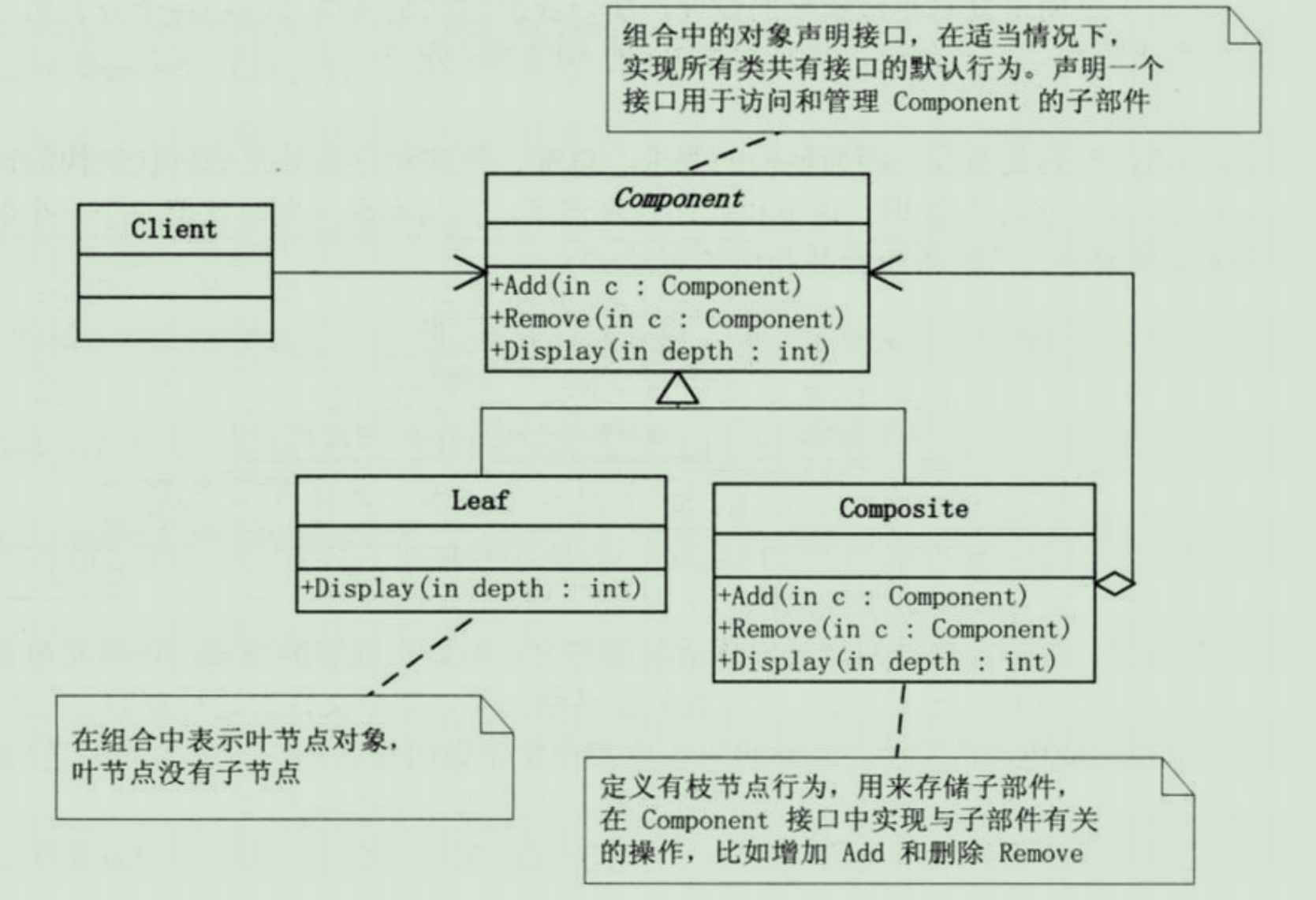
组合模式(Composite):将对象组合成树形结构以表示‘部分—整体’的层次结构。组合模式使得对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
UML图:
package com.thpin.repository.designpattern;
import com.thpin.repository.collection.util.ArrayList;
import com.thpin.repository.collection.util.List;
public class CompositeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component1 root = new Composite("root");
root.add(new Leaf("Leaf A"));
root.add(new Leaf("Leaf B"));
Component1 copositeA = new Composite("Composite A");
copositeA.add(new Leaf("Leaf AA"));
copositeA.add(new Leaf("Leaf AB"));
root.add(copositeA);
Component1 copositeB = new Composite("Composite B");
copositeB.add(new Leaf("Leaf BA"));
copositeB.add(new Leaf("Leaf BB"));
root.add(copositeB);
Component1 leafC = new Leaf("C");
root.add(leafC);
root.remove(leafC);
root.disply(1);
}
}
/*
* 组合接口
*/
abstract class Component1 {
private String name;
public Component1(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract void add(Component1 c);
public abstract void remove(Component1 c);
// 每个组件都拥有的能力
public abstract void disply(int depth);
// 生成填充符,无意义
protected String getBlank(int depth) {
String ret = "";
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {
ret += "-";
}
return ret;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
/*
* 叶子
*/
class Leaf extends Component1 {
public Leaf(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void add(Component1 c) {
System.out.println("Cannot add a leaf");
}
public void remove(Component1 c) {
System.out.println("Cannot remove from a leaf");
}
public void disply(int depth) {
System.out.println(getBlank(depth) + getName());
}
}
/*
* 组合
*/
class Composite extends Component1 {
private List<Component1> children = new ArrayList<>();
public Composite(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void add(Component1 c) {
children.add(c);
}
public void remove(Component1 c) {
children.remove(c);
}
public void disply(int depth) {
System.out.println(getBlank(depth) + getName());
for (Component1 c : children) {
c.disply(depth + 2);
}
}
}结果:
-root
---Leaf A
---Leaf B
---Composite A
-----Leaf AA
-----Leaf AB
---Composite B
-----Leaf BA
-----Leaf BB
需求中是体现部分与整体层次的结构时,希望用户可以忽略组合对象和单个对象的不同,统一的使用组合结构的所有对象时,就应该考虑使用组合模式
基本对象可以被组合成更复杂的组合对象,而这个组合对象又可以被组合,这样不断递归下去,客户端代码中,任何用到基本对象的地方都可以使用组合对象了。用户不用关心到底是处理一个叶节点还是处理一个组合组件,也就用不着为组合而写选择判断语句了。组合模式使得客户可以一致的使用组合对象和单个对象。
学过数据结构的人看到这个组合模式,会很自然的想到树,上面的代码其实就类似于树的实现,可能功能上略显简单些,但不可否认组合结构就是树,二叉树是特例,有自己的实现,这里的树是叶子结点不做区分的。display()相当于toString()可以对树结构进行遍历。






















 327
327

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








