一、双向队列Deque
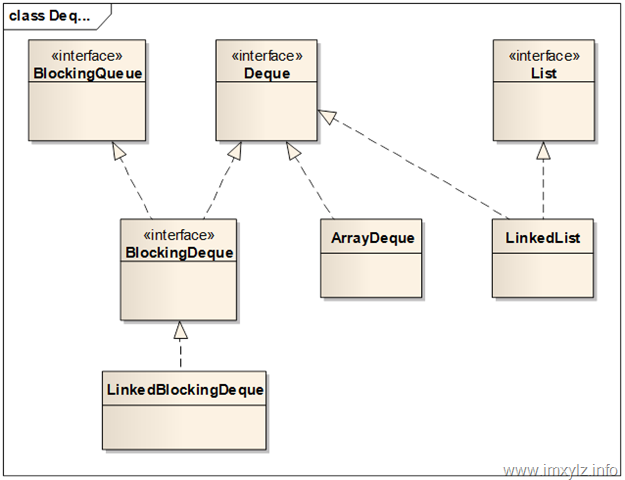
Queue除了前面介绍的实现外,还有一种双向的Queue实现Deque。这种队列允许在队列头和尾部进行入队出队操作,因此在功能上比Queue显然要更复杂。下图描述的是Deque的完整体系图。需要说明的是LinkedList也已经加入了Deque的一部分(LinkedList是从jdk1.2 开始就存在数据结构)。
Deque在Queue的基础上增加了更多的操作方法。
从上图可以看到,Deque不仅具有FIFO的Queue实现,也有FILO的实现,也就是不仅可以实现队列,也可以实现一个堆栈。
同时在Deque的体系结构图中可以看到,实现一个Deque可以使用数组(ArrayDeque),同时也可以使用链表(LinkedList),还可以同实现一个支持阻塞的线程安全版本队列LinkedBlockingDeque。
1、ArrayDeque实现Deque
 22
22
对于数组实现的Deque来说,数据结构上比较简单,只需要一个存储数据的数组以及头尾两个索引即可。由于数组是固定长度的,所以很容易就得到数组的头和尾,那么对于数组的操作只需要移动头和尾的索引即可。
特别说明的是ArrayDeque并不是一个固定大小的队列,每次队列满了以后就将队列容量扩大一倍(doubleCapacity()),因此加入一个元素总是能成功,而且也不会抛出一个异常。也就是说ArrayDeque是一个没有容量限制的队列。
同样继续性能的考虑,使用System.arraycopy复制一个数组比循环设置要高效得多。
1.1、ArrayDeque的源码解析
//数组双端队列ArrayDeque的源码解析
public class ArrayDeque<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable{
/**
* 存放队列元素的数组,数组的长度为“2的指数”
*/
private transient E[] elements;
/**
*队列的头部索引位置,(被remove()或pop()操作的位置),当为空队列时,首尾index相同
*/
private transient int head;
/**
* 队列的尾部索引位置,(被 addLast(E), add(E), 或 push(E)操作的位置).
*/
private transient int tail;
/**
* 队列的最小容量(大小必须为“2的指数”)
*/
private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
// ****** Array allocation and resizing utilities ******
/**
* 根据所给的数组长度,得到一个比该长度大的最小的2^p的真实长度,并建立真实长度的空数组
*/
private void allocateElements(int numElements) {
int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
initialCapacity = numElements;
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
initialCapacity++;
if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
}
elements = (E[]) new Object[initialCapacity];
}
/**
* 当队列首尾指向同一个引用时,扩充队列的容量为原来的两倍,并对元素重新定位到新数组中
*/
private void doubleCapacity() {
assert head == tail;
int p = head;
int n = elements.length;
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
int newCapacity = n << 1;
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
elements = (E[])a;
head = 0;
tail = n;
}
/**
* 拷贝队列中的元素到新数组中
*/
private <T> T[] copyElements(T[] a) {
if (head < tail) {
System.arraycopy(elements, head, a, 0, size());
} else if (head > tail) {
int headPortionLen = elements.length - head;
System.arraycopy(elements, head, a, 0, headPortionLen);
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, headPortionLen, tail);
}
return a;
}
/**
* 默认构造队列,初始化一个长度为16的数组
*/
public ArrayDeque() {
elements = (E[]) new Object[16];
}
/**
* 指定元素个数的构造方法
*/
public ArrayDeque(int numElements) {
allocateElements(numElements);
}
/**
* 用一个集合作为参数的构造方法
*/
public ArrayDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
allocateElements(c.size());
addAll(c);
}
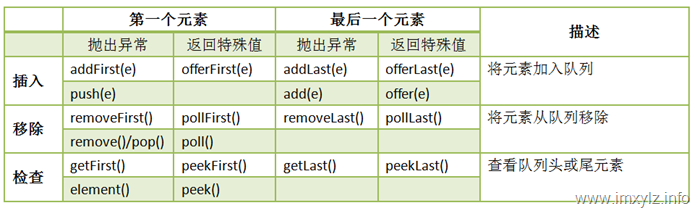
//插入和删除的方法主要是: addFirst(),addLast(), pollFirst(), pollLast()。
//其他的方法依赖于这些实现。
/**
* 在双端队列的前端插入元素,元素为null抛异常
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
if (head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}
/**
*在双端队列的末端插入元素,元素为null抛异常
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[tail] = e;
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}
/**
* 在前端插入,调用addFirst实现,返回boolean类型
*/
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
/**
* 在末端插入,调用addLast实现,返回boolean类型
*/
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* 删除前端,调用pollFirst实现
*/
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
/**
* 删除后端,调用pollLast实现
*/
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
//前端出对(删除前端)
public E pollFirst() {
int h = head;
E result = elements[h]; // Element is null if deque empty
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}
//后端出对(删除后端)
public E pollLast() {
int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
E result = elements[t];
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[t] = null;
tail = t;
return result;
}
/**
* 得到前端头元素
*/
public E getFirst() {
E x = elements[head];
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
/**
* 得到末端尾元素
*/
public E getLast() {
E x = elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E peekFirst() {
return elements[head]; // elements[head] is null if deque empty
}
public E peekLast() {
return elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
}
/**
* 移除此双端队列中第一次出现的指定元素(当从头部到尾部遍历双端队列时)。
*/
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
int mask = elements.length - 1;
int i = head;
E x;
while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) {
if (o.equals(x)) {
delete(i);
return true;
}
i = (i + 1) & mask;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 移除此双端队列中最后一次出现的指定元素(当从头部到尾部遍历双端队列时)。
*/
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
int mask = elements.length - 1;
int i = (tail - 1) & mask;
E x;
while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) {
if (o.equals(x)) {
delete(i);
return true;
}
i = (i - 1) & mask;
}
return false;
}
// *** 队列方法(Queue methods) ***
/**
* add方法,添加到队列末端
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* 同上
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
/**
* remove元素,删除队列前端
*/
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* 弹出前端(出对,删除前端)
*/
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
// *** 栈 方法(Stack methods) ***
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
private void checkInvariants() { …… }
private boolean delete(int i) { …… }
// *** 集合方法(Collection Methods) ***
……
// *** Object methods ***
……
}
2、LinkedList实现Deque
对于LinkedList本身而言,数据结构就更简单了,除了一个size用来记录大小外,只有head一个元素Entry。对比Map和Queue的其它数据结构可以看到这里的Entry有两个引用,是双向的队列。
在示意图中,LinkedList总是有一个“傀儡”节点,用来描述队列“头部”,但是并不表示头部元素,它是一个执行null的空节点。
队列一开始只有head一个空元素,然后从尾部加入E1(add/addLast),head和E1之间建立双向链接。然后继续从尾部加入E2,E2就在head和E1之间建立双向链接。最后从队列的头部加入E3(push/addFirst),于是E3就在E1和head之间链接双向链接。
双向链表的数据结构比较简单,操作起来也比较容易,从事从“傀儡”节点开始,“傀儡”节点的下一个元素就是队列的头部,前一个元素是队列的尾部,换句话说,“傀儡”节点在头部和尾部之间建立了一个通道,是整个队列形成一个循环,这样就可以从任意一个节点的任意一个方向能遍历完整的队列。
同样LinkedList也是一个没有容量限制的队列,因此入队列(不管是从头部还是尾部)总能成功。
3、小结
上面描述的ArrayDeque和LinkedList是两种不同方式的实现,通常在遍历和节省内存上ArrayDeque更高效(索引更快,另外不需要Entry对象),但是在队列扩容下LinkedList更灵活,因为不需要复制原始的队列,某些情况下可能更高效。
同样需要注意的上述两个实现都不是线程安全的,因此只适合在单线程环境下使用,下面章节要介绍的LinkedBlockingDeque就是线程安全的可阻塞的Deque。事实上也应该是功能最强大的Queue实现,当然了实现起来也许会复杂一点。
二、双向并发阻塞队列 LinkedBlockingDeque
1、LinkedBlockingDeque数据结构
双向并发阻塞队列。所谓双向是指可以从队列的头和尾同时操作,并发只是线程安全的实现,阻塞允许在入队出队不满足条件时挂起线程,这里说的队列是指支持FIFO/FILO实现的链表。
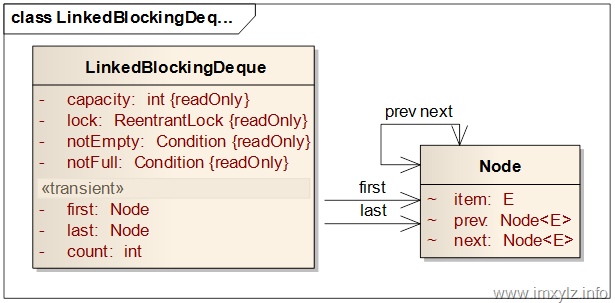
首先看下LinkedBlockingDeque的数据结构。通常情况下从数据结构上就能看出这种实现的优缺点,这样就知道如何更好的使用工具了。
从数据结构和功能需求上可以得到以下结论:
- 要想支持阻塞功能,队列的容量一定是固定的,否则无法在入队的时候挂起线程。也就是capacity是final类型的。
- 既然是双向链表,每一个结点就需要前后两个引用,这样才能将所有元素串联起来,支持双向遍历。也即需要prev/next两个引用。
- 双向链表需要头尾同时操作,所以需要first/last两个节点,当然可以参考LinkedList那样采用一个节点的双向来完成,那样实现起来就稍微麻烦点。
- 既然要支持阻塞功能,就需要锁和条件变量来挂起线程。这里使用一个锁两个条件变量来完成此功能。
2、LinkedBlockingDeque源码分析
public class LinkedBlockingDeque<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingDeque<E>, java.io.Serializable {
/** 包含前驱和后继节点的双向链式结构 */
static final class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> prev;
Node<E> next;
Node(E x, Node<E> p, Node<E> n) {
item = x;
prev = p;
next = n;
}
}
/** 头节点 */
private transient Node<E> first;
/** 尾节点 */
private transient Node<E> last;
/** 元素个数*/
private transient int count;
/** 队列容量 */
private final int capacity;
/** 锁 */
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/** notEmpty条件 */
private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
/** notFull条件 */
private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
/** 构造方法 */
public LinkedBlockingDeque() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public LinkedBlockingDeque(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public LinkedBlockingDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for (E e : c)
add(e);
}
/**
* 添加元素作为新的头节点
*/
private boolean linkFirst(E e) {
if (count >= capacity)
return false;
++count;
Node<E> f = first;
Node<E> x = new Node<E>(e, null, f);
first = x;
if (last == null)
last = x;
else
f.prev = x;
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
/**
* 添加尾元素
*/
private boolean linkLast(E e) {
if (count >= capacity)
return false;
++count;
Node<E> l = last;
Node<E> x = new Node<E>(e, l, null);
last = x;
if (first == null)
first = x;
else
l.next = x;
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
/**
* 返回并移除头节点
*/
private E unlinkFirst() {
Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
return null;
Node<E> n = f.next;
first = n;
if (n == null)
last = null;
else
n.prev = null;
--count;
notFull.signal();
return f.item;
}
/**
* 返回并移除尾节点
*/
private E unlinkLast() {
Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
return null;
Node<E> p = l.prev;
last = p;
if (p == null)
first = null;
else
p.next = null;
--count;
notFull.signal();
return l.item;
}
/**
* 移除节点x
*/
private void unlink(Node<E> x) {
Node<E> p = x.prev;
Node<E> n = x.next;
if (p == null) {//x是头的情况
if (n == null)
first = last = null;
else {
n.prev = null;
first = n;
}
} else if (n == null) {//x是尾的情况
p.next = null;
last = p;
} else {//x是中间的情况
p.next = n;
n.prev = p;
}
--count;
notFull.signalAll();
}
//--------------------------------- BlockingDeque 双端阻塞队列方法实现
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (!offerFirst(e))
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
public void addLast(E e) {
if (!offerLast(e))
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
lock.lock();
try {
return linkFirst(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
lock.lock();
try {
return linkLast(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void putFirst(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
lock.lock();
try {
while (!linkFirst(e))
notFull.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void putLast(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
lock.lock();
try {
while (!linkLast(e))
notFull.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean offerFirst(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
if (linkFirst(e))
return true;
if (nanos <= 0)
return false;
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean offerLast(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
if (linkLast(e))
return true;
if (nanos <= 0)
return false;
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E pollFirst() {
lock.lock();
try {
return unlinkFirst();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E pollLast() {
lock.lock();
try {
return unlinkLast();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E takeFirst() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
E x;
while ( (x = unlinkFirst()) == null)
notEmpty.await();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E takeLast() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
E x;
while ( (x = unlinkLast()) == null)
notEmpty.await();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E pollFirst(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
E x = unlinkFirst();
if (x != null)
return x;
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E pollLast(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
E x = unlinkLast();
if (x != null)
return x;
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E getFirst() {
E x = peekFirst();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E getLast() {
E x = peekLast();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E peekFirst() {
lock.lock();
try {
return (first == null) ? null : first.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E peekLast() {
lock.lock();
try {
return (last == null) ? null : last.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> p = last; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//---------------------------------- BlockingQueue阻塞队列 方法实现
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
putLast(e);
}
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return offerLast(e, timeout, unit);
}
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
return takeFirst();
}
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return pollFirst(timeout, unit);
}
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
//------------------------------------------- Stack 方法实现
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
//------------------------------------------- Collection 方法实现
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeFirstOccurrence(o);
}
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return count;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next)
if (o.equals(p.item))
return true;
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
boolean removeNode(Node<E> e) {
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (p == e) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
……
} 3、LinkedBlockingDeque的优缺点
有了上面的结论再来研究LinkedBlockingDeque的优缺点。
优点当然是功能足够强大,同时由于采用一个独占锁,因此实现起来也比较简单。所有对队列的操作都加锁就可以完成。同时独占锁也能够很好的支持双向阻塞的特性。
凡事有利必有弊。缺点就是由于独占锁,所以不能同时进行两个操作,这样性能上就大打折扣。从性能的角度讲LinkedBlockingDeque要比LinkedBlockingQueue要低很多,比CocurrentLinkedQueue就低更多了,这在高并发情况下就比较明显了。
前面分析足够多的Queue实现后,LinkedBlockingDeque的原理和实现就不值得一提了,无非是在独占锁下对一个链表的普通操作。
4、LinkedBlockingDeque的序列化、反序列化
有趣的是此类支持序列化,但是Node并不支持序列化,因此fist/last就不能序列化,那么如何完成序列化/反序列化过程呢?
清单4 LinkedBlockingDeque的序列化、反序列化
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
lock.lock();
try {
// Write out capacity and any hidden stuff
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next)
s.writeObject(p.item);
// Use trailing null as sentinel
s.writeObject(null);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
count = 0;
first = null;
last = null;
// Read in all elements and place in queue
for (;;) {
E item = (E)s.readObject();
if (item == null)
break;
add(item);
}
} 清单4 描述的是LinkedBlockingDeque序列化/反序列化的过程。序列化时将真正的元素写入输出流,最后还写入了一个null。读取的时候将所有对象列表读出来,如果读取到一个null就表示结束。这就是为什么写入的时候写入一个null的原因,因为没有将count写入流,所以就靠null来表示结束,省一个整数空间。
http://hi.baidu.com/yao1111yao/item/1a1346f65a50d9c8521c266d
集合框架 Queue篇(7)---LinkedBlockingDeque
http://hi.baidu.com/yao1111yao/item/b1649cff2cf60be91a111f6d
深入浅出 Java Concurrency (24): 并发容器 part 9 双向队列集合 Deque
http://www.blogjava.net/xylz/archive/2010/08/12/328587.html
深入浅出 Java Concurrency (25): 并发容器 part 10 双向并发阻塞队列 BlockingDeque
http://www.blogjava.net/xylz/archive/2010/08/18/329227.html























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








