Chessboard Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 15832 Accepted: 4911
Description
Alice and Bob often play games on chessboard. One day, Alice draws a board with size M * N. She wants Bob to use a lot of cards with size 1 * 2 to cover the board. However, she thinks it too easy to bob, so she makes some holes on the board (as shown in the figure below).
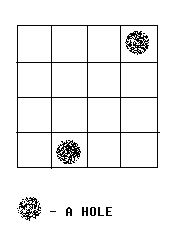
We call a grid, which doesn’t contain a hole, a normal grid. Bob has to follow the rules below:
Any normal grid should be covered with exactly one card.
One card should cover exactly 2 normal adjacent grids.
Some examples are given in the figures below:
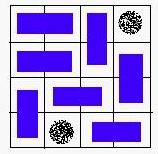
A VALID solution.
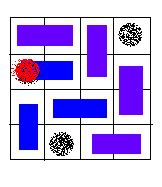
An invalid solution, because the hole of red color is covered with a card.
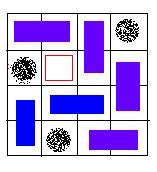
An invalid solution, because there exists a grid, which is not covered.
Your task is to help Bob to decide whether or not the chessboard can be covered according to the rules above.
Input
There are 3 integers in the first line: m, n, k (0 < m, n <= 32, 0 <= K < m * n), the number of rows, column and holes. In the next k lines, there is a pair of integers (x, y) in each line, which represents a hole in the y-th row, the x-th column.
Output
If the board can be covered, output “YES”. Otherwise, output “NO”.
Sample Input
4 3 2
2 1
3 3
Sample Output
YES
Hint
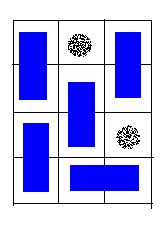
A possible solution for the sample input.
题解:
说一下我的做法(很扯):我们把棋盘染色(对,就是染色),按照对角线染黑白把棋盘转化成如图所示的情况,这样就把棋盘变成了二分图。很容易证明每块砖都是盖住一黑一白两个点,这样的话我们在读入的时候把黑色点附近的能盖住的白色点记为连通,用匈牙利算法跑一遍,如果最大覆盖的砖块数量*2恰好等于棋盘格子数减去hole的数量那么输出yes,反之则是no
include
include
include
include
define maxn 40
using namespace std;
bool g[maxn*maxn][maxn*maxn],state[maxn*maxn],hole[maxn][maxn];
int result[maxn*maxn];
int m,n,s,v,cnt=0,k;
bool find(int k1)
{
int x1=k1/m+1;
int y1=k1%m;
if(y1==0){
y1=m;
x1–;
}
if(y1>1)
{
int k2=k1-1;
if(!state[k2]&&g[k1][k2])
{
state[k2]=1;
if(result[k2]==0||find(result[k2]))
{
result[k2]=k1;
return true;
}
}
}
if(y1<m)
{
int k2=k1+1;
if(!state[k2]&&g[k1][k2])
{
state[k2]=1;
if(result[k2]==0||find(result[k2]))
{
result[k2]=k1;
return true;
}
}
}
if(x1>1)
{
int k2=k1-m;
if(!state[k2]&&g[k1][k2])
{
state[k2]=1;
if(result[k2]==0||find(result[k2]))
{
result[k2]=k1;
return true;
}
}
}
if(x1<n)
{
int k2=k1+m;
if(!state[k2]&&g[k1][k2])
{
state[k2]=1;
if(result[k2]==0||find(result[k2]))
{
result[k2]=k1;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf(“%d %d %d”,&n,&m,&k))
{
cnt=0;
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
memset(hole,0,sizeof(hole));
memset(state,0,sizeof(state));
memset(result,0,sizeof(result));
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
int a,b;
scanf(“%d%d”,&a,&b);
hole[b][a]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
if(hole[i][j])continue;
int k1=(i-1)*m+j;
if((i+j)%2==0)
{
if(!hole[i-1][j]&&i>1)
{
int k2=(i-2)*m+j;
g[k1][k2]=1;
}
if(!hole[i][j-1]&&j>1)
{
int k2=(i-1)*m+j-1;
g[k1][k2]=1;
}
if(!hole[i+1][j]&&i<n)
{
int k2=i*m+j;
g[k1][k2]=1;
}
if(!hole[i][j+1]&&j<m)
{
int k2=(i-1)*m+j+1;
g[k1][k2]=1;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
memset(state,0,sizeof(state));
if(hole[i][j])continue;
if(find((i-1)*m+j))cnt+=2;
}
if(m*n-cnt==k)cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
//uva1395 uva1151


























 195
195

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








