std::vector::push_back的实现原理
背景
- C++标准库的
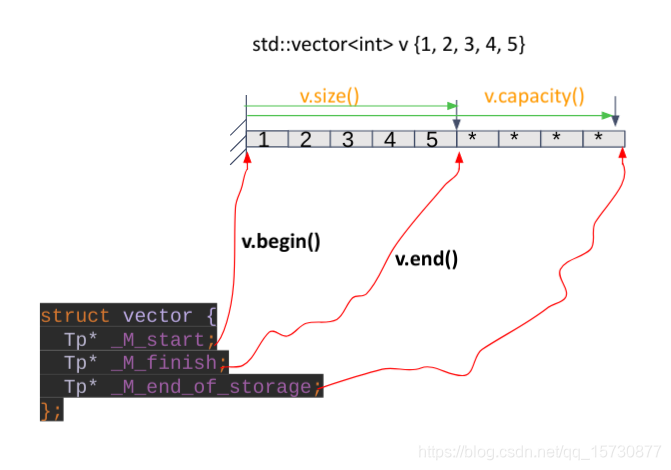
std::vector<Tp>容器的内存是连续存储的,这在某些应用中具有很大的优势,比如兼容C语言的已有操作,我们在vector中存储了n个POD类型数据,比如std::vector<double> vec(20),我想清空这些数据为0,可以用memset(vec.data(), 0, vec.size() * sizeof(vec[-1]))。对于其他容器,比如list就只能用 for loop 遍历并一一清除了。vector可以自动生长,隐藏了底层的内存分配和对象构造行为,这对程序开发者很友好,这里的自动生长不是在已有的内存后面继续分配内存(realloc),而是分配新空间-移动旧数据-构造对象-释放源空间这样的过程。 vector在尾部插入和删除元素的均摊时间复杂度为O(1)。vector的数据结构很简单,只需要3个指针即可,可以定义为
template <typename Tp>
class vector{
public:
// ...
protected:
Tp* M_start_;_M_start
Tp* _M_finish;
Tp* _M_end_of_storage;
}
vector的基本内存视图看起来是这样:
vector::push_back是如何实现的
- 今天我们看看std::vector::push_back(const Tp& val)的实现。
- 在开始之前,有几个重要的内存分配和对象构造方面的基础知识点需要说明下;
// 1. 非定位版本 operator new / delete
// 内存分配函数
void* operator new(std::size_t);
// 内存释放函数
void operator delete(void*);
// 2. 定位版本的 operator new delete.
// Default placement versions of operator new.
inline void* operator new(std::size_t, void* __p) { return __p; }
// Default placement versions of operator delete.
inline void operator delete (void*, void*) {}
// 3. 运算符
new / delete
- 上面这几个概念容易混淆。
3版本是将分配内存、指针转型和对象构造一起做完了;1版本只负责分配内存;2版本只负责在指定位置调用构造函数构造对象,神奇吧,还可在指定位置构造对象,以前的对象构造只有new完才知道对象地址。 - 之所以提供
1、 2版本,是将对象的空间分配和对象构造分开,在这标准库的容器实现中,提供了极大的灵活性,对效率有很大帮助。比如,我可以先分配一块原始的内存(1 版本 new),然后在该内存上构造对象(2 版本 new)。如果直接用C++new运算符(3 版本 new)的话,就没有这种灵活性。 - 我们定义一个用于测试的构造类型
Person。
class Person {
public:
Person() : age_(0), name_("anonymous"), is_male_(false) {}
Person(int age, std::string name, bool is_male)
: age_(age), name_(std::move(name)), is_male_(is_male) {}
// 拷贝构造函数
Person(constPerson &other) {
this->age_ = other.age_;
this->name_ = other.name_;
this->is_male_ = other.is_male_;
}
// 移动构造函数
Person(Person &&person) {
this->age_ = other.age_;
this->name_ = std::move(other.age_);
this->is_male_ = other.is_male_;
}
~Person() = default;
private:
int age_;
std::string name_;
bool is_male_;
};
- 我们调用如下的代码片段,
void main() {
std::vector<Person> v(2);
// 创建一个名叫星期五的18岁女孩.
person person(18, "Friday", false);
// 放入vec后面.
v.push_back(person);
}
- 期望将一个
Person对象push_back到vector<Person>对象v的后面。如果v后面的空间足够,则push_back直接在v后面构造对象(定位new),并将表征size的内部数据结构执行++操作即可完成,这种情况比较简单,这里不予考虑。我们假设在push_back调用之前std::vector<Person> v(2)的内存视图如下所示,可用空间已满,v.size() == v.capacity()此时push_back就要进行分配新空间-移动旧数据-构造对象-释放源空间这样操作才能完成push_back操作。

分配新空间
// 按照2倍扩容
int new_capacity = v.size() * 2;
// 调用 1版本的new;并将分配的内存转型为 Person*
Person* new_ptr = static_cast<Person*>(::operator new(new_capacity * sizeof(Person)));
- 此时空间配置情况如下图所示

- 这一步只是分配了内存空间,未做任何初始化操作,所以该空间的内存值都是未知的。
移动旧数据到新空间
// 调用标准库函数将旧数据拷贝到新空间,
#if 1
Person* end_ptr = std::uninitialized_copy(v.begin(), v.end(), new_ptr);
#else
// 这种写法是错误的,你知道为什么吗?
for(Person* iter = v.begin(); iter != v.end(); ++iter {
*new_ptr++ = * iter; // 调用 Person& operator(const Person& other)
}
#endif
-
这里虽然名字叫做
std::uninitialized_copy(...),但实际上会根据容器所存储的对象的特性,比如是否可移动,是否需要构造,来决定调用对象的拷贝构造函数或者是移动构造函数或者是memmove来提高效率,避免不必要的拷贝。 -
对于POD类型,即不需要构造的类型对象,会直接调用
memmove来移动内存。 -
对于可以移动构造
is_move_constructible的对象,会调用移动构造函数来构造 -
对于其他类型,会调用拷贝构造函数来拷贝对象。这是效率最低但也是最安全的操作。
-
这里
Person定义了移动构造函数,也就是说Person对象可移动,所以调用的是Person::Person(Person&&)版本。移动前后的内存对比如下:

构造待插入的对象
// 在end_ptr位置构造对象,调用定位new
::new(end_ptr) Person(18, "Friday", false);
this->_M_finish++; // this->size()增1
- 这就完成了一次
push_back操作。对了,还有旧空间需要释放,不然会导致内存泄露。
释放旧空间
auto b = std::move(a),std::move()会保证移后源a是可以正确析构的。- 我们要做的是对原来空间的所有对象一一析构,然后再进行一次空间释放,请注意这是两回事。我们看着这张图进行理解和操作。

// 1. 析构原来的对象
for(Person* iter = v.begin(); iter != v.end(); ++iter) {
iter->~Person();
}
// or 直接调用标准库 std::_Destroy(...) 函数。
std::_Destroy(v.begin(), v.end());
// 2. 释放旧空间
size_t num = v.size();
Person* base_ptr = &*v.begin();
::operator delete(base_ptr, num); // 调用 " 1. 非定位版本 operator delete "
重新设置 vector 数据成员的值
_M_start = new_ptr;
_M_finish = end_ptr;
_M_end_of_storage = new_ptr + new_capacity;
// 放入了一个新元素,所以要执行 ++ 操作。
++_M_finish;
- 至此,完成了
vector的一次push_back操作。
汇总为统一的代码
- 下面的实现中,内存分配使用的的标准库提供的
std::allocator<Tp>;跟上面演示代码片段的直接操作operator new/delete不同。
void push_back(const typename std::vector<Tp>::value_type &val) {
// case 1 : capacity 足够
if (this->size() < this->capacity()) {
std::_Construct(&*this->end(), val);
++this->_M_finish;
}
// case 2 : capacity 不够
else {
// 分配新空间
size_t len = this->size() == 0 ? 1 : this->size() * 2;
typename std::vector<Tp>::pointer new_start =
this->get_allocator().allocate(len);
// 移动旧数据到新空间
typename std::vector<Tp>::pointer new_finish =
std::uninitialized_copy(this->begin(), this->end(), new_start);
// 在新位置构造带插入元素
std::_Construct(new_finish, val);
++new_finish;
// 释放旧空间
std::_Destroy(this->begin(), this->end());
this->get_allocator().deallocate(this->data(), this->size());
// 重新设置 vector 数据成员的值
this->__M_start = new_start;
this->_M_finish = new_finish;
this->_M_end_of_storage = new_start + len;
}
}
总结
- 今天重点分析了
vector::push_back()的操作,希望读者能够对内存分配,对象构造,对象析构,内存释放的构成烂熟于心,并能够对操作细节有所掌握。 - 理解
std::uninitialized_copy的过程。 - 理解
std::move和移动构造函数在优化效率方面的作用。





 本文详细介绍了C++ std::vector::push_back的实现原理,包括内存分配、对象构造、空间移动和释放等步骤。在容量不足时,vector会进行2倍扩容,使用std::uninitialized_copy进行数据迁移,并调用适当构造函数构造新对象。文章还讨论了std::move和移动构造函数在效率优化中的作用,以及std::uninitialized_copy的智能处理。通过一个具体的Person类实例,展示了push_back操作的完整流程。
本文详细介绍了C++ std::vector::push_back的实现原理,包括内存分配、对象构造、空间移动和释放等步骤。在容量不足时,vector会进行2倍扩容,使用std::uninitialized_copy进行数据迁移,并调用适当构造函数构造新对象。文章还讨论了std::move和移动构造函数在效率优化中的作用,以及std::uninitialized_copy的智能处理。通过一个具体的Person类实例,展示了push_back操作的完整流程。
















 2238
2238

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








