目录
一、前言
1.1 之前在练习了Django的博客项目,前后端不分离的,现在就想着把Flask框架也再熟悉一下,后续把接口返回的数据用vue显示。python 比较流行的框架是Django 和Flask,重要性不言而喻
1.2 刚好是五一,发文符合劳动节精神,深圳又下雨,在家搬砖
二、环境准备
2.1 安装python
确保你的电脑安装了python,并正确配置好环境变量。查看版本命令:
python -V本文内容运行在python 3.6.1
![]()
2.2 安装mysql
确保你的电脑安装了mysql,并正确设置账号和密码,本机账号和密码为 root/root
mysql -V本文内容mysql 5.7中运行通过

三、工具准备
3.1 安装pycharm
确保你的电脑安装了pycharm,我这里用的是pycharm professional 2017.3(已pojie)

3.2 安装Navicat
可视化数据库查询工具准备,工具很多,本文用的是拿手的Navicat

3.3 安装postman
postman是一款必会的工具,开发和测试都在用

四、mysql数据库准备
4.1 Navicat连接
连接名起一个test,主机输入localhost或者127.0.0.1,默认端口3306,输入用户名和密码root/root,点击链接测试,链接成功

4.2 数据库准备
在链接上test数据源后,在test处右键,新建数据库,数据库名books,字符集utf-8,排序规则选择utf8_general_ci,点击确认,数据新建完成


注意:此处不新建表,从代码里面通过模型类建表
五、增删改查接口(服务)开发
开发前先做一些准备工作,新建flask项目,file ->new project

创建完成。我这里book是根目录,主文件我改名字app.py,不该也可以此时就可以右键启动了
控制台会打印 访问地址,点击访问 浏览器页面显示 Hello World!,我这里代码删了不贴图了。

安装一些用的库,点击file->settings,flask、PyMySQL、SQLAlchemy、flask-sqlalchemy等(注意有些库使用的时候的名字和导入的时候的名字不一样,比如导入flask-sqlalchemy,代码里面却是flask_sqlalchemy)

接着,逐步把以下代码添加到app.py文件中。先导入一些要用到的库
import pymysql
from flask import Flask
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from flask import make_response,request
from flask_cors import CORS
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()数据库设计,使用flask框架模型类添加,代码如下
先连接数据库,修改账号、密码、主机名、端口号、数据库名为你们使用的即可
app = Flask(__name__)
# ------------------database----------------------------
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'mysql://root:root@localhost:3306/books'
# 指定数据库文件
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True
# 允许修改跟踪数据库
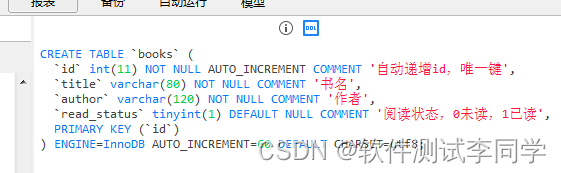
db = SQLAlchemy(app)模型类代码:下面建立一个books表,字段有id、title、author、read_status,注意字段大小和类型,这些都是事先要把需求确定好,不然测试肯定有问题。比如:有需求说作者不能超过20个字,下面这种设计120大小就不合适。这就是实际开发和学习的区别
class Books(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, comment='自动递增id,唯一键')
title = db.Column(db.String(80), nullable=False, comment='书名')
author = db.Column(db.String(120), nullable=False, comment='作者')
read_status = db.Column(db.Boolean, comment='阅读状态,0未读,1已读')
通过下面这行代码把表创建好
db.create_all() # 创建表(表创建好后可注释掉)查看数据库表DDL
5.1 表的增删改查操作
以下是增删改查方法代码:
# 增加数据
def insert_data(title, author, read_status):
book = Books(title=title, author=author, read_status=read_status)
db.session.add_all([book])
db.session.commit()
# 查询所有
def select_data_all():
book_list = []
books = Books.query.all()
# 类似于 select * from Books
for s in books:
dic = {}
dic['id'] = s.id
dic['title'] = s.title
dic['author'] = s.author
dic['read_status'] = s.read_status
book_list.append(dic)
return book_list
# 通过id查询
def select_data_by_id(id):
book = Books.query.get(id)
if not book:
return False
dic = {}
dic['id'] = book.id
dic['title'] = book.title
dic['author'] = book.author
dic['read_status'] = book.read_status
return dic
# 通过id删除数据
def delete_data(id):
# 类似于 select * from Books where id = id
delete_id = Books.query.get(id)
if not delete_id:
return False
db.session.delete(delete_id)
db.session.commit()
# 提交操作到数据库
# 修改数据
def update_data(id, title='', author='', read_status='', new_id=''):
book = Books.query.get(id)
if not title == '':
book.title = title
if not author == '':
book.author = author
if not read_status == '':
book.read_status = read_status
if not new_id == '':
book.id = new_id
db.session.commit()插播,以下代码解决跨域问题(这是我为后面准备开发页面用的)
# 解决浏览器浏览器访问输出乱码问题
app.config['JSON_AS_ASCII'] = False
@app.after_request
def after(resp):
resp = make_response(resp)
resp.headers['Access-Control-Allow-Origin'] = '*' # 允许跨域地址
resp.headers['Access-Control-Allow-Methods'] = '*' # 请求 ‘*’ 就是全部
resp.headers['Access-Control-Allow-Headers'] = 'x-requested-with,content-type' # 头部
resp.headers['Access-Control-Allow-Credentials'] = 'True'
return resp
CORS(app, resources=r'/*', supports_credentials=True)5.2 增加接口服务
讲增加接口服务前,定义以下需要传的参数title、author、read_status,title不能重复,
title、author、read_status是必传参数,title、author不能为空,read_status阅读状态只能为0和1
后续测试场景就从这里来,后面的同理
# 前端通过传参title、author、read_status增加书籍
@app.route('/add', methods=['POST'])
def add():
response_object = {'status': 'success'}
if request.method == 'POST':
post_data = request.get_json()
print('调用add方传过来的参数是', post_data)
book_list = select_data_all()
for i in range(len(book_list)):
title_list = book_list[i]['title']
if post_data.get('title') in title_list:
response_object['message'] = '书名(title)重复!'
response_object["status"]= 'fail'
return response_object
if post_data.get('title') is None:
response_object['message'] = 'title是必传参数!'
response_object["status"]= 'fail'
return response_object
if post_data.get('author') is None:
response_object['message'] = 'author是必传参数!'
response_object["status"]= 'fail'
return response_object
if post_data.get('read_status') is None:
response_object['message'] = &#







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 2513
2513

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










