ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentSkipListMap 是由跳表实现的Map。跳表是一个随机化的数据结构,实质就是一种可以进行二分查找的有序链表。跳表在原有的有序链表上面增加了多级索引,通过索引来实现快速查找。跳表不仅能提高搜索性能,同时也可以提高插入和删除操作的性能。

一、ConcurrentSkipListMap中关键的数据结构
每一层索引的头节点索引
/* ---------------- Head nodes -------------- */
/**
* Nodes heading each level keep track of their level.
*/
static final class HeadIndex<K,V> extends Index<K,V> {
final int level;
HeadIndex(Node<K,V> node, Index<K,V> down, Index<K,V> right, int level) {
super(node, down, right);
this.level = level;
}
}
索引节点
static class Index<K,V> {
final Node<K,V> node;
final Index<K,V> down;
volatile Index<K,V> right;
/**
* Creates index node with given values.
*/
Index(Node<K,V> node, Index<K,V> down, Index<K,V> right) {
this.node = node;
this.down = down;
this.right = right;
}
/**
* compareAndSet right field
*/
final boolean casRight(Index<K,V> cmp, Index<K,V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, rightOffset, cmp, val);
}
/**
* Returns true if the node this indexes has been deleted.
* @return true if indexed node is known to be deleted
*/
final boolean indexesDeletedNode() {
return node.value == null;
}
/**
* Tries to CAS newSucc as successor. To minimize races with
* unlink that may lose this index node, if the node being
* indexed is known to be deleted, it doesn't try to link in.
* @param succ the expected current successor
* @param newSucc the new successor
* @return true if successful
*/
final boolean link(Index<K,V> succ, Index<K,V> newSucc) {
Node<K,V> n = node;
newSucc.right = succ;
return n.value != null && casRight(succ, newSucc);
}
/**
* Tries to CAS right field to skip over apparent successor
* succ. Fails (forcing a retraversal by caller) if this node
* is known to be deleted.
* @param succ the expected current successor
* @return true if successful
*/
final boolean unlink(Index<K,V> succ) {
return node.value != null && casRight(succ, succ.right);
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long rightOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = Index.class;
rightOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("right"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
数据节点
static final class Node<K,V> {
final K key;
volatile Object value;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
/**
* Creates a new regular node.
*/
Node(K key, Object value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
/**
* Creates a new marker node. A marker is distinguished by
* having its value field point to itself. Marker nodes also
* have null keys, a fact that is exploited in a few places,
* but this doesn't distinguish markers from the base-level
* header node (head.node), which also has a null key.
*/
Node(Node<K,V> next) {
this.key = null;
this.value = this;
this.next = next;
}
}
- Node 数据节点中包含了 key,value, next 三个属性,next是指向下一个节点的引用,整个数据节点其实是一个有序的单项连表。
- Index 中包含 node ,right ,down 三个属性,node属性是存储数据节点的引用,right 是指向同层索引的下一个索引节点,down 指向了下级索引的索引节点。
- HeadIndex 索引头结点,继承自 Index ,存储当前索引层级。
二、插入流程
从构造函数开始梳理
public ConcurrentSkipListMap() {
this.comparator = null;
initialize();
}
private void initialize() {
keySet = null;
entrySet = null;
values = null;
descendingMap = null;
head = new HeadIndex<K,V>(new Node<K,V>(null, BASE_HEADER, null),
null, null, 1);
}
在 initialize 方法中创建了HeadIndex 节点,并且HeadIndex中的node 为 BASE_HEADER,类似与下图。

ConcurrentSkipListMap 到这里就初始化完成。由于插入过程中,需要查找前驱节点,这里先梳理一遍查找流程。
findPredecessor 方法是通过索引层级去找到比key 小的数据节点node,这个方法返回后会找到 比key小的某一个前驱节点node, 再通过node.next 进行顺序对比就可以确定key是否在map中。
private Node<K,V> findPredecessor(Object key, Comparator<? super K> cmp) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // don't postpone errors
for (;;) {
for (Index<K,V> q = head, r = q.right, d;;) {
if (r != null) {
Node<K,V> n = r.node;
K k = n.key;
if (n.value == null) {
if (!q.unlink(r))
break; // restart
r = q.right; // reread r
continue;
}
//TODO 比较 key 与 r 节点的大小,如果 key > r q,r 均向右移动
if (cpr(cmp, key, k) > 0) {
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
//TODO 如果已经到达了 1 级索引,直接返回。到达这一步时,可以确定 key <= r
if ((d = q.down) == null)
return q.node;
//TODO 查找下一级索引
q = d;
r = d.right;
}
}
}
下面为findPredecessor 查找数据节点3 的执行流程



接下来,继续梳理put方法,再put方法中,实际去往跳表中添加元素的执行方法是doPut, 直接看doPut方法。由于doPut方法比较长,我们三部分去了解。
查找插入位置,插入元素
Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;
outer: for (;;) {
// TODO findPredecessor 方法是为了查找前驱节点
for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) {
//TODO 如果map为空,n 为 null,不会查找第一个大于key的节点
if (n != null) {
Object v; int c;
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read
break;
if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted
break;
// TODO 如果将要插入的key大于 n , b和n 向右移动
if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
//TODO key 已经在map中存在
if (c == 0) {
if (onlyIfAbsent || n.casValue(v, value)) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v;
return vv;
}
break; // restart if lost race to replace value
}
// else c < 0; fall through
}
//TODO b 为需要插入节点的前驱节点,n 为后继节点
//TODO 创建节点,后继节点为 n
z = new Node<K,V>(key, value, n);
//TODO 使用cas设置 b 的后继节点。此处就已经将需要插入的节点与已存在的节点连接到一起
//TODO b -> n ====> b -> z -> n
if (!b.casNext(n, z))
break; // restart if lost race to append to b
break outer;
}
}
findPredecessor 已经找了某一个小于key的节点 b,for循环中会根据findPredecessor 找到的b去遍历查找第一个大于 key的n,创建一个新的节点z 并将n设置为 node 的next,并将 b 的next 设置为 z (b -> n ==> b -> z -> n),这一步完成后数据节点链表就已经完成插入。
假设插入节点3 ,这个步骤完成后节点3已经加入node链表中

创建索引、升级索引、
跳表索引的创建是非常重要的,jdk是通过随机数和 0x80000001 计算出是否需要给新加节点创建索引,升级索引。
int rnd = ThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed();
//TODO 0x80000001 = 10000000000000000000000000000001
//TODO rnd & 0x80000001 == 0 何时成立,rnd这个随机数的 最低位 和 最高位 同时为0的时候成立,概率为 1/4
if ((rnd & 0x80000001) == 0) { // test highest and lowest bits
int level = 1, max;
// TODO >>> 无符号右移 >>>= 无符号右移赋值。rnd 从第二位开始,向左延伸,判断有多少个连续的 1 , level就自增多少次
while (((rnd >>>= 1) & 1) != 0)
++level;
Index<K,V> idx = null;
HeadIndex<K,V> h = head;
//TODO 如果现有的 层级大于等于需要增加的层级,则按level 生成对应个数的 Index索引。否则,就只提高一个层级
if (level <= (max = h.level)) {
//TODO 新加节点创建索引
// Index level
// ↓
// Index level-1
// ↓
// Index 1
for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i)
idx = new Index<K,V>(z, idx, null);
}
// 提高一个层级
else { // try to grow by one level
level = max + 1; // hold in array and later pick the one to use
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Index<K,V>[] idxs =
(Index<K,V>[])new Index<?,?>[level+1];
//TODO 新加节点创建索引, 这里创建Index 的顺序是由低到高
// Index level
// ↓
// Index level-1
// ↓
// Index 1
for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i)
idxs[i] = idx = new Index<K,V>(z, idx, null);
//TODO 创建headIndex,设置 head 指向为新的 headIndex
for (;;) {
h = head;
int oldLevel = h.level;
if (level <= oldLevel) // lost race to add level
break;
HeadIndex<K,V> newh = h;
Node<K,V> oldbase = h.node;
//TODO 创建 headIndex
for (int j = oldLevel+1; j <= level; ++j)
newh = new HeadIndex<K,V>(oldbase, newh, idxs[j], j);
//TODO 设置head 指向新的headIndex
if (casHead(h, newh)) {
h = newh;
idx = idxs[level = oldLevel];
break;
}
}
}
jdk 通过rnd & 0x80000001 == 0 计算来决定是否生成索引。再通过随机数 rnd 从第二位开始有多个连续的1来计算出升级后的索引高度。如果计算出的索引高度小于当前索引高度,则只生成索引,不提高索引层级。但是不能无限增加索引高度,每次只是在原有的层级上加1。
假设插入节点3并且需要升级索引,在这个步骤完成跳表的结构如下图所示,节点3 的三个索引还没有加入到索引层级中。
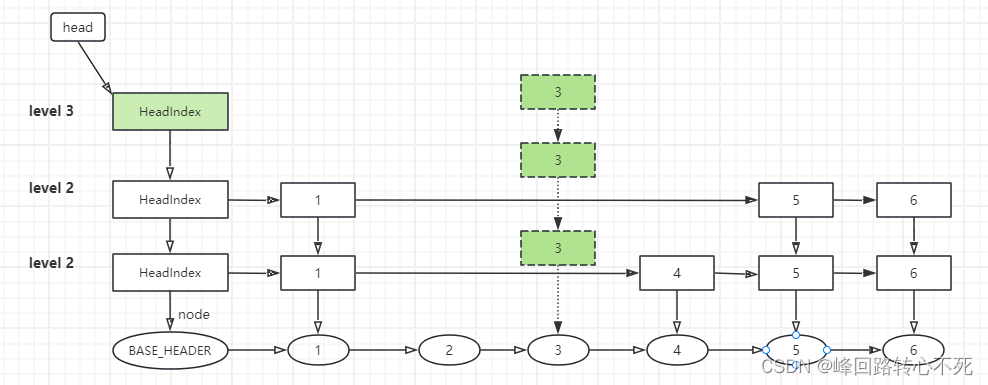
整理索引
在前两个步骤完成后,需要整理新创建的 Index 。
// find insertion points and splice in 查找插入点并在中进行拼接
splice: for (int insertionLevel = level;;) {
int j = h.level;
for (Index<K,V> q = h, r = q.right, t = idx;;) {
if (q == null || t == null)
break splice;
//TODO 此处主要是为了找到 新加索引节点的 后继节点
if (r != null) {
Node<K,V> n = r.node;
// compare before deletion check avoids needing recheck
int c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key);
if (n.value == null) {
if (!q.unlink(r))
break;
r = q.right;
continue;
}
//TODO 当 r 节点值大于等于新加阶段值 也就是 c<=0 时继续执行后续程序,q,r不在右移
if (c > 0) {
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
//TODO 这里的 j 实际上是为了解决并发操作问题
if (j == insertionLevel) {
//TODO 连接q、r、t q → r ===> q → t → r
if (!q.link(r, t))
break; // restart
if (t.node.value == null) {
findNode(key);
break splice;
}
//TODO 插入层级 -1
if (--insertionLevel == 0)
break splice;
}
//TODO 如果出现并发,j 可能大于 level ,这时 t 不能下移,以防止连错层级
if (--j >= insertionLevel && j < level)
// TODO t 下移
t = t.down;
// TODO q 下移
q = q.down;
r = q.right;
}
}
这个步骤很简单,先找到每一层新加索引节点的后继节点,然后将新加索引节点插入到索引层级中。j == insertionLevel 这个判断很有意思,其实j 变量的存在是为了解决并发操作的问题,正在整理索引层级时,其他put操作做可能会引发索引层级的再次升高。因为在上一个步骤中可能已经创建了新的HeadIndex , 索引层级已经升高,而在其他put操作中拿到head 属性,又再次将索引层级升高。如果不加判断可能会导致新加的索引节点连错层级。
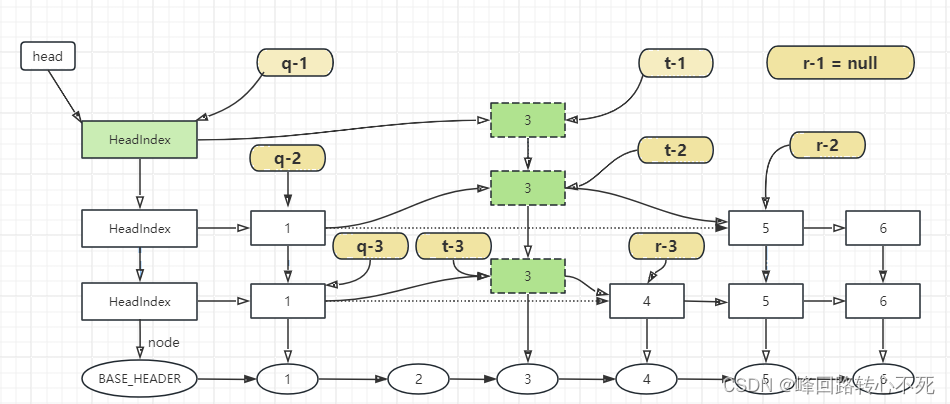
开始q 指向新的headIndex, r 则会等于null,不会进入寻找第一个大于索引节点的逻辑,而是直接连接。下降索引处理层级后,r 可能不为空,这时就需要寻找比新增索引节点大的节点,如果小于q,r就会依次后移。
三、删除流程
final V doRemove(Object key, Object value) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;
outer: for (;;) {
//TODO 查找删除key 的前驱节点
for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) {
Object v; int c;
if (n == null)
break outer;
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read
break;
if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted
break;
//TODO findPredecessor 返回的节点 b < key
//TODO 如果 key < n 那表示key 可能已经被删除,或者不存在,因为 b 和 n 是相邻的节点,跳表的节点是有序的
//TODO 注意:在这里是遍历node链表,而不是索引
if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) < 0)
break outer;
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
//TODO 这里支持同时传入key 和 value ,当 value 不为Null 时会和当前节点对比,相等删除,不相等不删除
if (value != null && !value.equals(v))
break outer;
//TODO cas 设置当前删除节点value 为 null
if (!n.casValue(v, null))
break;
//TODO 为当前节点标记删除 删除节点
if (!n.appendMarker(f) || !b.casNext(n, f))
//TODO 如果标记失败,删除失败调用 findNode 方法,findNode方法中会对 value == null 的节点进行删除
findNode(key); // retry via findNode
else {
//TODO findPredecessor 执行过成功会对 value == null 的索引节点进行删除
findPredecessor(key, cmp); // clean index
if (head.right == null)
//TODO 删除索引节点后,headIndex 的后继节点可能为null,对headIndex进行删减
tryReduceLevel();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v;
return vv;
}
}
return null;
}
删除节点逻辑比较简单,先通过findPredecessor 找到删除节点的某一个前驱节点,而后遍历node链表,找到待删除节点后设置value 为 null ,然后标记删除节点,在node 链表中删除节点,最后再整理 HeadIndex
findNode 和 findPredecessor 中不仅是查找节点作用, **findNode ** 方法中会删除value = null 的数据节点,findPredecessor 会删除value=null 的索引节点
private Node<K,V> findNode(Object key) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // don't postpone errors
Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;
outer: for (;;) {
for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) {
Object v; int c;
if (n == null)
break outer;
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read
break;
//TODO 删除value == null 的数据节点
if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
//TODO 刪除 vaule == null 或 value == node (value 属性存储的是node自身的引用)
if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted
break;
if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) == 0)
return n;
if (c < 0)
break outer;
b = n;
n = f;
}
}
return null;
}
private Node<K,V> findPredecessor(Object key, Comparator<? super K> cmp) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // don't postpone errors
for (;;) {
for (Index<K,V> q = head, r = q.right, d;;) {
if (r != null) {
Node<K,V> n = r.node;
K k = n.key;
//TODO 删除数据节点中value == null 的索引节点
if (n.value == null) {
if (!q.unlink(r))
break; // restart
r = q.right; // reread r
continue;
}
//TODO 比较 key 与 r 节点的大小,如果 key > r q,r 均向右移动
if (cpr(cmp, key, k) > 0) {
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
//TODO 如果已经到达了 1 级索引,直接返回。到达这一步时,可以确定 key <= r
if ((d = q.down) == null)
return q.node;
//TODO 查找下一级索引
q = d;
r = d.right;
}
}
}
上面代码看完后删除的整体思路就已经很清晰了,无法就是找到删除的node , 从数据链表中删除,将Node 的value 置为 null , 然后去删除数据数据节点,以及对应的索引节点
对于标记删除方法的作用还是有些不理解,如下,if 判断中有两个步骤,n.appendMarker(f)
b.casNext(n, f) 。
//TODO 为当前节点标记删除 删除节点
if (!n.appendMarker(f) || !b.casNext(n, f))
//TODO 如果标记失败,删除失败调用 findNode 方法,findNode方法中会对 value == null 的节点进行删除
findNode(key);
appendMarker到底做了些什么?下面一探究竟
/**
* Tries to append a deletion marker to this node.
* @param f the assumed current successor of this node
* @return true if successful
*/
boolean appendMarker(Node<K,V> f) {
return casNext(f, new Node<K,V>(f));
}
boolean casNext(Node<K,V> cmp, Node<K,V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
/**
* Creates a new marker node. A marker is distinguished by
* having its value field point to itself. Marker nodes also
* have null keys, a fact that is exploited in a few places,
* but this doesn't distinguish markers from the base-level
* header node (head.node), which also has a null key.
*/
Node(Node<K,V> next) {
this.key = null;
this.value = this;
this.next = next;
}
事实上标记删除,就是给删除节点的后面增加了一个删除节点,并且这个节点的key = null ,value 执行了自身。如图, 假设需要删除节点 3

如果删除节点增加失败,会直接去执行findNode(key),这是为何呢?我的见解就是出现并发情况,要删除的节点后面已经增加了新的数据节点,b.casNext(n, f) 这个方法肯定会失败,所以执行去执行findNode 方法,去删除value == null 的节点。
如果标记节点增加成功,说明此时没删除节点后没有新增节点可以尝试使用 b.casNext(n, f) 去直接删除数据节点3和新增的删除节点。如果b.casNext(n, f) 执行失败,还是会进入到 findNode(key) 方法中,对value == null 和 value == this 的节点进行删除。
以上是再下对ConcurrentSkipListMap 源码的浅薄的理解,有不对之处恳请大家不吝赐教。





















 293
293











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








