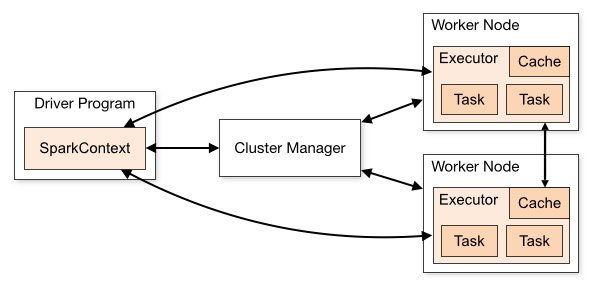
官网对图下面几点说明: (1)不同的Spark应用程序对应该不同的Executor,这些Executor在整个应用程序执行期间都存在并且Executor中可以采用多线程的方式执行Task。这样做的好处是,各个Spark应用程序的执行是相互隔离的。除Spark应用程序向外部存储系统写数据进行数据交互这种方式外,各Spark应用程序间无法进行数据共享。 (2)Spark对于其使用的集群资源管理器没有感知能力,只要它能对Executor进行申请并通信即可。这意味着不管使用哪种资源管理器,其执行流程都是不变的。这样Spark可以不同的资源管理器进行交互。 (3)Spark应用程序在整个执行过程中要与Executors进行来回通信。 (4)Driver端负责Spark应用程序任务的调度,因此最好Driver应该靠近Worker节点。
Spark目前支持的集群管理器包括:
Standalone Apache Mesos Hadoop YARN 在提交Spark应用程序时,Spark支持下列几种Master URL
SparkContext源码中比较重要的内容
// Create and start the scheduler // 根据sparkContext和master创建TaskScheduler,返回SchedulerBackend及TaskScheduler val (sched, ts) = SparkContext.createTaskScheduler(this, master) _schedulerBackend = sched _taskScheduler = ts // 根据sparkContext对象创建DAGScheduler _dagScheduler = new DAGScheduler(this) _heartbeatReceiver.ask[Boolean](TaskSchedulerIsSet) // start TaskScheduler after taskScheduler sets DAGScheduler reference in DAGScheduler's // constructor _taskScheduler.start() _applicationId = _taskScheduler.applicationId() _applicationAttemptId = taskScheduler.applicationAttemptId() _conf.set("spark.app.id", _applicationId) _env.blockManager.initialize(_applicationId)
进入 createTaskScheduler 方法
private def createTaskScheduler( sc: SparkContext, master: String): (SchedulerBackend, TaskScheduler) = { import SparkMasterRegex._ // When running locally, don't try to re-execute tasks on failure. val MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES = 1 master match { // 本地单线程运行 case "local" => // schedule 使用TaskSchedulerImpl val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES, isLocal = true) // LocalBackend 使用LocalBackend val backend = new LocalBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, 1) scheduler.initialize(backend) (backend, scheduler) // 本地多线程运行方式local[n] case LOCAL_N_REGEX(threads) => def localCpuCount: Int = Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors() // local[*] estimates the number of cores on the machine; local[N] uses exactly N threads. val threadCount = if (threads == "*") localCpuCount else threads.toInt if (threadCount <= 0) { throw new SparkException(s"Asked to run locally with $threadCount threads") } // scheduler 使用TaskSchedulerImpl val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES, isLocal = true) // backend 使用LocalBackend val backend = new LocalBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, threadCount) scheduler.initialize(backend) (backend, scheduler) // 本地运行模式+重试次数local[*, M]和local[N, M] case LOCAL_N_FAILURES_REGEX(threads, maxFailures) => def localCpuCount: Int = Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors() // local[*, M] means the number of cores on the computer with M failures // local[N, M] means exactly N threads with M failures val threadCount = if (threads == "*") localCpuCount else threads.toInt val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, maxFailures.toInt, isLocal = true) val backend = new LocalBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, threadCount) scheduler.initialize(backend) (backend, scheduler) // spark standalone 运行模式 case SPARK_REGEX(sparkUrl) => val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc) val masterUrls = sparkUrl.split(",").map("spark://" + _) val backend = new SparkDeploySchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, masterUrls) scheduler.initialize(backend) (backend, scheduler) // 匹配local-cluster运行模式 case LOCAL_CLUSTER_REGEX(numSlaves, coresPerSlave, memoryPerSlave) => // Check to make sure memory requested <= memoryPerSlave. Otherwise Spark will just hang. val memoryPerSlaveInt = memoryPerSlave.toInt if (sc.executorMemory > memoryPerSlaveInt) { throw new SparkException( "Asked to launch cluster with %d MB RAM / worker but requested %d MB/worker".format( memoryPerSlaveInt, sc.executorMemory)) } val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc) val localCluster = new LocalSparkCluster( numSlaves.toInt, coresPerSlave.toInt, memoryPerSlaveInt, sc.conf) val masterUrls = localCluster.start() val backend = new SparkDeploySchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, masterUrls) scheduler.initialize(backend) backend.shutdownCallback = (backend: SparkDeploySchedulerBackend) => { localCluster.stop() } (backend, scheduler) //"yarn-standalone"或"yarn-cluster"运行模式 case "yarn-standalone" | "yarn-cluster" => if (master == "yarn-standalone") { logWarning( "\"yarn-standalone\" is deprecated as of Spark 1.0. Use \"yarn-cluster\" instead.") } val scheduler = try { val clazz = Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.YarnClusterScheduler") val cons = clazz.getConstructor(classOf[SparkContext]) cons.newInstance(sc).asInstanceOf[TaskSchedulerImpl] } catch { // TODO: Enumerate the exact reasons why it can fail // But irrespective of it, it means we cannot proceed ! case e: Exception => { throw new SparkException("YARN mode not available ?", e) } } val backend = try { val clazz = Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.YarnClusterSchedulerBackend") val cons = clazz.getConstructor(classOf[TaskSchedulerImpl], classOf[SparkContext]) cons.newInstance(scheduler, sc).asInstanceOf[CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend] } catch { case e: Exception => { throw new SparkException("YARN mode not available ?", e) } } scheduler.initialize(backend) (backend, scheduler) //yarn-client运行模式 case "yarn-client" => val scheduler = try { val clazz = Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.YarnScheduler") val cons = clazz.getConstructor(classOf[SparkContext]) cons.newInstance(sc).asInstanceOf[TaskSchedulerImpl] } catch { case e: Exception => { throw new SparkException("YARN mode not available ?", e) } } val backend = try { val clazz = Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.YarnClientSchedulerBackend") val cons = clazz.getConstructor(classOf[TaskSchedulerImpl], classOf[SparkContext]) cons.newInstance(scheduler, sc).asInstanceOf[CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend] } catch { case e: Exception => { throw new SparkException("YARN mode not available ?", e) } } scheduler.initialize(backend) (backend, scheduler) // Mesos运行模式 case mesosUrl MESOS_REGEX(_) => MesosNativeLibrary.load() val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc) val coarseGrained = sc.conf.getBoolean("spark.mesos.coarse", false) val url = mesosUrl.stripPrefix("mesos://") // strip scheme from raw Mesos URLs val backend = if (coarseGrained) { new CoarseMesosSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, url, sc.env.securityManager) } else { new MesosSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, url) } scheduler.initialize(backend) (backend, scheduler) //Spark IN MapReduce V1运行模式 case SIMR_REGEX(simrUrl) => val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc) val backend = new SimrSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, simrUrl) scheduler.initialize(backend) (backend, scheduler) case _ => throw new SparkException("Could not parse Master URL: '" + master + "'") } }
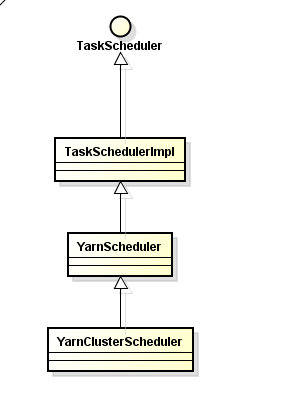
scheduler类继承图
注意上面类中的initialize方法
def initialize(backend: SchedulerBackend) { this.backend = backend // temporarily set rootPool name to empty rootPool = new Pool("", schedulingMode, 0, 0) schedulableBuilder = { schedulingMode match { case SchedulingMode.FIFO => new FIFOSchedulableBuilder(rootPool) case SchedulingMode.FAIR => new FairSchedulableBuilder(rootPool, conf) } } schedulableBuilder.buildPools() }
初始化主要是SchedulerBackend的初始化,它主要时通过集群的配置来获得调度模式,现在支持的调度模式是FIFO和公平调度,默认的是FIFO。
下面看一下start方法
override def start() { backend.start() if (!isLocal && conf.getBoolean("spark.speculation", false)) { logInfo("Starting speculative execution thread") speculationScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable { override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryOrStopSparkContext(sc) { checkSpeculatableTasks() } }, SPECULATION_INTERVAL_MS, SPECULATION_INTERVAL_MS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) } }
主要是backend的启动.






















 4256
4256

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








