文章目录
一、KMP算法说明
要判断s1字符串是否包含s2字符串,如果包含返回s1中包含s2的最左开头位置,不包含返回-1
暴力方法就是s1的每个位置都做开头,然后去匹配s2整体,时间复杂度O(n*m),其中n为s1长度,m为s2长度
KMP算法可以做到时间复杂度O(n+m)
二、详细实现
1. next数组定义
字符串s的next数组为int数组,长度等于s的长度。next[i]表示在s中下标i之前子串的前缀和后缀的最大匹配长度(不包含整体)
以字符串"aabaabs"为例
// i=0,规定next[0]为-1
// i=1,由于s[1]之前只有a,除去整体,前缀和后缀只能是空,所以规定next[1]=0
// i=2, "aa",前缀"a",后缀"a",最大匹配长度1,next[2]=1
// i=3, "aab",没有可以匹配的前缀和后缀,next[3]=0
// i=4, "aaba", 前缀"a", 后缀"a", next[4]=1
// i=5, "aabaa", 前缀"aa", 后缀"aa", next[5]=2
// i=6, "aabaab", 前缀"aab", 后缀"aab", next[6]=3
// 扩充的next是可以多计算一位的
// i=7, "aabaabs",没有可以匹配的前缀和后缀,next[7]=0
2. 使用next加速匹配
func kmp(s1, s2 string) int {
if len(s1) < len(s2) {
return -1
}
next := nextArr(s2)
x, y := 0, 0
for x < len(s1) && y < len(s2) {
if s1[x] == s2[y] {
x++
y++
} else if y > 0 {
y = next[y]
} else {
x++
}
}
if y == len(s2) {
return x - y
} else {
return -1
}
}
3. next数组如何快速生成
func nextArr(s string) []int {
if len(s) <= 1 {
return []int{-1}
}
next := make([]int, len(s))
next[0], next[1] = -1, 0
cp := 0
for i := 2; i < len(s); {
if s[i-1] == s[cp] {
cp++
next[i] = cp
i++
} else if cp > 0 {
cp = next[cp]
} else {
next[i] = 0
i++
}
}
return next
}
4. 时间复杂度O(m+n)的证明
a) next生成的时间复杂度
// for循环中我们关注i和i-cp
// i的范围是2~m
// i-cp的范围是0~m
// 分支1:i变大, i-cp不变
// 分支2:i-cp变大
// 分支3:i变大,i-cp变大
// 因此时间复杂度O(m)
b) 匹配过程时间复杂度
// for循环中关注x和x-y
// ...
// 同理时间复杂度O(n)
三、例题
1. leetcode#572
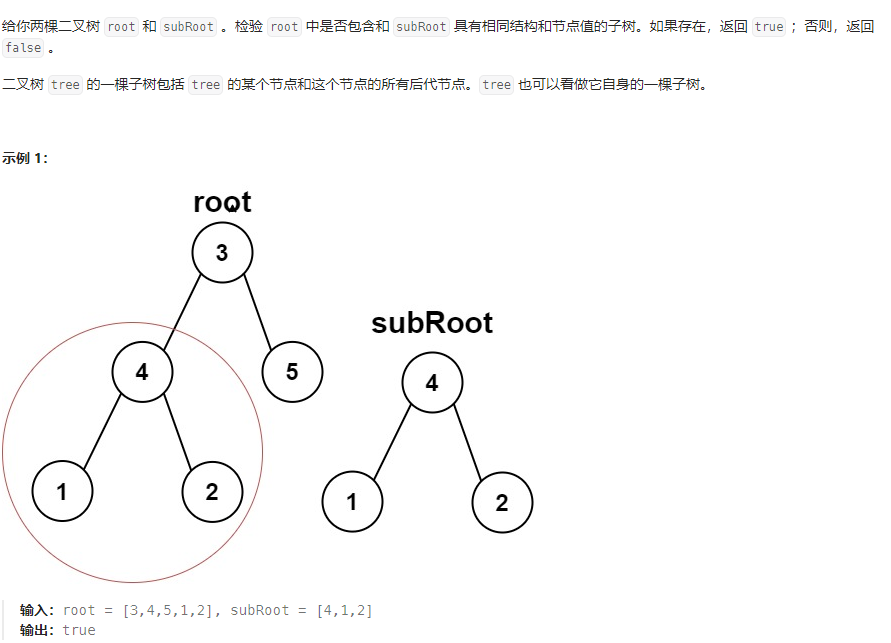
// 思路:将两棵树都序列化为sRoot和sSubRoot,然后判断sSubRoot是否为sRoot的子串
func isSubtree(root *TreeNode, subRoot *TreeNode) bool {
const nullVal = 1e4 + 1
var s1, s2 []int
s1 = encode(root, make([]int, 0), nullVal)
s2 = encode(subRoot, make([]int, 0), nullVal)
return kmp2(s1, s2) >= 0
}
func encode(root *TreeNode, list []int, nullVal int) []int {
if root == nil {
list = append(list, nullVal)
return list
}
list = append(list, root.Val)
list = encode(root.Left, list, nullVal)
list = encode(root.Right, list, nullVal)
return list
}
func kmp2(s1, s2 []int) int {
if len(s1) < len(s2) {
return -1
}
next := nextArrInt(s2)
x, y := 0, 0
for x < len(s1) && y < len(s2) {
if s1[x] == s2[y] {
x++
y++
} else if y > 0 {
y = next[y]
} else {
x++
}
}
if y == len(s2) {
return x - y
} else {
return -1
}
}
func nextArrInt(s []int) []int {
if len(s) <= 1 {
return []int{-1}
}
next := make([]int, len(s))
next[0], next[1] = -1, 0
cp := 0
for i := 2; i < len(s); {
if s[i-1] == s[cp] {
cp++
next[i] = cp
i++
} else if cp > 0 {
cp = next[cp]
} else {
next[i] = 0
i++
}
}
return next
}
2. leetcode#1367

func isSubPath(head *ListNode, root *TreeNode) bool {
if head == nil {
return true
}
if root == nil {
return false
}
list := make([]int, 0)
for head != nil {
list = append(list, head.Val)
head = head.Next
}
next := nextArrInt(list)
return find(root, list, next, 0)
}
func find(cur *TreeNode, list []int, next []int, index int) bool {
if index == len(list) {
return true
}
if cur == nil {
return false
}
for index >= 0 && cur.Val != list[index] {
index = next[index]
}
// index=-1 => index=0
// 匹配 => index+1
index++
return find(cur.Left, list, next, index) || find(cur.Right, list, next, index)
}





















 1852
1852











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








