本人博客原地址:spring源码笔记-instantiateUsingFactoryMethod与autowireConstructor两个Bean实例化方法
创作时间: 2019.06.30 19:34:20
基于springboot2.1.4
1、instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#instantiateUsingFactoryMethod–>org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver#instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs)
public BeanWrapper instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(
String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
BeanWrapperImpl bw = new BeanWrapperImpl();
this.beanFactory.initBeanWrapper(bw);
Object factoryBean;
Class<?> factoryClass;
boolean isStatic;
// 通过beanDefinition获取到factoryBeanName ,实际就是@Bean注解的方法
//所在的configuration类
String factoryBeanName = mbd.getFactoryBeanName();
if (factoryBeanName != null) {
if (factoryBeanName.equals(beanName)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"factory-bean reference points back to the same bean definition");
}
// 获取configuration类的实例
factoryBean = this.beanFactory.getBean(factoryBeanName);
if (mbd.isSingleton() && this.beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException();
}
factoryClass = factoryBean.getClass();
isStatic = false;
}
else {
// It's a static factory method on the bean class.
if (!mbd.hasBeanClass()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"bean definition declares neither a bean class nor a factory-bean reference");
}
factoryBean = null;
factoryClass = mbd.getBeanClass();
isStatic = true;
}
Method factoryMethodToUse = null;
ArgumentsHolder argsHolderToUse = null;
Object[] argsToUse = null;
//如果在调用getBean方法时有传参,那就用传的参作为
//@Bean注解的方法(工厂方法)的参数,
// 一般懒加载的bean才会传参,启动过程就实例化的实际上都没有传参
if (explicitArgs != null) {
argsToUse = explicitArgs;
}
else {
Object[] argsToResolve = null;
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
factoryMethodToUse = (Method) mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
//不为空表示已经使用过工厂方法,现在是再次使用工厂方法,
// 一般原型模式和Scope模式采用的上,直接使用该工厂方法和缓存的参数
if (factoryMethodToUse != null && mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved) {
// Found a cached factory method...
argsToUse = mbd.resolvedConstructorArguments;
if (argsToUse == null) {
argsToResolve = mbd.preparedConstructorArguments;
}
}
}
if (argsToResolve != null) {
argsToUse = resolvePreparedArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, factoryMethodToUse, argsToResolve, true);
}
}
// 调用getBean方法没有传参,同时也是第一次使用工厂方法
if (factoryMethodToUse == null || argsToUse == null) {
// Need to determine the factory method...
// Try all methods with this name to see if they match the given arguments.
factoryClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(factoryClass);
// 获取configuration类的所有候选方法
Method[] rawCandidates = getCandidateMethods(factoryClass, mbd);
List<Method> candidateList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Method candidate : rawCandidates) {
// 查找到与工厂方法同名的候选方法,没有@Bean的同名方法不被考虑
if (Modifier.isStatic(candidate.getModifiers()) == isStatic && mbd.isFactoryMethod(candidate)) {
candidateList.add(candidate);
}
}
//当与工厂方法同名的候选方法只有一个,且调用getBean方法时没有传参,
// 且没有缓存过参数,直接通过调用实例化方法执行该候选方法
if (candidateList.size() == 1 && explicitArgs == null && !mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues()) {
Method uniqueCandidate = candidateList.get(0);
if (uniqueCandidate.getParameterCount() == 0) {
mbd.factoryMethodToIntrospect = uniqueCandidate;
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = uniqueCandidate;
mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved = true;
mbd.resolvedConstructorArguments = EMPTY_ARGS;
}
bw.setBeanInstance(instantiate(beanName, mbd, factoryBean, uniqueCandidate, EMPTY_ARGS));
return bw;
}
}
Method[] candidates = candidateList.toArray(new Method[0]);
// 有多个与工厂方法同名的候选方法时,进行排序。public的方法会往前排,然后参数个数多的方法往前排
//具体排序代码--->org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AutowireUtils#sortConstructors
ConstructorArgumentValues resolvedValues = null;
boolean autowiring = (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);
int minTypeDiffWeight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Set<Method> ambiguousFactoryMethods = null;
int minNrOfArgs;
// 如果调用getBean方法时有传参,那么工厂方法最少参数个数要等于传参个数
if (explicitArgs != null) {
minNrOfArgs = explicitArgs.length;
}
else {
// We don't have arguments passed in programmatically, so we need to resolve the
// arguments specified in the constructor arguments held in the bean definition.
if (mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues()) {
ConstructorArgumentValues cargs = mbd.getConstructorArgumentValues();
resolvedValues = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
minNrOfArgs = resolveConstructorArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, cargs, resolvedValues);
}
else {
minNrOfArgs = 0;
}
}
LinkedList<UnsatisfiedDependencyException> causes = null;
// 遍历同名候选方法
for (Method candidate : candidates) {
// 获取候选方法的参数列表
Class<?>[] paramTypes = candidate.getParameterTypes();
if (paramTypes.length >= minNrOfArgs) {
ArgumentsHolder argsHolder;
//在调用getBean方法时传的参数不为空,则工厂方法的参数个数需要与
// 传入的参数个数严格一致
if (explicitArgs != null) {
// Explicit arguments given -> arguments length must match exactly.
if (paramTypes.length != explicitArgs.length) {
continue;
}
argsHolder = new ArgumentsHolder(explicitArgs);
}
else {
// Resolved constructor arguments: type conversion and/or autowiring necessary.
try {
String[] paramNames = null;
ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd = this.beanFactory.getParameterNameDiscoverer();
if (pnd != null) {
paramNames = pnd.getParameterNames(candidate);
}
//当传入的参数为空,需要根据工厂方法的参数类型注入相应的
// bean。详细的注入代码可查看
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#resolveDependency
//暂不过多解析,如有需要再另外开篇记录
argsHolder = createArgumentArray(beanName, mbd, resolvedValues, bw,
paramTypes, paramNames, candidate, autowiring, candidates.length == 1);
}
catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Ignoring factory method [" + candidate + "] of bean '" + beanName + "': " + ex);
}
// Swallow and try next overloaded factory method.
if (causes == null) {
causes = new LinkedList<>();
}
causes.add(ex);
continue;
}
}
/**计算工厂方法的权重,分严格模式和宽松模式,计算方式可以看本文最后的附录
严格模式会校验子类(注入参数)继承了多少层父类(方法参数)层数越多权重越大,越不匹配
,宽松模式,只要是注入参数类型是方法参数类型的子类就行。
默认宽松模式 在argsHolders中会有arguments和rawArguments,;
例如在注入bean时,如果有经历过createArgumentArray方法中的TypeConverter
(如有有定义并且注册到beanFactory中)的,arguments和rawArguments的值是不一样的
如果没有经过转换,两者是一样的。通过getBean传入的参数两者通常都是一样的
所以都是先将工厂方法的参数类型与arguments的比较,不同则赋予最大权重值,
相同则与rawArguments比较,与rawArguments中的相同,就会赋最大权重值-1024,
不相同,则赋最大权重值-512,经过类型转换一定会执行最大权重值-512的操作。
权重值越大,该工厂方法越不匹配。总的来说就是传入的参数或者注入的参数类型
与工厂方法参数类型的比对。**/
int typeDiffWeight = (mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution() ?
argsHolder.getTypeDifferenceWeight(paramTypes) : argsHolder.getAssignabilityWeight(paramTypes));
// Choose this factory method if it represents the closest match.
if (typeDiffWeight < minTypeDiffWeight) {
/** 当权重小时,重新设置factoryMethodToUse 和argsHolderToUse ,argsToUse ,
并把当前权重值设置为最小权重值,等待遍历的下一个候选工厂方法比对,
并且将ambiguousFactoryMethods (表示有含糊同样权重的候选方法)设置为空**/
factoryMethodToUse = candidate;
argsHolderToUse = argsHolder;
argsToUse = argsHolder.arguments;
minTypeDiffWeight = typeDiffWeight;
ambiguousFactoryMethods = null;
}
// Find out about ambiguity: In case of the same type difference weight
// for methods with the same number of parameters, collect such candidates
// and eventually raise an ambiguity exception.
// However, only perform that check in non-lenient constructor resolution mode,
// and explicitly ignore overridden methods (with the same parameter signature).
/** 当遍历到下一个候选方法的时候,已经设置了factoryMethodToUse 且权重值
与上一次的最小权重值相等时,ambiguousFactoryMethods填值,这个ambiguousFactoryMethods不为空
表示有两个候选方法的最小权重相等,spring无法匹配出最适合的工厂方法,
如果再继续往下遍历候选器,有更小的权重值,那ambiguousFactoryMethods会
再次被设置为空**/
else if (factoryMethodToUse != null && typeDiffWeight == minTypeDiffWeight &&
!mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution() &&
paramTypes.length == factoryMethodToUse.getParameterCount() &&
!Arrays.equals(paramTypes, factoryMethodToUse.getParameterTypes())) {
if (ambiguousFactoryMethods == null) {
ambiguousFactoryMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>();
ambiguousFactoryMethods.add(factoryMethodToUse);
}
ambiguousFactoryMethods.add(candidate);
}
}
}
if (factoryMethodToUse == null) {
if (causes != null) {
UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex = causes.removeLast();
for (Exception cause : causes) {
this.beanFactory.onSuppressedException(cause);
}
throw ex;
}
List<String> argTypes = new ArrayList<>(minNrOfArgs);
if (explicitArgs != null) {
for (Object arg : explicitArgs) {
argTypes.add(arg != null ? arg.getClass().getSimpleName() : "null");
}
}
else if (resolvedValues != null) {
Set<ValueHolder> valueHolders = new LinkedHashSet<>(resolvedValues.getArgumentCount());
valueHolders.addAll(resolvedValues.getIndexedArgumentValues().values());
valueHolders.addAll(resolvedValues.getGenericArgumentValues());
for (ValueHolder value : valueHolders) {
String argType = (value.getType() != null ? ClassUtils.getShortName(value.getType()) :
(value.getValue() != null ? value.getValue().getClass().getSimpleName() : "null"));
argTypes.add(argType);
}
}
String argDesc = StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(argTypes);
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"No matching factory method found: " +
(mbd.getFactoryBeanName() != null ?
"factory bean '" + mbd.getFactoryBeanName() + "'; " : "") +
"factory method '" + mbd.getFactoryMethodName() + "(" + argDesc + ")'. " +
"Check that a method with the specified name " +
(minNrOfArgs > 0 ? "and arguments " : "") +
"exists and that it is " +
(isStatic ? "static" : "non-static") + ".");
}
//返回类型不能为void
else if (void.class == factoryMethodToUse.getReturnType()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Invalid factory method '" + mbd.getFactoryMethodName() +
"': needs to have a non-void return type!");
}
//存在含糊的两个工厂方法,不知选哪个
else if (ambiguousFactoryMethods != null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Ambiguous factory method matches found in bean '" + beanName + "' " +
"(hint: specify index/type/name arguments for simple parameters to avoid type ambiguities): " +
ambiguousFactoryMethods);
}
if (explicitArgs == null && argsHolderToUse != null) {
mbd.factoryMethodToIntrospect = factoryMethodToUse;
argsHolderToUse.storeCache(mbd, factoryMethodToUse);
}
}
Assert.state(argsToUse != null, "Unresolved factory method arguments");
// 到达这里,恭喜,可以完成实例化了
bw.setBeanInstance(instantiate(beanName, mbd, factoryBean, factoryMethodToUse, argsToUse));
return bw;
}
看下例子
@Bean
public String getStr20(){
System.out.println("helloTest in HelloConfigurationInner20");
return "helloTest";
}
@Bean
public Executor getStr20(Executor executor){
System.out.println("helloTest in HelloConfigurationInner20");
return executor;
}
// 两者参数个数一样多,权重也一样,两者的参数都不是通过转换类型得来的,无法判断哪个才是被选召的孩子
// @Bean
// public String getStr20(OrderBean hello){
// System.out.println("helloTest in HelloConfigurationInner20");
// return "helloTest"+hello;
// }
2、autowireConstructor
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#autowireConstructor—>org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver#autowireConstructor(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd,
@Nullable Constructor<?>[] chosenCtors, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs)
构造器方法的过程有很多跟工厂方法相似的地方,比如,传入参数的处理,候选方法的排序,参数的注入,权重计算等。不同的是instantiateUsingFactoryMethod有factoryBean的查找,重要的逻辑基本差不多,就不重复记录了,重点说下在调用autowireConstructor前就要先获取到构造器,并作为参数传入,重点来关注spring默认的获取构造方法的逻辑
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance–>org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors遍历所有的SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor实例,执行其determineCandidateConstructors方法(如有需要可以自定义SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,按需求重写determineCandidateConstructors方法)默认的processor为AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor接着进入org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#determineCandidateConstructors看关键部分
//如果之前已经有用构造方法实例化bean,就会有缓存,原型模式和scope模式会有再次使用的时候
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
Constructor<?>[] candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
// Fully synchronized resolution now...
synchronized (this.candidateConstructorsCache) {
candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
Constructor<?>[] rawCandidates;
try {
//缓存中不存在的时候使用getDeclaredConstructors方法获取所有的构造方法
rawCandidates = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Resolution of declared constructors on bean Class [" + beanClass.getName() +
"] from ClassLoader [" + beanClass.getClassLoader() + "] failed", ex);
}
List<Constructor<?>> candidates = new ArrayList<>(rawCandidates.length);
Constructor<?> requiredConstructor = null;
Constructor<?> defaultConstructor = null;
//优先的构造方法是从kotlin文件获取,没玩过kotlin,不知道怎么弄,先不管
Constructor<?> primaryConstructor = BeanUtils.findPrimaryConstructor(beanClass);
int nonSyntheticConstructors = 0;
for (Constructor<?> candidate : rawCandidates) {
if (!candidate.isSynthetic()) {
nonSyntheticConstructors++;
}
else if (primaryConstructor != null) {
continue;
}
//查找是否有@Autowired注解
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(candidate);
if (ann == null) {
//如果没有@Autowired注解,查找父类的构造方法有没有@Autowired注解
Class<?> userClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanClass);
if (userClass != beanClass) {
try {
Constructor<?> superCtor =
userClass.getDeclaredConstructor(candidate.getParameterTypes());
ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(superCtor);
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// Simply proceed, no equivalent superclass constructor found...
}
}
}
if (ann != null) {
// 当@Autowired注解的构造方法不止一个,那上一次处理的候选构造方法
// 已经设置到requiredConstructor 中,那么第二个@Autowired注解的
// 候选构造方法处理的时候就会抛异常
if (requiredConstructor != null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Invalid autowire-marked constructor: " + candidate +
". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation already: " +
requiredConstructor);
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
if (required) {
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Invalid autowire-marked constructors: " + candidates +
". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation: " +
candidate);
}
//第一个处理的有@autowired处理的构造方法设置requiredConstructor ,并设置到candidates中
requiredConstructor = candidate;
}
candidates.add(candidate);
}
//当构造方法没有@Autowired注解且参数个数为0,选为defaultConstructor
else if (candidate.getParameterCount() == 0) {
defaultConstructor = candidate;
}
}
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
// Add default constructor to list of optional constructors, as fallback.
if (requiredConstructor == null) {
if (defaultConstructor != null) {
//往候选方法中加入defaultConstructor
//(好像requiredConstructor 为null,candidates就会为null,感觉此句永远不会执行)
candidates.add(defaultConstructor);
}
else if (candidates.size() == 1 && logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Inconsistent constructor declaration on bean with name '" + beanName +
"': single autowire-marked constructor flagged as optional - " +
"this constructor is effectively required since there is no " +
"default constructor to fall back to: " + candidates.get(0));
}
}
//候选方法不为空的时候进入此处,此时就一个@Autowired注解的构造方法
candidateConstructors = candidates.toArray(new Constructor<?>[0]);
}
//当获取的所有构造方法只有一个,且不是@autowired注解的(注解的在上面处理了)
//且参数在一个以上,该方法作为候选的构造方法
else if (rawCandidates.length == 1 && rawCandidates[0].getParameterCount() > 0) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {rawCandidates[0]};
}
//后面primaryConstructor 的都不看了
else if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 2 && primaryConstructor != null &&
defaultConstructor != null && !primaryConstructor.equals(defaultConstructor)) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {primaryConstructor, defaultConstructor};
}
else if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 1 && primaryConstructor != null) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {primaryConstructor};
}
else {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[0];
}
//缓存选定的候选构造方法,供原型模式和scope模式第二次实例化时使用
this.candidateConstructorsCache.put(beanClass, candidateConstructors);
}
}
}
返回选定的构造函数列表
return (candidateConstructors.length > 0 ? candidateConstructors : null);
上demo
/**首先永远不必理会无参构造方法,他最后都是不会通过autowireConstructor方法实例化,
如果只有一个带参构造方法,那他就被选择为候选构造方法,如果有多个带参构造方法,
则需要通过@Autowired注解其中一个,不能有多个@Autowired注解的构造方法**/
// public TestService(){}
// @Autowired
public TestService(OrderBean orderBean) {
this.orderBean = orderBean;
}
// @Autowired
// public TestService(Executor executor,OrderBean orderBean){}
附
关于权重值的计算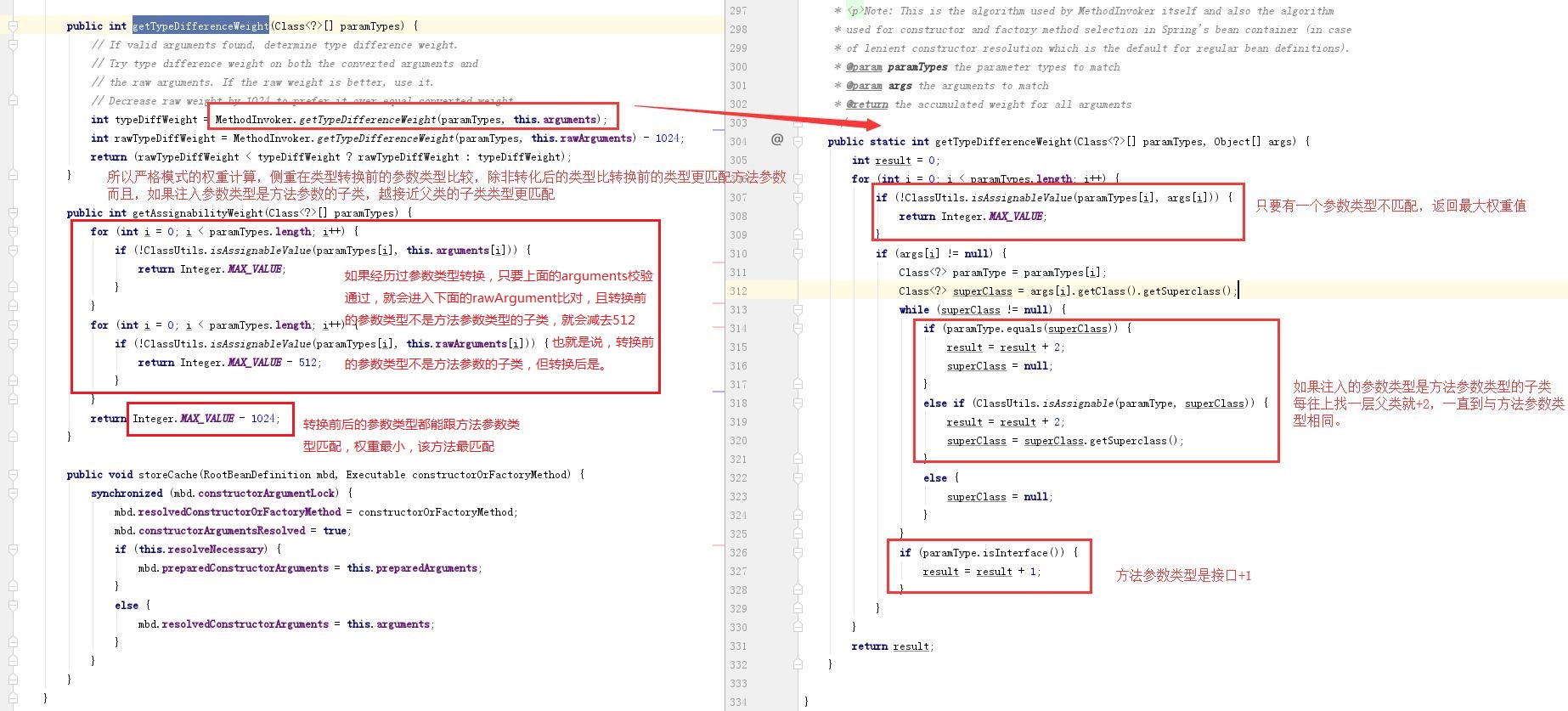
关于候选方法排序






















 290
290











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








