以下是自己从别人那里借鉴过来的资料,如有雷同纯属巧合,谢谢
time.h(ctime)是c time library,定义了获取和操作日期和时间的函数。
1. 结构 view plain coptypedef long time_t;
time_t是长整型,表示的是距(1970年,1月1日08:00:00)的秒数,常常通过time函数获得。 copy- struct tm {
- int tm_sec; //秒 0-59(一般)
- int tm_min; //分 0-59
- int tm_hour; //小时0-23
- int tm_mday;//day 1-31
- int tm_mon; //月0-11
- int tm_year; //<span style="font-family:verdana,arial,helvetica,sans-serif"> 距 1900 的年数 如2013-1900 = 113</span>
- int tm_wday; //星期 0-6
- int tm_yday; //距1月1号天数,0-365
- int tm_isdst;
2.函数
[cpp] view plain copy
- time_t time ( time_t * timer );//获取当前时间
- time_t mktime ( struct tm * timeptr );//将struct tm转换为time_t
- struct tm * localtime ( const time_t * timer ); //将time_t转换为struct tm
- size_t strftime ( char * ptr, size_t maxsize, const char * format,
- const struct tm * timeptr ); //将struct tm转换为特定格式的字符串输出
- char *strptime(const char *buf,const char *format,struct tm *timeptr); //将format形式的时间字符串转换为struct tm
3.常用
[cpp] view plain copy
- #include <time.h>
- time_t now;
- now = time(NULL);//获取当前时间
- struct tm *timeinfo;
- timeinfo = localtime(&now);//转换为tm
- time_t seconds;
- seconds = mktime(timeinfo);//转换为time_t
[cpp] view plain copy
- time_t now = time(NULL);
- struct tm timeinfo = *localtime(&now);
- char buf[40];
- strftime(buf, sizeof(buf), "%Y%m%d%H%M%S", &timeinfo);
- cout << buf << endl;//20130207142133
- strptime("20130207112305", "%Y%m%d%H%M%S", &timeinfo);
- cout << timeinfo.tm_sec << endl;//5
-
- 4.获取当前时间的ms值
- #include <time.h>
- #include <sys/time.h>
- struct timeval tv;
- gettimeofday (&tv, NULL);
- uint64_t mseconds=tv.tv_sec * 1000 + tv.tv_usec / 1000;
timeval用于指定时间值,结构如下
[cpp] view plain copy
- timeval{
- time_t tv_sec; //秒 [long int]
- suseconds_t tv_usec; //微秒 [long int]
- };
常用于计算一个方法的响应时间。
字符拼接的方法:
1、多个字串拼接时用+操作符
1)
代码:
如果不加红色部分的代码,则需要采用_sntprintf代替sntprintf。
[cpp] view plain copy
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);"><span style="color:#FF0000;">#if _MSC_VER
- #define snprintf _snprintf
- #endif</span></span>
- using namespace std;
- string intToString(int v)
- {
- char buf[32] = {0};
- snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%u", v);
- string str = buf;
- return str;
- }
- int main()
- {
- string data;
- int myid=7;
- string data1=intToString(myid) ;
- string data2;
- data = "{\"status\":200, \"id\":\"" +intToString(myid) + "\"}";
- //为实现字符的相加而实现拼接,必须#include string,否则string的运算符操作无法使用。不包含该头文件下,string是可以定义使用的。这是运算操作上面不行。
- cout<<data.c_str()<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
2)引申使用str += "a", str =str+ "a" 效率差距:
str =str+ "a"加的运算产生的是一个新的对象,再把结果返回,而str += "a" 涉及到的应该是对象的引用,操作之后直接返回引用,避免了产生新的对象。因此,两者的性能有一定的差距。
[cpp] view plain copy
- int main()
- {
- static int num = 1000000;
- time_t timeBegin, timeEnd;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str = "";
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- // str = ""; //多一条,时间花费一些
- str =str + "a";
- }
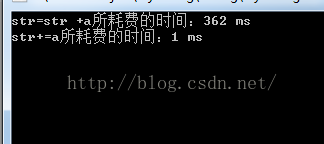
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"str=str +a所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- //num = 100W ,使用str += "a"表达, 花费18ms
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str1 = "";
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- str1 += "a";
- }
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"str+=a所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
2、使用append。
[cpp] view plain copy
- string s1 = "Hello ";
- string s2 = "World! ";
- string s3 = " China";
- string s4;
- s4.append(s1);
- cout<<s4.c_str()<<endl;
- s4.append(s2);
- cout<<s4.c_str()<<endl;
- s4.append(s3);
- cout<<s4.c_str()<<endl;
[cpp] view plain copy
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <time.h>
- using namespace std;
- //获得当前的系统时间,返回一个long类型的数据
- int main()
- {
- static int num = 100000000;//这里的时间是上面的100倍
- time_t timeBegin, timeEnd;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str1 = "";
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- str1 += "a";
- }
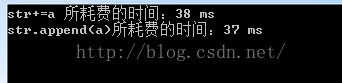
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"str+=a 所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str2 = "";
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- str2.append("a");
- }
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"str.append(a)所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
总体运行效率差不多:
3、stringstream
结合这两种方法与上述方法进行对比:
[cpp] view plain copy
- #include <iostream>
- #include <map>
- #include <string>
- #include <time.h>
- #include <sstream>
- using namespace std;
- //获得当前的系统时间,返回一个long类型的数据
- int main()
- {
- static int num = 100000000;
- time_t timeBegin, timeEnd;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str1 = "";
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- str1 += "a";
- }
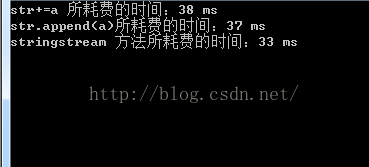
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"str+=a 所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str2 = "";
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- str2.append("a");
- }
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"str.append(a)所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str3 = "";
- stringstream ss;
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- ss<<"a";
- }
- str3=ss.str();
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"stringstream 方法所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
运行结果如下:可知stringstream方法是最快的!(这里的循环次数和上面是一样,对比运行时间也是可以看出)
4、sprintf进行字符的拼接
代码:
[cpp] view plain copy
- #include <iostream>
- #include <map>
- #include <string>
- #include <time.h>
- #include <sstream>
- using namespace std;
- //获得当前的系统时间,返回一个long类型的数据
- static int num = 100000000;
- int main()
- {
- time_t timeBegin, timeEnd;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str1 = "";
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- str1 += "a";
- }
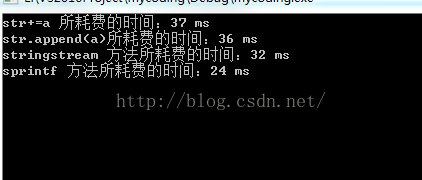
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"str+=a 所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str2 = "";
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- str2.append("a");
- }
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"str.append(a)所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string str3 = "";
- stringstream ss;
- for(int i =0; i<num; i++)
- {
- ss<<"a";
- }
- str3=ss.str();
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"stringstream 方法所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- timeBegin = time(NULL);
- string s4 = "";
- //char tmp[5];//="abc";
- char* cp = new char [num];
- char *tt=cp;
- char *t1="a";
- size_t strLength=sizeof(t1);
- for(int i=0; i<num; i++)
- {
- sprintf(cp,"%s",t1 );//t1所处的位置,必须是变量,不能是常理,如“a”这样的形式是不行的。
- //cout<<tt<<endl;
- cp++;
- }
- s4 = cp;
- timeEnd = time(NULL);
- cout<<"sprintf 方法所耗费的时间:"<<timeEnd - timeBegin<<" ms"<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
从中可以知道,sprintf是目前这四者速度最快的。其次分别是stringstream、str.append和str+=a方法。
注意,sprintf是不安全的,该函数无法检查目的缓存区是否溢出,现在一般采用snprint对其进行替代使用。类似的函数还有gets,strcat和strcpy,建议分别用fgets,strncat和strncpy进行替代使用。





















 388
388

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








