简介:
我们知道java内存中对象的分配 一般的粗略的分配是, 堆、栈上。在Java的创建每一个对象的时候,所以的实例变量都要在堆上分配。同时,也有一个栈帧的(Stack Frane)的创建,用于存储局部变量、操作栈、方法等信息。局部变量存放一些在编译期可知的各种基本的数据的类型(如:boolean byte char string long double) 对象引用等。
在构造器中传递引用和基本的数据的类型
1、构造器 传递的是 对象的引用
public class TestYingyong4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestYingyong4().test();
}
User user=new User();
String string = null;
private void test() {
new Thread(){
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
string=i+" 自己生成的数据";
user.username=string;
}
};
}.start();
/**
* 参数传递为一个对象的引用 ,引用指向的是堆上面的数据
*/
new Dispatcher4(user,"1").start();
new Dispatcher4(user,"2").start();
}
}
class Dispatcher4 extends Thread{
User user;
String string2;
public Dispatcher4(User user, String string2) {
this.user=user;
this.string2=string2;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
while (true) {
System.out.println(user.username+" "+string2);
try {
// 由于不是阻塞模式的 ,这样便于查看更新的值 (需要手动结束进程)
Thread.sleep(400);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class User{
public String username;
}
结果:
2、参数传递为一个基本类型 存在于栈上面
public class TestYingyong3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestYingyong3().test();
}
String string = null;
private void test() {
new Thread(){
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
string=i+"自己生成的数据";
}
};
}.start();
/**
* 参数传递为一个基本类型 存在于栈上面
*/
new Dispatcher3(string,"1").start();
new Dispatcher3(string,"2").start();
}
}
class Dispatcher3 extends Thread{
String string;
String string2;
public Dispatcher3(String arrayList, String string2) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.string=arrayList;
this.string2=string2;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
while (true) {
System.out.println(string+" "+string2);
try {
// 由于不是阻塞模式的 ,这样便于查看更新的值 (需要手动结束进程)
Thread.sleep(400);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
结果:
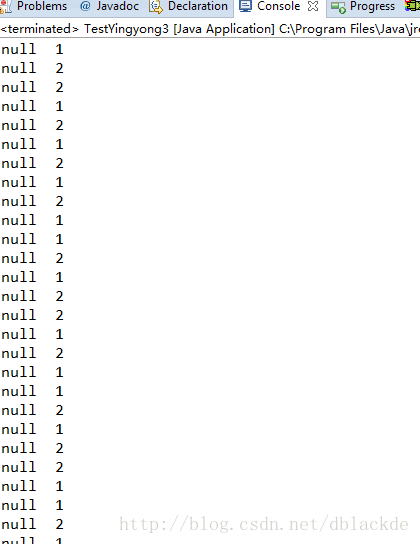
1、取的数据来自于user的引用,引用指向其堆上面,堆上面的数据发生了的变化,其引用对其读取,对其发生的变化是可见的。
2、读取的数据 直接在其栈上面。 TestYingyong3 中的string和 Dispatcher3中的string 都在各自的栈上面,数据发生变化,不会影响到各自。
ps: 上面的内容是我个人的YY, 自己感觉是这个样子,有什么东东,请指教呀...谢谢..
参考:
《深入理解Java虚拟机:JVM高级特性与最佳实践》























 7458
7458

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








