【LeetCode】133. Clone Graph 克隆图(Medium)(JAVA)
题目地址: https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/
题目描述:
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity sake, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val = 1, the second node with val = 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
Adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
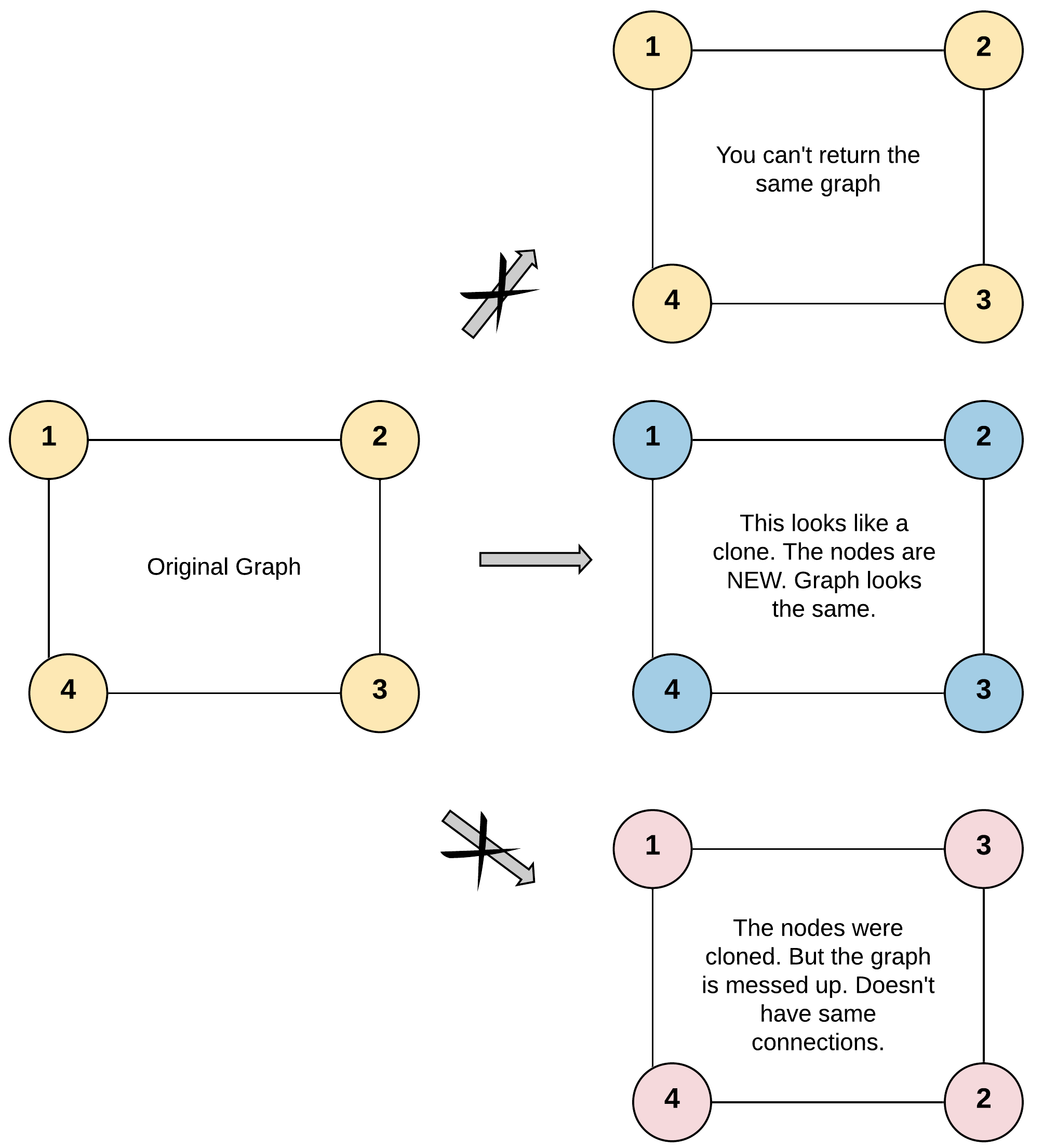
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
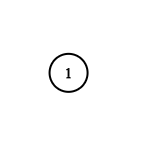
Input: adjList = [[]]
Output: [[]]
Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = []
Output: []
Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Example 4:
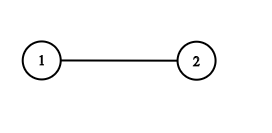
Input: adjList = [[2],[1]]
Output: [[2],[1]]
Constraints:
- 1 <= Node.val <= 100
- Node.val is unique for each node.
- Number of Nodes will not exceed 100.
- There is no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
题目大意
给你无向 连通 图中一个节点的引用,请你返回该图的 深拷贝(克隆)。
图中的每个节点都包含它的值 val(int) 和其邻居的列表(list[Node])。
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
测试用例格式:
简单起见,每个节点的值都和它的索引相同。例如,第一个节点值为 1(val = 1),第二个节点值为 2(val = 2),以此类推。该图在测试用例中使用邻接列表表示。
邻接列表 是用于表示有限图的无序列表的集合。每个列表都描述了图中节点的邻居集。
给定节点将始终是图中的第一个节点(值为 1)。你必须将 给定节点的拷贝 作为对克隆图的引用返回。
提示:
- 节点数不超过 100 。
- 每个节点值 Node.val 都是唯一的,1 <= Node.val <= 100。
- 无向图是一个简单图,这意味着图中没有重复的边,也没有自环。
- 由于图是无向的,如果节点 p 是节点 q 的邻居,那么节点 q 也必须是节点 p 的邻居。
- 图是连通图,你可以从给定节点访问到所有节点。
解题方法
- 这一题的主要问题是存在环,如果不解开环的话,必然会循环调用
- 为了解开环,因为题目里指明了 node.val 是独一无二的,用一个 map 来存储,key 值就是 node.val,在往下遍历前,先把当前元素存入 map 中
class Solution {
Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (node == null) return null;
if (map.get(node.val) != null) return map.get(node.val);
ArrayList<Node> neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
map.put(node.val, new Node(node.val, neighbors));
for (int i = 0; i < node.neighbors.size(); i++) {
neighbors.add(cloneGraph(node.neighbors.get(i)));
}
return map.get(node.val);
}
}
执行耗时:33 ms,击败了97.89% 的Java用户
内存消耗:38.7 MB,击败了95.85% 的Java用户






















 289
289











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








