上节我们对XmlBeanFactory进行了初步了解
简化版源码:
/**
* public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this.registry = registry;
*/
//reader的registry得到初始化值为XmlBeanFactory对象,this指代的就是此时创建的XmlBeanFactory对象
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);首先分析一下上面这段代码(调用有参构造函数);
/**
* 在XmlBeanFactory进行了实例化操作,传递XmlBeanFactory对象参数
*/
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
/**
*
*/
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;属性初始化XmlBeanFactory对象
this.registry = registry;
//private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;赋值
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();//初始化,创建StandardEnvironment对象
}this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
/**
* 默认构造函数,初始化
* Create a new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver with a DefaultResourceLoader.
*/
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
/**
* Create a new DefaultResourceLoader.
*/
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
} /**
* 返回类加载器
* Return the default ClassLoader to use: typically the thread context
*/
public static ClassLoader getDefaultClassLoader() {
ClassLoader cl = null;
//获得类加载器
cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
return cl;
}
返回的是同一个类加载器;
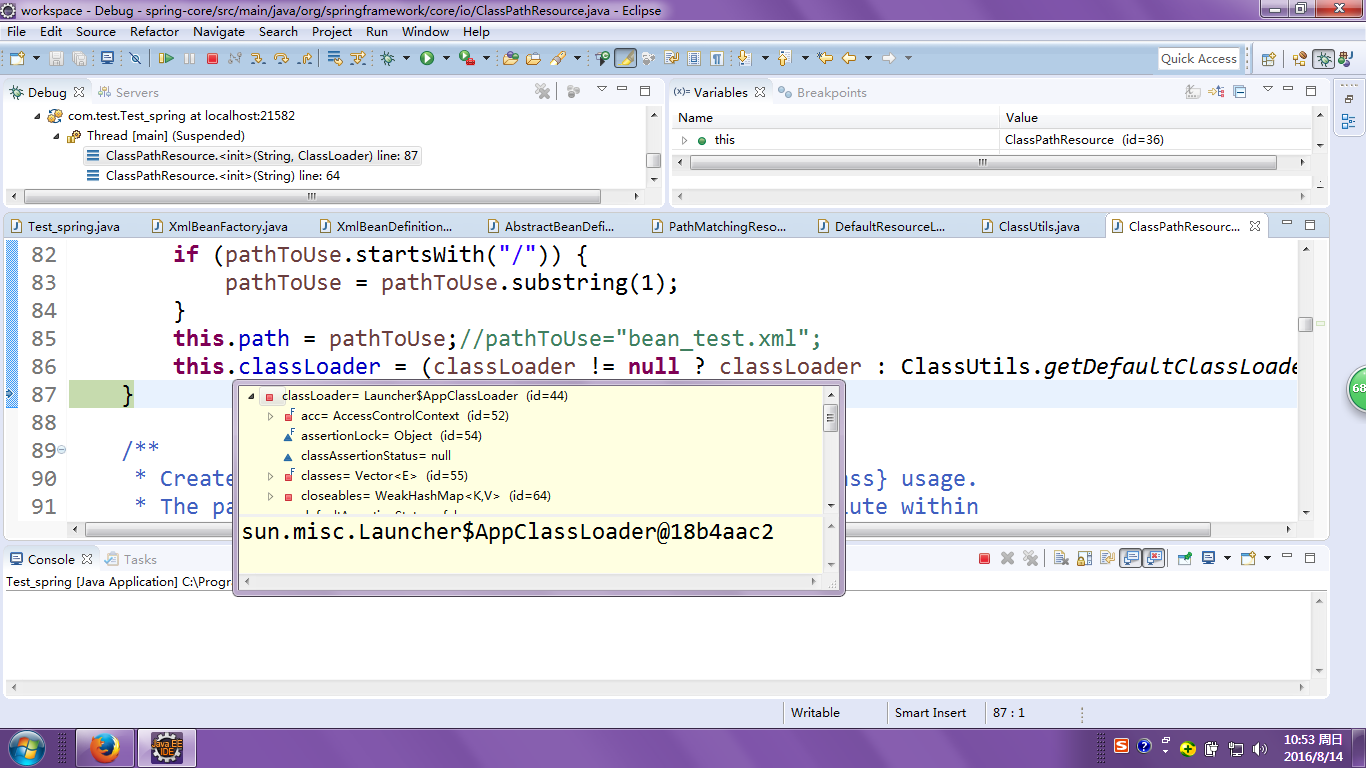
通过以上操作:
我们得到了什么?
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//对象的属性
this.registry = registry;
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();对象的属性
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
new DefaultResourceLoader();对象的属性
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();赋值与ClassPathResource同一个类加载器
综上所述:reader可以获取到XmlBeanFactory对象和类加载器!!!
原版代码:
/**
* public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
*/
//reader的registry得到初始化值为XmlBeanFactory对象,this指代的就是此时创建的XmlBeanFactory对象
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);首先分析一下上面这段代码(调用有参构造函数);
/**
* 在XmlBeanFactory进行了实例化操作,传递XmlBeanFactory对象参数
* Create new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory.
* @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into,
* in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry
*/
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
/**
* Create a new AbstractBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory.
* <p>If the passed-in bean factory does not only implement the BeanDefinitionRegistry
* interface but also the ResourceLoader interface, it will be used as default
* ResourceLoader as well. This will usually be the case for
* {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} implementations.
* <p>If given a plain BeanDefinitionRegistry, the default ResourceLoader will be a
* {@link org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver}.
* <p>If the passed-in bean factory also implements {@link EnvironmentCapable} its
* environment will be used by this reader. Otherwise, the reader will initialize and
* use a {@link StandardEnvironment}. All ApplicationContext implementations are
* EnvironmentCapable, while normal BeanFactory implementations are not.
* @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into,
* in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry
* @see #setResourceLoader
* @see #setEnvironment
*/
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
// private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;属性初始化XmlBeanFactory对象
this.registry = registry;
// Determine ResourceLoader to use.
//false
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry;
}
else {
//private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;赋值
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
// Inherit Environment if possible
if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment();
}
else {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();//初始化,创建StandardEnvironment对象
}
}this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
/**
* 默认构造函数,初始化
* Create a new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver with a DefaultResourceLoader.
* <p>ClassLoader access will happen via the thread context class loader.
* @see org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader
*/
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
/**
* Create a new DefaultResourceLoader.
* <p>ClassLoader access will happen using the thread context class loader
* at the time of this ResourceLoader's initialization.
* @see java.lang.Thread#getContextClassLoader()
*/
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
} /**
* 返回类加载器
* Return the default ClassLoader to use: typically the thread context
* ClassLoader, if available; the ClassLoader that loaded the ClassUtils
* class will be used as fallback.
* <p>Call this method if you intend to use the thread context ClassLoader
* in a scenario where you clearly prefer a non-null ClassLoader reference:
* for example, for class path resource loading (but not necessarily for
* {@code Class.forName}, which accepts a {@code null} ClassLoader
* reference as well).
* @return the default ClassLoader (only {@code null} if even the system
* ClassLoader isn't accessible)
* @see Thread#getContextClassLoader()
* @see ClassLoader#getSystemClassLoader()
*/
public static ClassLoader getDefaultClassLoader() {
ClassLoader cl = null;
try {
//获得类加载器
cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Cannot access thread context ClassLoader - falling back...
}
if (cl == null) {
// No thread context class loader -> use class loader of this class.
cl = ClassUtils.class.getClassLoader();
if (cl == null) {
// getClassLoader() returning null indicates the bootstrap ClassLoader
try {
cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Cannot access system ClassLoader - oh well, maybe the caller can live with null...
}
}
}
return cl;
}
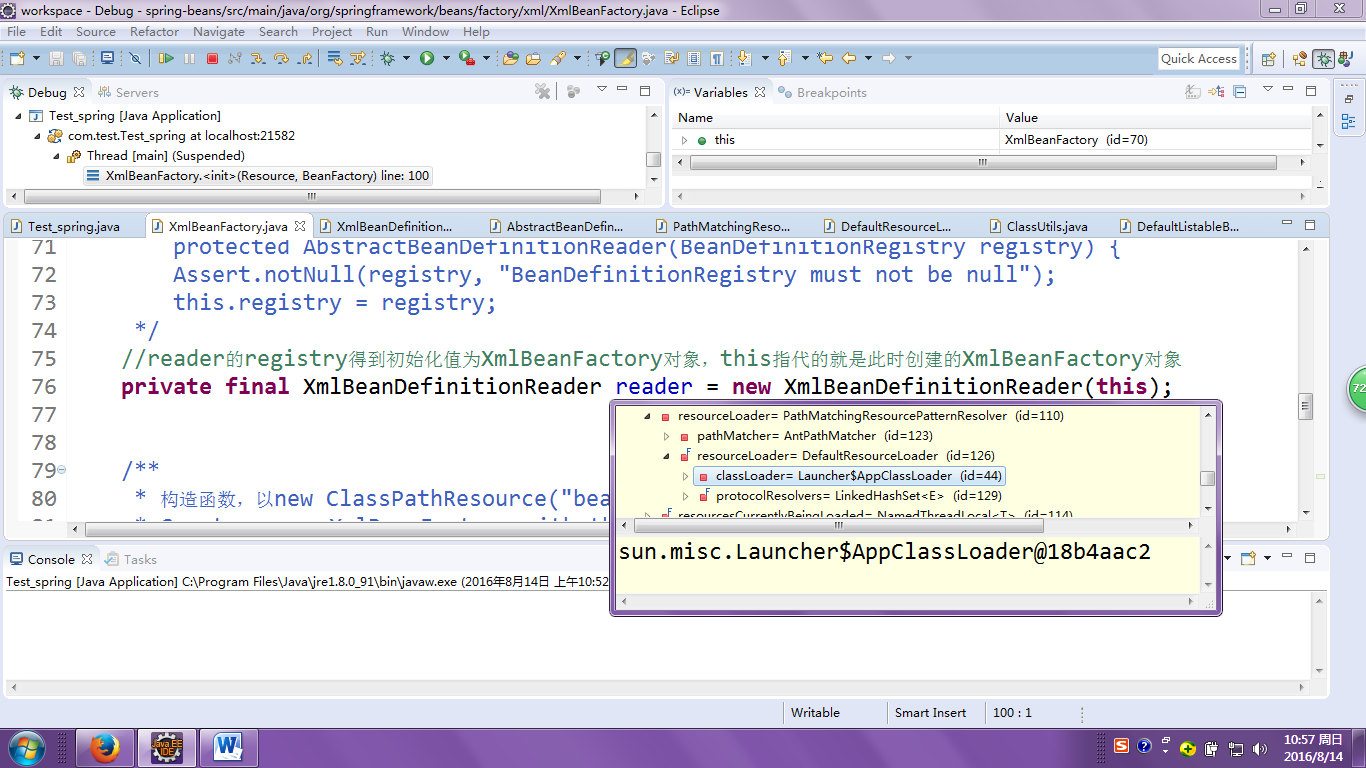
返回的是同一个类加载器;

通过以上操作:
我们得到了什么?
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//对象的属性
this.registry = registry;
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();对象的属性
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
new DefaultResourceLoader();对象的属性
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();赋值与ClassPathResource同一个类加载器
综上所述:reader可以获取到XmlBeanFactory对象和类加载器!!!






















 344
344











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








