ctimes = 1;
int i;
//遍历数组,并标记
for(i=1;i<array_length;i++)
{
//变更candidate的情况:candidate数换成下一个数,同时将ctimes置1
if(ctimes==0)
{
candidate = array[i];
ctimes = 1;
}
else
{
if( array[i] != candidate )
ctimes--;
else
ctimes++;
}
}
return candidate;
}值得一提的是,方法三这种特殊解法也同样适用于解决:数组中有一个数出现的次数是数组长度的一半,找出这个数 的问题
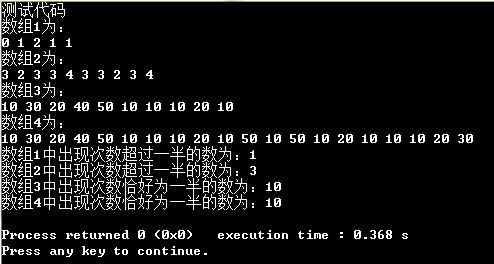
方法三测试代码和结果如下:
int main()
{
printf("测试代码\n");
int array1[5] = {0,1,2,1,1};
int array2[10] = {3,2,3,3,4,3,3,2,3,4};
int array3[10] = {10,30,20,40,50,10,10,10,20,10};
int array4[20] = {10,30,20,40,50,10,10,10,20,10,50,10,50,10,20,10,10,10,20,30};
int i;
printf("数组1为:\n");
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
printf("%d ",array1[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("数组2为:\n");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
printf("%d ",array2[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("数组3为:\n");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
printf("%d ",array3[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("数组4为:\n");
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
printf("%d ",array4[i]);
printf("\n");
int ans1 = Remark2number_find_key(array1,5);
int ans2 = Remark2number_find_key(array2,10);
int ans3 = Remark2number_find_key(array3,10);
int ans4 = Remark2number_find_key(array4,20);
printf("数组1中出现次数超过一半的数为:%d \n",ans1);
printf("数组2中出现次数超过一半的数为:%d \n",ans2);
printf("数组3中出现次数恰好为一半的数为:%d \n",ans3);
printf("数组4中出现次数恰好为一半的数为:%d \n",ans4);
return 0;
}
























 512
512

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








