public class Solution {
/**
* @param grid a boolean 2D matrix
* @return an integer
*/
public int numIslands(boolean[][] grids) {
// Write your code here
if(grids.length==0){
return 0;
}
int [][]grid=new int[grids.length][grids[0].length];
for(int i=0;i<grids.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grids[0].length;j++){
if(grids[i][j]){
grid[i][j]=1;
}else{
grid[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
ArrayList<Point> list=new ArrayList<Point>();
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
Point p=new Point(grid[i][j], 0,1);
if(grid[i][j]==1){
if(list.isEmpty()){
p.where=++count;
list.add(p);
}else{
if(i>0){
Point temp=list.get(list.size()-grid[0].length);
if(temp.where>0){
p.where=temp.where;
}
}
if(j>0){
Point temp=list.get(list.size()-1);
if(temp.where>0){
if(p.where>0){
if(p.where>temp.where){
for(int k=0;k<list.size();k++){
if(list.get(k).where==p.where){
list.get(k).where=temp.where;
}
}
count--;
p.where=temp.where;
}else if(p.where<temp.where){
for(int k=0;k<list.size();k++){
if(list.get(k).where==temp.where){
list.get(k).where=p.where;
}
}
p.where=p.where;
count--;
}else{
p.where=temp.where;
}
}else{
p.where=temp.where;
}
}
}
if(p.where>0){
list.add(p);
// System.out.println("***************"+i+" "+j+" "+p.where);
}else{
p.where=++count;
// System.out.println("----------"+i+" "+j+" "+p.where);
list.add(p);
}
}
}else{
list.add(p);
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
class Point{
int value;//值
int where;//属于哪一个类0
int visited;//是否访问过
public Point(int value,int where,int visited){
this.value=value;
this.where=where;
this.visited=visited;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getWhere() {
return where;
}
public void setWhere(int where) {
this.where = where;
}
public int getVisited() {
return visited;
}
public void setVisited(int visited) {
this.visited = visited;
}
}










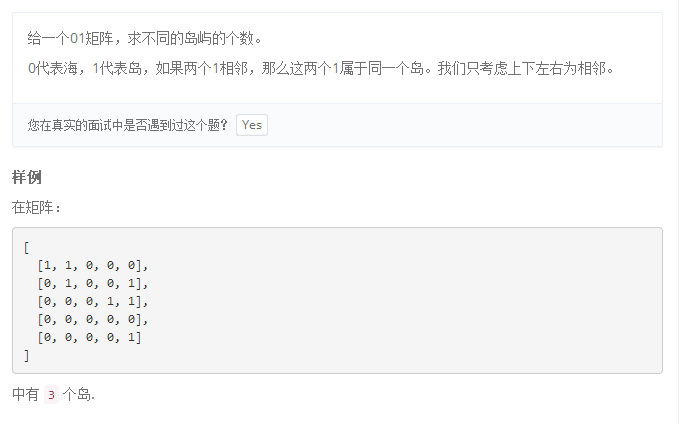
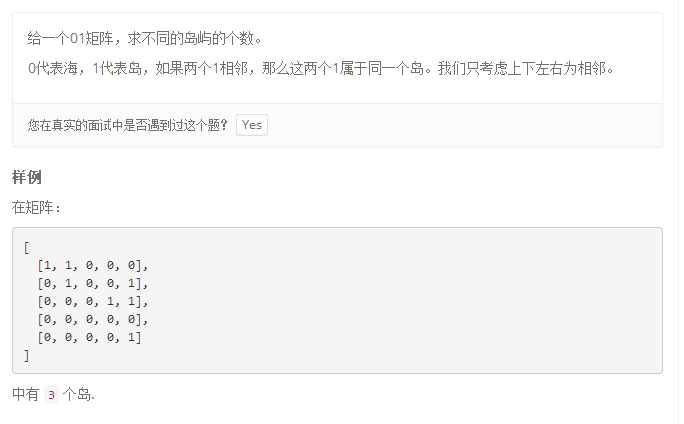















 607
607

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










