本篇文章参考自AngularJS权威教程。
1.简介
事件是解耦的好工具,Angular应用提供了很好的事件响应机制,让我们能够在应用中嵌套的各组件之间进行通信。
2.事件传播
由于作用域是有层次的,所以我们可以在作用域链上传递事件,也正因为此,各作用域接收事件是有次序的。Angular提供了两个方法, $emit()和$broadcast方法,分别能够向上和向下传播事件。注意,$emit()方法我们可以终止其传播,$broadcast()方法则不能,不过能通知子作用域不要去处理它。两个方法中第一个参数必须是事件的名称,后面可以跟任意多个参数,参数会传到监听器中。
3.事件监听
要监听一个事件,我们用$on()方法,这个方法为具有某个特定名称的事件注册了一个监听器。不管什么时候事件被触发,监听器都会被调用。
$on方法第一个参数是要监听的事件名称,第二个参数是一个函数,在监听到对应的事件后会执行,该函数的第一个参数是一个事件对象,后面的参数就对应着$emit()和$broadcast()传过来的参数。$on方法还会返回一个反注册函数。
$scope.$emit('myEvent',arg1,arg2,arg3);
unregist = $scope.$on('myEvent',function(event,arg1,arg2,arg3) {
//当接收到myEvent事件时执行,在这里做你想做的事情
//event为事件对象,arg1,arg2,arg3为$emit()或$broadcast()附加的参数
});
//直接调用unregist()就可以取消该监听器4.事件对象
事件对象有以下属性。
- targetScope(作用域对象)
这个属性是发送或者广播事件的作用域。 - currentScope(作用域对象)
这个对象包含了当前处理事件的作用域。 - name(字符串)
这个字符串是触发之后,我们正在处理的事件名称。 - stopPropagation(函数)
stopPropagation()函数取消通过$emit触发的事件的进一步传播。 - preventDefault(函数)
preventDefault把defaultPrevented标志设置为true。(有点冗余)尽管不能停止$broadcast事件的传播,但我们可以告诉子作用域无需处理这个事件。 - defaultPrevented(布尔值)
调用preventDefault()会把defaultPrevented设置为true。
5.实例
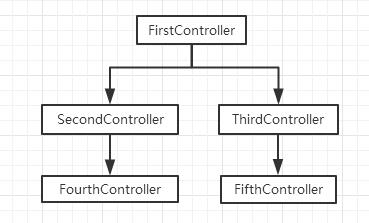
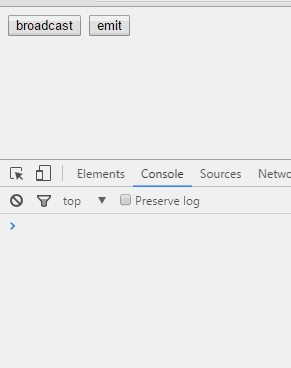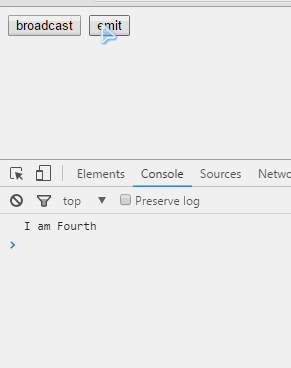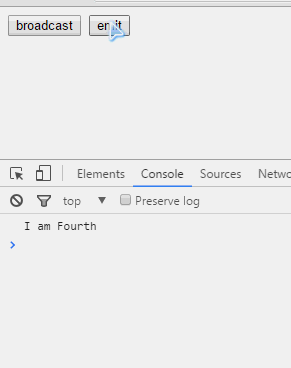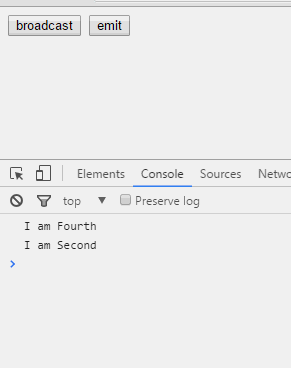
第一个例子是关于$emit()和$broadcast是如何在作用域链上作用的。首先看看各个作用域之间的继承关系。
<body ng-app="myApp" >
<div ng-controller="FirstController">
<div ng-controller="SecondController">
<input type="button" value="broadcast" ng-click="broadcast()"/>
<input type="button" value="emit" ng-click="emit()"/>
<div ng-controller="FourthController">
</div>
</div>
<div ng-controller="ThirdController">
<div ng-controller="FifthController">
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module("myApp",['ionic']);
app.controller("FirstController",function($scope) {
$scope.$on('to-child',function(event) {
console.log("I am First");
});
$scope.$on('to-parent',function(event){
console.log("I am First");
});
});
app.controller("SecondController",function($scope) {
$scope.emit = function () {
$scope.$emit('to-parent');
};
$scope.broadcast = function() {
$scope.$broadcast("to-child");
};
$scope.$on('to-child',function(event) {
console.log("I am Second");
});
$scope.$on('to-parent',function(event){
console.log("I am Second");
});
});
app.controller("ThirdController",function($scope) {
$scope.$on('to-child',function(event) {
console.log("I am Third");
});
$scope.$on('to-parent',function(event){
console.log("I am Third");
});
});
app.controller("FourthController",function($scope) {
$scope.$on('to-child',function(event) {
console.log("I am Fourth");
});
$scope.$on('to-parent',function(event){
console.log("I am Fourth");
});
});
app.controller("FifthController",function($scope) {
$scope.$on('to-child',function(event) {
console.log("I am Fifth");
});
$scope.$on('to-parent',function(event){
console.log("I am Fifth");
});
});
</script>
</body>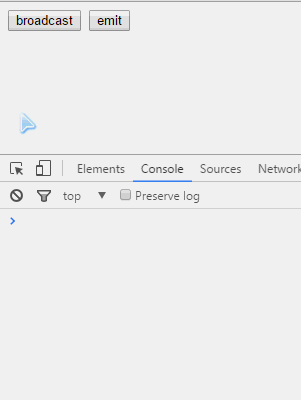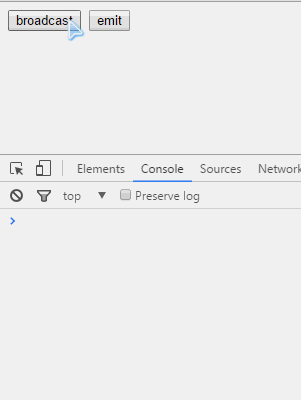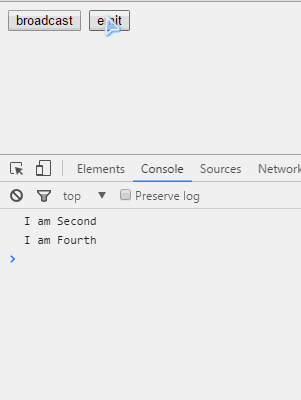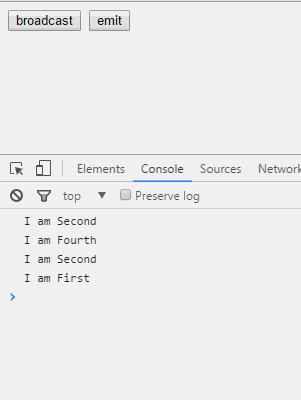
我们看到,无论是$emit()还是$broadcast(),发出者本身都能够接收到。然后,$emit()其父亲能够收到,$broadcast()其子女能够收到,兄弟或兄弟的儿女都无法接收。
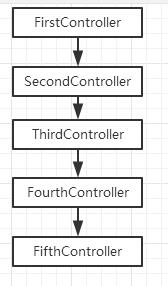
接下来的例子演示如何用事件对象来取消事件的进一步传播,$emit()方法是可以直接阻止传播的,$broadcast()方法只能告知子作用域请忽略它,子作用域还得添加对应的处理。下面的例子我们把作用域结构改成线性的,继承关系如下。
<body ng-app="myApp" >
<div ng-controller="FirstController">
<div ng-controller="SecondController">
<div ng-controller="ThirdController">
<div ng-controller="FourthController">
<div ng-controller="FifthController">
<input type="button" value="broadcast" ng-click="broadcast()"/>
<input type="button" value="emit" ng-click="emit()"/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module("myApp",['ionic']);
app.controller("FirstController",function($scope) {
$scope.$on('to-parent',function(event){
console.log("I am First");
});
});
app.controller("SecondController",function($scope) {
$scope.$on('to-parent',function(event){
event.stopPropagation();
console.log("I am Second");
});
});
app.controller("ThirdController",function($scope) {
$scope.emit = function () {
var x = $scope.$emit('to-parent');
};
$scope.broadcast = function() {
$scope.$broadcast("to-child");
};
});
app.controller("FourthController",function($scope) {
$scope.$on('to-child',function(event) {
event.preventDefault();
console.log("I am Fourth");
});
});
app.controller("FifthController",function($scope) {
$scope.$on('to-child',function(event) {
if(!event.defaultPrevented) //这里必须添加判断,要不然仍会执行
console.log("I am Fifth");
});
});
</script>
</body>6. 事件相关的核心服务
下面是AngularJS核心框架发送的事件,我们监听之后完成我们想做的操作,可以用事件来让自己的AngularJS对象能在全局事件的不同状态上与应用交互。对于这类事件监听大部分都写在运行块中(run方法)。
核心系统的$emitted事件
- $includeContentLoaded
$includeContentLoaded事件当ngInclude的内容重新加载时,从ngInclude指令上触发。 - $includeContentRequested
$includeContentRequested事件从调用ngInclude的作用域上发送。每次ngInclude的内容被请求时,它都会被发送。 - $viewContentLoaded
$viewContentLoaded事件每当ngView内容被重新加载时,从当前ngView作用域上发送。
核心系统的$broadcast事件
- $locationChangeStart
当Angular从$loaction服务对浏览器的地址作更新时,会触发该事件。 - $locationChangeSuccess
当浏览器地址成功变更,且$locationChangeStart事件没被阻止的情况下,该事件会从$rootScope广播出来。 - $routeChangeStart
在路由变更发生之前,$routeChangeStart事件从$rootScope广播出来。也就是在路由服务开始解析路由变更所需的所有依赖项时。 - $routeChangeSuceess
在所有路由依赖性跟着$routeChangeStart被解析之后,$routeChangeSuccess被$rootScope上广播出来。 - $routeChangeError
如果路由对象上任意的resolve属性被拒绝了,该事件就会从$rootScope上广播出来。 - $routeUpdate
如果$routeProvider上的reloadOnSearch属性被设置成false,并且使用了控制器的同一个实例,$routeUpdate事件就会从$rootScope上广播。 - $destroy
在作用域销毁之前,$destroy事件会在作用域上广播,子作用域可以称父作用域真正被移除之前做一些事情(比如清理自身,让已设置的定时函数失效等)。
























 3447
3447

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








