在数据结构中,二叉树是树中我们见得最多的,二叉查找树可以加速我们查找的效率,那么输出一个二叉树也变得尤为重要了。
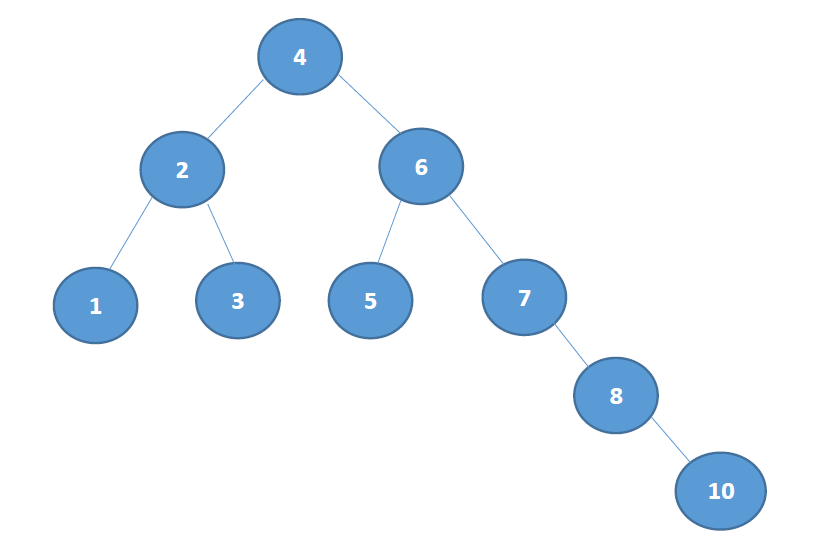
二叉树的遍历方法分为三种,分别为前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历。下图即为一个二叉树。
- 前序遍历:先遍历根结点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树。
结果为:4 2 1 3 6 5 7 8 10 - 中序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后遍历根结点,最后遍历右子树。
结果为:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 - 后序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后遍历根节点。
结果为:1 3 2 5 10 8 7 6 4
按照上面的规则,就可以很快地对一颗二叉树进行遍历,并且快速写出结果,下面我附上我使用递归的方法对二叉树实施三种遍历的Java代码。
public class Tree<AnyType extends Comparable<? super AnyType>>
{
private static class BinaryNode<AnyType>
{
BinaryNode(AnyType theElement)
{
this(theElement, null, null);
}
BinaryNode(AnyType theElement, BinaryNode<AnyType> lt, BinaryNode<AnyType> rt)
{
element = theElement;
left = lt;
right = rt;
}
AnyType element;
BinaryNode<AnyType> left;
BinaryNode<AnyType> right;
}
private BinaryNode<AnyType> root;
public void insert(AnyType x)
{
root = insert(x, root);
}
private BinaryNode<AnyType> insert(AnyType x, BinaryNode<AnyType> t)
{
if(t == null)
{
return new BinaryNode<>(x, null, null);
}
int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.element);
if(compareResult < 0)
{
t.left = insert(x, t.left);
}
else if(compareResult > 0)
{
t.right = insert(x, t.right);
}
else
{
;
}
return t;
}
/**
* 前序遍历
*/
public void preOrder(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node)
{
if (Node != null)
{
System.out.print(Node.element + " ");
preOrder(Node.left);
preOrder(Node.right);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*/
public void midOrder(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node)
{
if (Node != null)
{
midOrder(Node.left);
System.out.print(Node.element + " ");
midOrder(Node.right);
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历
*/
public void posOrder(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node)
{
if (Node != null)
{
posOrder(Node.left);
posOrder(Node.right);
System.out.print(Node.element + " ");
}
}
public static void main( String[] args )
{
int[] input = {4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10};
Tree<Integer> tree = new Tree<>();
for(int i = 0; i < input.length; i++)
{
tree.insert(input[i]);
}
System.out.print( "前序遍历 :" );
tree.preOrder(tree.root);
System.out.print( "\n中序遍历 :" );
tree.midOrder(tree.root);
System.out.print( "\n后序遍历 :" );
tree.posOrder(tree.root);
}
}以上就完成了对二叉树的三种遍历,但是这只是递归方法的遍历,下次我再来用非递归的方法实现对二叉树的遍历。






















 1678
1678

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








