关于设计模式
设计模式是起源于建筑学, 某些情况下理论与实践的结合才是最好的, 从实践中不断地总结然后形成一个知识体系,为我们后面学习的人提供了很好的思路和解决方案, 同时我们也可以少走很多弯路,我们下面就来看常用设计模式中的一种--------中介者设计模式, 这只是学习过程中的一个记录,欢迎大神指点微笑
一、什么是中介者模式
中介者模式是一种行为设计模式,它允许我们公开一个统一的接口,系统中的不同部分可以通过该接口进行通信。
二、中介者模式的基本实现
/*Mediator模式的简单实现,暴露了publish()和subscribe()来实现*/
var mediator = (function () {
//存储可被广播或监听的事件
var topics = {};
//订阅一个topic, 提供一个回调函数,一旦topic被广播就执行回调函数
var subscribe = function (topic, fn) {
if(!topics[topic]){
topics[topic] = [];
} else {
topics[topic].push({context: this, callback: fn});
}
return this;
};
//发布/广播事件到程序的剩余部分
var publish = function(topic) {
var args;
if(!topics[topic]){
return false;
}
args = Array.prototype.slice.call = function(arguments, 1);
for (var i=0; l = topics[topic].length; i < l; i++) {
var subscription = topics[topic][i];
subscription.callback.apply(subscription.context, args);
}
return this;
}
return {
Publish: publish;
Subscribe: subscribe;
installTo: function (obj){
obj.subscribe = subscribe;
obj.publish = publish;
}
};
})();三、中介者模式的高级实现
*一个Mediator的topic注册实例*/
//通过生成对象实例,之后我们可以和容易的更新订阅者,而不需要注销并重新注册它们。订阅者可以写成构造函数,该函数接收三个参数:一个可被调用的函数fn, 一个options对象和一个context(上下文)
//将context上下文传递给订阅者,默认上下文是windows对象
(function (root){
function guidGenerator(){/*...*/}
//订阅者构造函数
function Subscriber(fn, options, context){
if(!this instanceof Subscriber){
return new Subscriber(fn, options, context);
} else {
//guidGenerator() 是一个函数,用于为订阅者生成GUID, 以便之后很方便的引用它们
//为了简洁,跳过具体实现
this.id = guidGenerator();
this.fn = fn;
this.options = options;
this.context = context;
this.topic = null;
}
}
})(window);//这里传递任何内容, 在此把window对象附加到了Mediator对象上面, 也可以传递给其他对象
//Mediator中的topic 持有了一组回调函数和子topic列表,一旦Mediator.Publish方法在Mediator实例杉被调用时,这些回调函数就会被触发。它还包含用于操作数据列表的方法
//模拟Topic
//javascript允许我们使用Function对象作为原型的结合与新对象和构造函数一起调用
function Topic (namespace) {
if(!this instanceof Topic){
return new Topic(namespace);
} else {
this.namespace = namespace || "";
this._callback = [];
this._topics = [];
this.stopped = false;
}
}
//定义topic 的prototype原型, 包括添加订阅者和获取订阅者的方式
Topic.prototype = {
//添加订阅者
AddSubscriber: function (fn, options, context) {
var callback = new Subscriber(fn, options, context);
this.callbacks.push(callback);
callback.topic = this;
return callback;
},
...
}
//StopPropagation() 调用进一步的回调函数
StopPropagation: function () {
this.stopped = true;
},
//获取现有的订阅者
GetSubscriber: function (identifier) {
for(var x = 0, y=this._callbacks.length; x < y; x++){
if(this._callbacks[x].id == identifier || this.callbacks[x].fn == identifier){
return this._callbacks[x];
}
}
for(var z in this._topics){
if(this._topics.hasOwnProperty(z)){
var sub = this._topics[z].GetSubscriber(identifier);
if(sub !== undefined){
return sub;
}
}
}
},
//根据需要对topic 进行不的操作
//添加新的topic
AddTopic: function (topic) {
this._topics[topic] = new Topic((this.namespace ? this.namespace + ":" : "") + topic);
},
//检查现有的topic
HasTopic: function (topic) {
return this._topics.hasOwnProperty(topic);
},
//获取topic
returnTopic: function (topic) {
return this._topics[topic];
}
//如果不在需要订阅者,可以显式的删除它们
RemoveSubscrieber: function (identifier) {
if(!identifier){
this._callbacks = [];
for(var z in this._topics){
if(this._topics.hasOwnProperty(z)){
this._topics[z].RemoveSubscrieber(identifier);
}
}
}
for(var y = 0; x = this._callbacks.length; y < x; y++){
if(this._callbacks[y].fn == identifier || this._callbacks[y].id == identifier){
this._callbacks[y].topic == null;
this._callbacks.splice(y, 1);
x--; y--;
}
}
},
//通过子Topic 递归向订阅者发布(Publish)任意参数
Publish: function (data){
for(var y = 0; x =this._callbacks.length; y < x; y++){
var callback = this._callbacks[y], l;
callback.fn.apply(callback.context, data);
l = this._callbacks.length;
if(l < x){
y--;
x = l;
}
}
for(var x in this._topics){
if(!this.stopped){
if(this._topics.hasOwnProperty(x)){
this._topics[x].Publish(data);
}
}
}
this.stopped = false;
};
//事件在topic上的注册和移除
function Mediator(){
if(!this instanceof Mediator){
return new Mediator();
} else {
this._topics = new topic("");
}
};
//GetTopic根据命名空间返回相应的主题实例
//让Mediator 支持用于inbox:messages: new: read
Mediator.prototype = {
GetTopic: function (namespace){
var topic = this._topics;
//
namespaceHierarchy = namespace.split(":");
if(namespace == ""){
return topic;
}
if(namespaceHierarchy.length > 0){
for(var i = 0; j = namespaceHierarchy.length; i < j; i++){
if(!topic.HasTopic(namespaceHierarchy[i])){
topic.AddTopic(namespaceHierarchy[i]);
}
topic = topic.ReturnTopic(namespaceHierarchy[i]);
}
}
return topic;
}
},
//如果Mediator.Subscribe不存在,则创建一个
Subscribe: function (topicName, fn, options, context) {
var options = options || {},
context = context || {},
topic = this.GetTopic(topicName),
sub = topic.AddSubscriber(fn, options, context);
return sub;
}
},
//通过给定的订阅者ID/命名函数和topic命名空间返回一个订阅者
GetSubscriber: function(identifier, topic){
return this.GetTopic(topic, "").GetSubscriber(identifier);
},
//通过给定的订阅者ID或命名函数,从给定的命名空间递归删除一个订阅者
RemoveSubscrieber: function ( topicName,identifier) {
this.GetTopic(topicName).RemoveSubscrieber(identifier);
},
//Topic向下递归调用
Mediator.Publish("inbox:messages:new", args);
Publish: function(topicName) {
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
topic = this.GetTopic(topicName);
args.push(topicName);
this.GetTopic(topicName).Publish(args);
};
//将Mediator作为一个对象附加到root
root.Mediator = Mediator;
Mediator.topic = topic;
Mediator.Subscriber = Subscriber;四、中介者模式的典型应用—机场交通控制系统
机场控制塔(中介者)处理飞机的起飞和降落,因为所有通信(监听到或发出的通知)都是从飞机到控制塔,而不是从飞机和飞机直接互相通信的。
Mediator Pattern
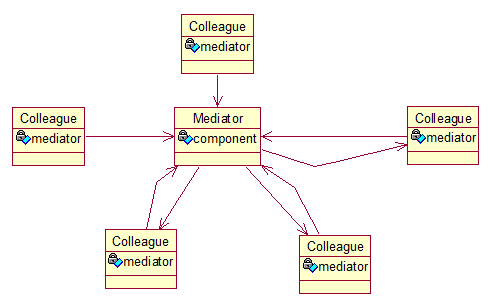
五、中介者模式的优点和缺点
- 优点:它能够将系统中的对象或组件之间通信渠道由多对多减少到多对一,由于它的松耦合,所以添加发布者或者订阅者也变得很容易; 即简化了对象之间的交互,减少了子类生成。
- 缺点:在具体中介者类中包含同事之间的交互细节,可能会导致具体中介者类非常复杂,是的系统难以维护。
























 617
617

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








