一、应用场景
1)一个系统有多个类,而区分它们的只是它们的直接行为;
2)需要在不同情况下使用不同的策略(算法),或者策略还可能在未来用其他方式实现;
3)对用户隐藏具体策略(算法)实现细节,彼此完全独立;
二、策略模式
一个类的行为或者算法可以在运行时更改;
意图:解决在有多种算法相似的情况下,使用if..else 所带来的复杂和难以维护问题。
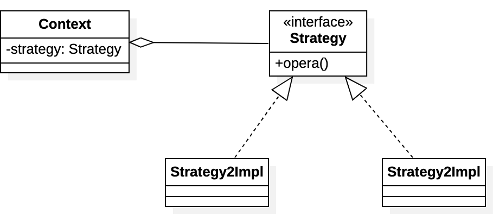
图 策略模式
场景描述:国庆回家方式有:1,高铁、2,绿皮火车,3、开车回去,要求根据不同情况来实现回家目的。
(一)if…else 方式来实现回家
/**
* 回家方案: 通过if...else 方式实现回家
*/
public class GoHomeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int randomNum = random.nextInt(3); //0,高铁,1 绿皮,2 开车
GoHomeTest goHomeTest = new GoHomeTest();
if (randomNum == 0) {
goHomeTest.byRail();
} else if (randomNum == 1) {
goHomeTest.byTrain();
} else {
goHomeTest.byCar();
}
}
private void byRail() {
System.out.println("坐高铁回家");
}
private void byTrain() {
System.out.println("坐绿皮火车回家");
}
private void byCar() {
System.out.println("开车回家");
}
}(二) 策略模式实现回家
/**
* 策略模式: 交通方式(策略)
*/
public interface Transportation {
void goHome();
}
public class RailTransportation implements Transportation{
@Override
public void goHome() {
System.out.println("坐高铁回家");
}
}
public class TrainTransportation implements Transportation{
@Override
public void goHome() {
System.out.println("坐绿皮火车回家");
}
}
public class CarTransportation implements Transportation{
@Override
public void goHome() {
System.out.println("开车回家");
}
}
/**
* 策略模式:回家条件(环境)
*/
public class GoHomeContext {
private Transportation transportation;
public GoHomeContext(Transportation transportation) {
this.transportation = transportation;
}
public void goHome() {
transportation.goHome();;
}
}
/**
* 回家方案:通过策略模式方式实现回家
*/
public class GoHomeTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int randomNum = random.nextInt(3); //0,高铁,1 绿皮,2 开车
Transportation railTransportation = new RailTransportation();
Transportation trainTransportation = new TrainTransportation();
Transportation carTransportation = new CarTransportation();
GoHomeContext context = null;
if (randomNum == 0) {
context = new GoHomeContext(railTransportation);
} else if (randomNum == 1) {
context = new GoHomeContext(trainTransportation);
} else {
context = new GoHomeContext(carTransportation);
}
context.goHome();
}
}三、优缺点
优点:
1)算法可自由切换;
2)避免使用多重条件判断;
3)扩展性良好;
缺点:
1)策略类会增多;
2)所有策略类都需对外暴露;
3)只适用于客户端知道所有的算法或行为的情况;






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








