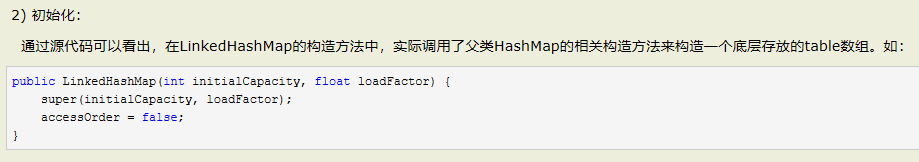
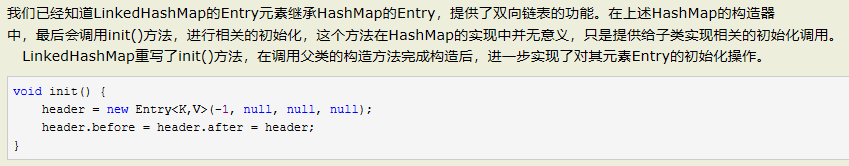
LinkedHashMap:


LinkedHashMap的实现细节:








https://www.cnblogs.com/ganchuanpu/p/8908093.html
ConcureentHashMap:
jdk1.8之前是利用分段锁机制保证线程安全的,jdk1.8之后是利用CAS+Synchronized机制保证线程安全的。





JDK7源码:
重要成员变量:
//默认的数组大小16(HashMap里的那个数组)
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
//扩容因子0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//ConcurrentHashMap中的数组
final Segment<K,V>[] segments
//默认并发标准16
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
//Segment是ReentrantLock子类,因此拥有锁的操作
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
//HashMap的那一套,分别是数组、键值对数量、阈值、负载因子
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
transient int count;
transient int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
Segment(float lf, int threshold, HashEntry<K,V>[] tab) {
this.loadFactor = lf;
this.threshold = threshold;
this.table = tab;
}
}
//换了马甲还是认识你!!!HashEntry对象,存key、value、hash值以及下一个节点
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V value;
volatile HashEntry<K,V> next;
}
//segment中HashEntry[]数组最小长度
static final int MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY = 2;
//用于定位在segments数组中的位置,下面介绍
final int segmentMask;
final int segmentShift;
构造函数(默认构造函数会调用带三个参数的构造函数):
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS)
concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS;
// Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments
//步骤① start
int sshift = 0;
int ssize = 1;
while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {
++sshift;
ssize <<= 1;
}
this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;
this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;
//步骤① end
//步骤② start
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int c = initialCapacity / ssize;
if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)
++c;
int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;
while (cap < c)
cap <<= 1;
//步骤② end
// create segments and segments[0]
//步骤③ start
Segment<K,V> s0 =
new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor),
(HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]);
Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize];
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0]
this.segments = ss;
//步骤③ end
}



put()方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment<K,V> s;
//步骤①注意valus不能为空!!!
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//根据key计算hash值,key也不能为null,否则hash(key)报空指针
int hash = hash(key);
//步骤②派上用场了,根据hash值计算在segments数组中的位置
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
//步骤③查看当前数组中指定位置Segment是否为空
//若为空,先创建初始化Segment再put值,不为空,直接put值。
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
private Segment<K,V> ensureSegment(int k) {
//获取segments
final Segment<K,V>[] ss = this.segments;
long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; // raw offset
Segment<K,V> seg;
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) {
//拷贝一份和segment 0一样的segment
Segment<K,V> proto = ss[0]; // use segment 0 as prototype
//大小和segment 0一致,为2
int cap = proto.table.length;
//负载因子和segment 0一致,为0.75
float lf = proto.loadFactor;
//阈值和segment 0一致,为1
int threshold = (int)(cap * lf);
//根据大小创建HashEntry数组tab
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap];
//再次检查
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) { // recheck
根据已有属性创建指定位置的Segment
Segment<K,V> s = new Segment<K,V>(lf, threshold, tab);
while ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s))
break;
}
}
}
return seg;
}

Segment的put()方法:
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
//步骤① start
HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
//步骤① end
V oldValue;
try {
//步骤② start
//获取Segment中的HashEntry[]
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
//算出在HashEntry[]中的位置
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
//找到HashEntry[]中的指定位置的第一个节点
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) {
//如果不为空,遍历这条链
if (e != null) {
K k;
//情况① 之前已存过,则替换原值
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
//情况② 另一个线程的准备工作
if (node != null)
//链表头插入方式
node.setNext(first);
else //情况③ 该位置为空,则新建一个节点(注意这里采用链表头插入方式)
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first);
//键值对数量+1
int c = count + 1;
//如果键值对数量超过阈值
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
//扩容
rehash(node);
else //未超过阈值,直接放在指定位置
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
//插入成功返回null
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
//步骤② end
} finally {
//步骤③
//解锁
unlock();
}
//修改成功,返回原值
return oldValue;
}


private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {
//通过Segment和hash值寻找匹配的HashEntry
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash);
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
HashEntry<K,V> node = null;
//重试次数
int retries = -1; // negative while locating node
//循环尝试获取锁
while (!tryLock()) {
HashEntry<K,V> f; // to recheck first below
//步骤①
if (retries < 0) {
//情况① 没找到,之前表中不存在
if (e == null) {
if (node == null) // speculatively create node
//新建 HashEntry 备用,retries改成0
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null);
retries = 0;
}
//情况② 找到,刚好第一个节点就是,retries改成0
else if (key.equals(e.key))
retries = 0;
//情况③ 第一个节点不是,移到下一个,retries还是-1,继续找
else
e = e.next;
}
//步骤②
//尝试了MAX_SCAN_RETRIES次还没拿到锁,简直B了dog!
else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {
//泉水挂机
lock();
break;
}
//步骤③
//在MAX_SCAN_RETRIES次过程中,key对应的entry发生了变化,则从头开始
else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&
(f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {
e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changed
retries = -1;
}
}
return node;
}

扩容操作:

private void rehash(HashEntry<K,V> node) {
/*
* Reclassify nodes in each list to new table. Because we
* are using power-of-two expansion, the elements from
* each bin must either stay at same index, or move with a
* power of two offset. We eliminate unnecessary node
* creation by catching cases where old nodes can be
* reused because their next fields won't change.
* Statistically, at the default threshold, only about
* one-sixth of them need cloning when a table
* doubles. The nodes they replace will be garbage
* collectable as soon as they are no longer referenced by
* any reader thread that may be in the midst of
* concurrently traversing table. Entry accesses use plain
* array indexing because they are followed by volatile
* table write.
*/
//旧数组引用
HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table;
//旧数组长度
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
//新数组长度为旧数组的2倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;
//修改新的阈值
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
//创建新表
HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable =
(HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity];
int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1;
//遍历旧表
for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) {
HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i];
if (e != null) {
HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
//确定在新表中的位置
int idx = e.hash & sizeMask;
//情况① 链表只有一个节点,指定转移到新表指定位置
if (next == null) // Single node on list
newTable[idx] = e;
else { // Reuse consecutive sequence at same slot
HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e;
int lastIdx = idx;
for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next;
last != null;
last = last.next) {
//情况② 扩容前后位置发生改变
int k = last.hash & sizeMask;
if (k != lastIdx) {
lastIdx = k;
lastRun = last;
}
}
//将改变的键值对放到新表的对应位置
newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun;
// Clone remaining nodes
//情况③ 把链表中剩下的节点拷到新表中
for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
V v = p.value;
int h = p.hash;
int k = h & sizeMask;
HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k];
newTable[k] = new HashEntry<K,V>(h, p.key, v, n);
}
}
}
}
//添加新的节点(链表头插入方式)
int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; // add the new node
node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]);
newTable[nodeIndex] = node;
table = newTable;
}



get()方法:
![]()
下面介绍一下jdk8的ConcurrentHashMap实现:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/5dbaa6707017

put()
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//1. 计算key的hash值
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
//2. 如果当前table还没有初始化先调用initTable方法将tab进行初始化
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
//3. tab中索引为i的位置的元素为null,则直接使用CAS将值插入即可
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
//4. 当前正在扩容
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
//5. 当前为链表,在链表中插入新的键值对
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 6.当前为红黑树,将新的键值对插入到红黑树中
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// 7.插入完键值对后再根据实际大小看是否需要转换成红黑树
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
//8.对当前容量大小进行检查,如果超过了临界值(实际大小*加载因子)就需要扩容
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}



private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
// 1. 保证只有一个线程正在进行初始化操作
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
// 2. 得出数组的大小
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 3. 这里才真正的初始化数组
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
// 4. 计算数组中可用的大小:实际大小n*0.75(加载因子)
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}



/**
* Helps transfer if a resize is in progress.
*/
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;
// 如果 table 不是空 且 node 节点是转移类型,数据检验
// 且 node 节点的 nextTable(新 table) 不是空,同样也是数据校验
// 尝试帮助扩容
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
// 根据 length 得到一个标识符号
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);
// 如果 nextTab 没有被并发修改 且 tab 也没有被并发修改
// 且 sizeCtl < 0 (说明还在扩容)
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
// 如果 sizeCtl 无符号右移 16 不等于 rs ( sc前 16 位如果不等于标识符,则标识符变化了)
// 或者 sizeCtl == rs + 1 (扩容结束了,不再有线程进行扩容)(默认第一个线程设置 sc ==rs 左移 16 位 + 2,当第一个线程结束扩容了,就会将 sc 减一。这个时候,sc 就等于 rs + 1)
// 或者 sizeCtl == rs + 65535 (如果达到最大帮助线程的数量,即 65535)
// 或者转移下标正在调整 (扩容结束)
// 结束循环,返回 table
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
// 如果以上都不是, 将 sizeCtl + 1, (表示增加了一个线程帮助其扩容)
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
// 进行转移
transfer(tab, nextTab);
// 结束循环
break;
}
}
return nextTab;
}
return table;
}
![]()
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
// 每核处理的量小于16,则强制赋值16
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1]; //构建一个nextTable对象,其容量为原来容量的两倍
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
// 连接点指针,用于标志位(fwd的hash值为-1,fwd.nextTable=nextTab)
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
// 当advance == true时,表明该节点已经处理过了
boolean advance = true;
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
// 控制 --i ,遍历原hash表中的节点
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
// 用CAS计算得到的transferIndex
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
// 已经完成所有节点复制了
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab; // table 指向nextTable
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1); // sizeCtl阈值为原来的1.5倍
return; // 跳出死循环,
}
// CAS 更扩容阈值,在这里面sizectl值减一,说明新加入一个线程参与到扩容操作
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
// 遍历的节点为null,则放入到ForwardingNode 指针节点
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
// f.hash == -1 表示遍历到了ForwardingNode节点,意味着该节点已经处理过了
// 这里是控制并发扩容的核心
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
else {
// 节点加锁
synchronized (f) {
// 节点复制工作
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
// fh >= 0 ,表示为链表节点
if (fh >= 0) {
// 构造两个链表 一个是原链表 另一个是原链表的反序排列
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
// 在nextTable i 位置处插上链表
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
// 在nextTable i + n 位置处插上链表
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
// 在table i 位置处插上ForwardingNode 表示该节点已经处理过了
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
// advance = true 可以执行--i动作,遍历节点
advance = true;
}
// 如果是TreeBin,则按照红黑树进行处理,处理逻辑与上面一致
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
// 扩容后树节点个数若<=6,将树转链表
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}


private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) {
Node<K,V> b; int n, sc;
if (tab != null) {
//如果整个table的数量小于64,就扩容至原来的一倍,不转红黑树了
//因为这个阈值扩容可以减少hash冲突,不必要去转红黑树
if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
tryPresize(n << 1);
else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {
synchronized (b) {
if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
for (Node<K,V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) {
//封装成TreeNode
TreeNode<K,V> p =
new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val,
null, null);
if ((p.prev = tl) == null)
hd = p;
else
tl.next = p;
tl = p;
}
//通过TreeBin对象对TreeNode转换成红黑树
setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd));
}
}
}
}
}
![]()
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
//更新baseCount,table的数量,counterCells表示元素个数的变化
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
//如果多个线程都在执行,则CAS失败,执行fullAddCount,全部加入count
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
//check>=0表示需要进行扩容操作
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
//当前线程发起库哦哦让操作,nextTable=null
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}

get()方法:

public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode()); //计算两次hash
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {//读取首节点的Node元素
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) { //如果该节点就是首节点就返回
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
//hash值为负值表示正在扩容,这个时候查的是ForwardingNode的find方法来定位到nextTable来
//查找,查找到就返回
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {//既不是首节点也不是ForwardingNode,那就往下遍历
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
size()方法:

public int size() {
long n = sumCount();
return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :
(int)n);
}
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a; //变化的数量
long sum = baseCount;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}
jdk8与jdk7的区别:
jdk8优化的根据:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yangfeiORfeiyang/p/9694383.html
























 820
820











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








