Netty笔记1:线程模型
Netty笔记2:零拷贝
Netty笔记3:NIO编程
Netty笔记4:Epoll
Netty笔记5:Netty开发实例
Netty笔记6:Netty组件
Netty笔记7:ChannelPromise通知处理
Netty笔记8:ByteBuf使用介绍
Netty笔记9:粘包半包
Netty笔记10:LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
Netty笔记11:编解码器
Netty笔记12:模拟Web服务器
Netty笔记13:序列化
模拟
Web服务器一般都是http协议的,而使用Netty的好处之一就是它提供了丰富的协议实现;
先定义一个自己的Handler用于处理Http协议解析后的API处理:
public class HttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> {
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception {
HttpMethod method = request.method();
System.out.println(method.name());
String uri = request.uri();
System.out.println(uri);
ByteBuf content = request.content();
System.out.println(content.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 这里是模拟web服务的API路由和响应
if (HttpMethod.GET.equals(method)) {
String data = ApiEntry.entry.get(uri);
if (StringUtil.isNullOrEmpty(data)) {
send(ctx, "404");
}
send(ctx,data);
} else if (HttpMethod.POST.equals(method)) {
String data = ApiEntry.entry.get(uri);
if (StringUtil.isNullOrEmpty(data)) {
send(ctx, "404");
}
send(ctx,data);
}
}
// 模拟响应
private void send(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String data) {
// 发送一个响应数据
HttpHeaders headers = new DefaultHttpHeaders();
headers.add(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, HttpHeaderValues.TEXT_HTML+";charset=utf-8");
DefaultFullHttpResponse res = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, Unpooled.copiedBuffer(data.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
res.headers().add(headers);
// 响应写出后关闭连接
ctx.writeAndFlush(res).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
这里假定ApiEntry是web服务中保存API接口和调用方法的容器:
public class ApiEntry {
public static Map<String, String> entry = new HashMap<>();
static {
entry.put("/test","测试数据");
entry.put("/user/", "用户");
}
}
定义主程序:
public class HttpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup group =new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(8080)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 请求报文解码
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec())
// 聚合为完整报文,即等待一个http的所有消息都接收到后组装成一个完整报文
.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65535))
// 自定义的handler
.addLast(new HttpServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture sync = bootstrap.bind().sync();
sync.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
}
FullHttpRequest:这个是HttpObjectAggregator处理后得到,这个类是用于确保接收到的消息是一个完整的消息,当出现粘包,或半包时,是很有用的;
HttpServerCodec/HttpClientCodec:Netty提供的编解码器;
HttpObjectAggregator:聚合http消息使用,在请求和响应过程中,可能没法一次传输完毕,所以这个类是为了将多个消息合并为一个完整的消息(FullHttpRequest/FullHttpResponse);
结果:
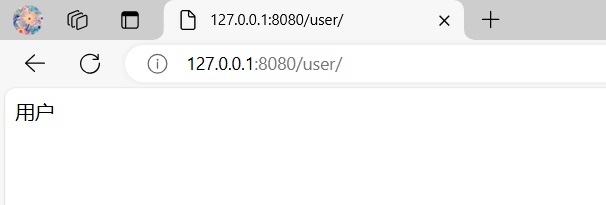
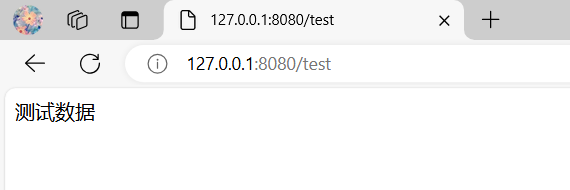
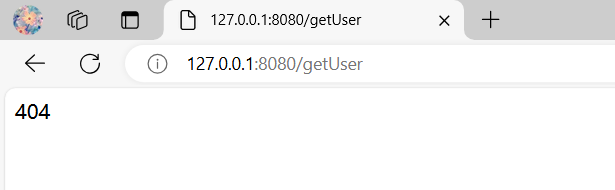
如果浏览器访问出现
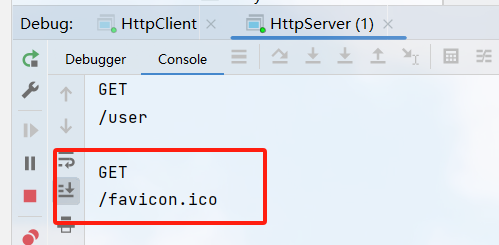
favicon.ico是Favorites Icon的缩写,也就是浏览器标签页显示的个性化图标。
http压缩
数据压缩可以减少传输的数据量,但同时也会提高CPU的开销;
需要注意的是,压缩一般是由服务器发回的响应会被压缩,请求一般都是数据量很小,性价比不高,如果服务端开启了压缩,那么接收端也是要支持的,因为压缩都是由特定算法的。
Netty中也提供了对应的压缩Handler:
出站:HttpContentCompressor,用于对出站的消息HttpResponse和HttpContent进行编码;
入站:HttpContentDecompressor,用于解码接收到的HttpRequest和HttpContent;
对Http消息进行压缩,格式为gzip或者deflate,而压缩的请求需要带上一个请求头,
发送端带上:Accept-Encoding:gzip ,表示接受这种类型的数据;
接收端带上:Content-Encoding:gzip,表示内容为这种类型的数据;
还有一点是压缩的参数,也就是压缩级别;
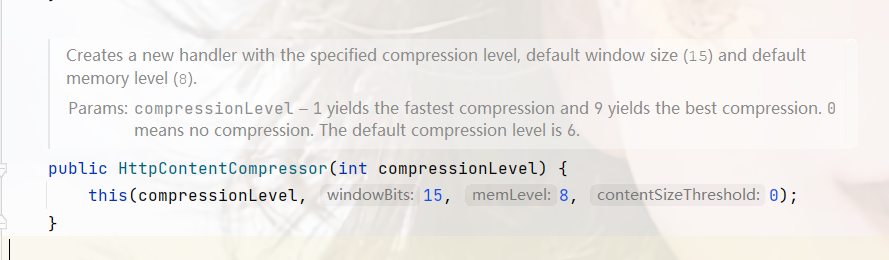
根据注释来看,由几点要注意:
compressionLevel:1 产生最快的压缩,9 产生最佳压缩。0 表示无压缩。默认压缩级别为 6。windowBits:历史缓冲区大小的基数为二对数。该值应在 9 到 15 之间(含 9 到 15 分)。值越大,压缩效果越好,但会牺牲内存使用率。默认值为 15。memLevel:应为内部压缩状态分配多少内存。1 使用最小内存,9 使用最大内存。值越大,压缩速度越好,速度越快,但会牺牲内存使用率。默认值为 8contentSizeThreshold:当响应正文的大小超过阈值时,将压缩响应正文。该值应为非负数。0 将为所有响应启用压缩。
这里写一个客户端来模拟一个http请求:
public class HttpClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int compressMax = 1024;
// 线程组
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
// 启动器
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
// 设置线程组
bootstrap.group(group)
// 治党channel
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
// 指定服务端地址
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080))
// 客户端都是socketChannel
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientCodec());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65535));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpContentDecompressor());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientHandler());
}
});
// 阻塞直到连接完成;
// sync()是阻塞
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync();
// 控制台输入
consoleInput(future);
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
System.out.println("连接关闭完成。");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
private static void consoleInput(ChannelFuture future) {
new Thread(() -> {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("客户端已准备号,等待输入...");
while (true) {
String data = scanner.nextLine();
if ("exist".equals(data)) {
System.out.println("客户端结束,等待关闭");
break;
}
// 构建消息对
FullHttpRequest request = new DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpMethod.GET, "/test");
// 直接发送实体对象消息,就会调用对应的encode
future.channel().writeAndFlush(request);
}
}).start();
}
}
public class HttpClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpResponse> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpResponse msg) throws Exception {
HttpHeaders headers = msg.headers();
System.out.println("请求头:");
headers.entries().forEach(e-> System.out.println(e.getKey()+":"+e.getValue()));
System.out.println(msg);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
}
}
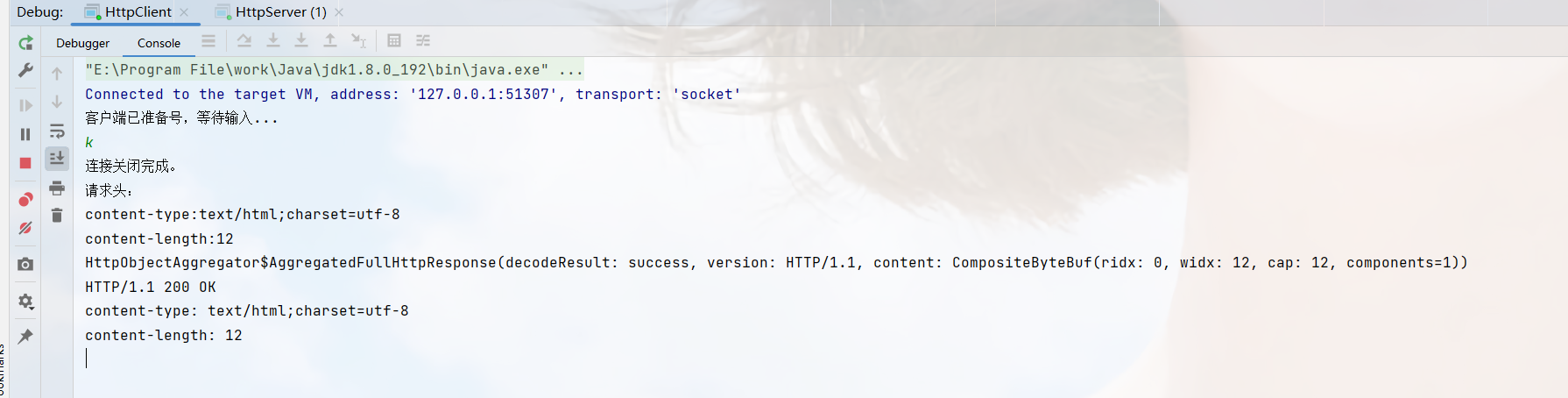
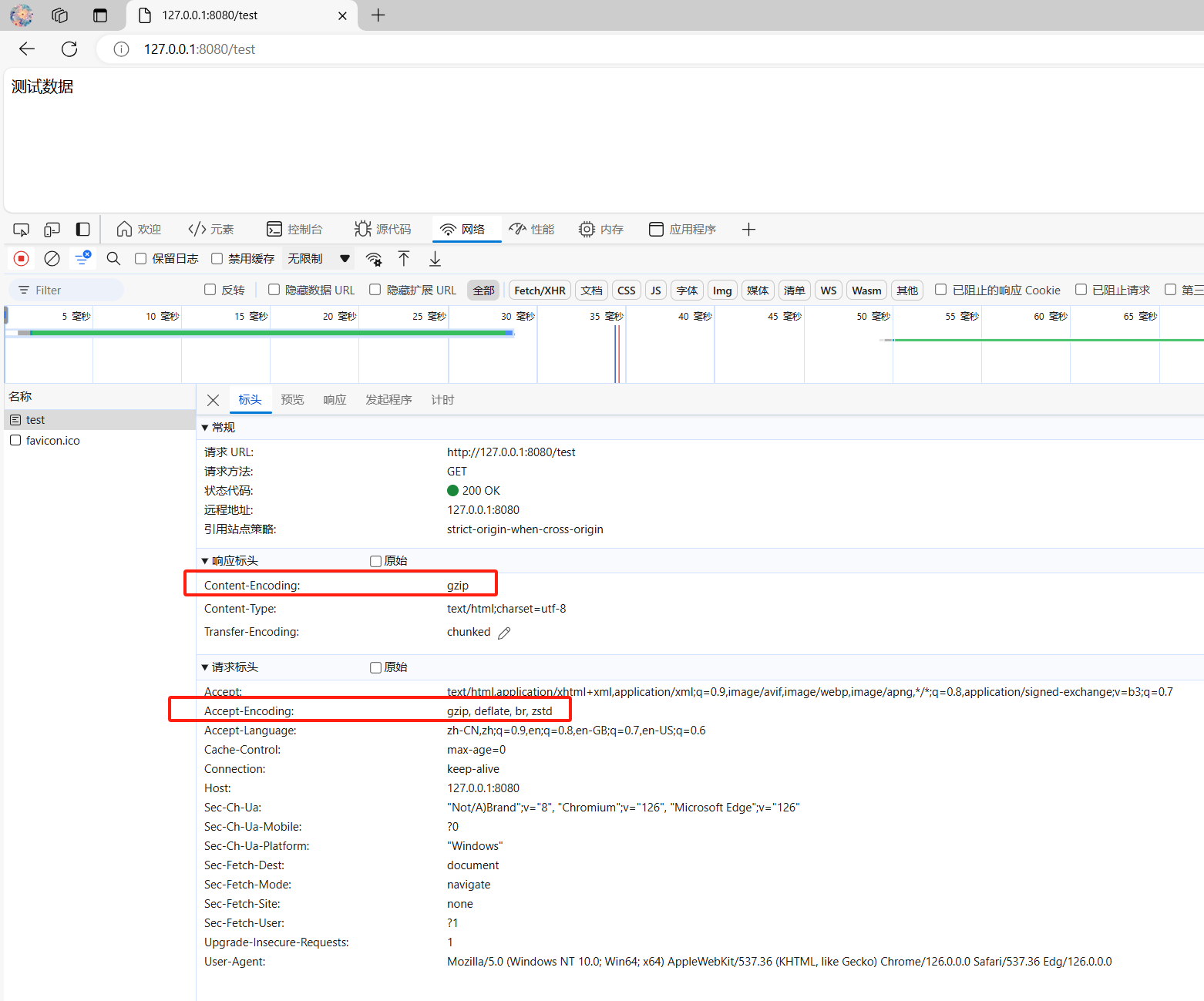
这个写的客户端没有之前我们说的Content-Encoding,我们用给浏览器看一下:
模拟SSL/TLS
要添加SSL/TLS需要先创建证书和密钥,这些都是客户端和服务端双方都需要验证的,其次就是我们要服务端添加SSL/TLS的handler就可以了,看着挺简单的。
我们在HTTP服务的基础上,增加SSL的处理器SslHandler就可以实现了;
**注意:**这个SslHandler要放在第一个,因为它是基于TCP/IP协议上的安全层,需要在数据传输之前完成验证;
ublic class HttpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, SSLException, CertificateException, FileNotFoundException {
SelfSignedCertificate ssc = new SelfSignedCertificate();
SslContext sslContext = SslContextBuilder.forServer(ssc.certificate(), ssc.privateKey()).build();
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(8080)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 请求报文解码
ch.pipeline().addLast(sslContext.newHandler(ch.alloc()));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec())
// 开启gzip,deflate
.addLast(new HttpContentCompressor())
// 聚合为完整报文,即等待一个http的所有消息都接收到后组装成一个完整报文
.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65535))
// 自定义的handler
.addLast(new HttpServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture sync = bootstrap.bind().sync();
sync.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
}
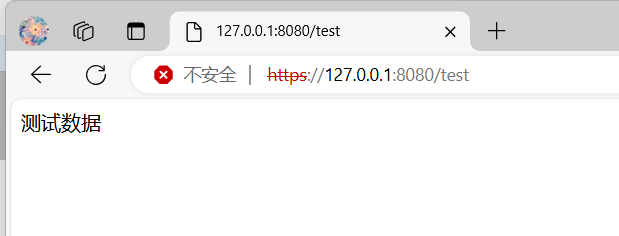
这个SSL还是没有完全搞懂,需要后面深入理解;
OptionalSslHandler


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








