AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
1. 获得锁
公平锁
final void lock() {
// 直接通过CAS获得锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
// 没有获得到 再次尝试获得 如果还是失败就放入等待队列
acquire(1);
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}2. 释放锁
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 释放当前锁
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
// unpark等待队列中的可被唤醒的节点
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// state减去入参
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 如果state=0 清空互斥锁持有线程
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
// 更新state
setState(c);
return free;
}3. 进入等待队列
首先将当前线程包装成node,然后通过CAS插入队列,成功则返回
失败则再次插入,并且是死循环 直到插入队列为止。
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 将当前线程中断并追加到队尾,状态为可被唤醒
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
4. 唤醒队列中的线程
/**
* Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
// 正常唤醒下一个节点
Node s = node.next;
// 如果下个节点的状态为取消,则直到找到下一个可以被唤醒的节点位置
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
// 底层使用UNSAFE的native方法实现
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}基于AQS实现的并发工具类:ReentrantLock,Semaphore,CountDownLatch,CyclicBarrier
Lock
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
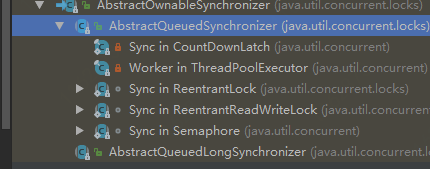
LockSupport
并发集合
1. ConcurrentHashMap 底层采用锁 单个数组下标 实现 不同数组下标可以并发读写
2. ConcurrentLinkedQueue 底层采用volatile + cas实现
3. CopyOnWriteArrayList 底层采用copy的方式实现读写并发。
4. BlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue,底层采用数组 + 线程阻塞唤醒机制实现
LinkedBlockingQueue, 底层采用链表 + 线程阻塞唤醒机制实现
PriorityBlockingQueue 底层采用红黑树 + 线程阻塞唤醒机制实现
DelayQueue 底层采用优先队列 + timer + 线程阻塞唤醒机制实现
package com.dack.test;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class DelayedTask implements Delayed {
public static DelayQueue<DelayedTask> queue;
// 任务的执行时间
private int executeTime = 0;
// 业务需要的参数
private String outStr = "";
public static void main(String[] args) {
DelayedTask.queue = new DelayQueue<DelayedTask>();
// 可有可无
DelayedTask.queue.add(new DelayedTask(2, "hello"));
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + "服务启动");
while (true) {
DelayedTask delayedTask = DelayedTask.queue.poll();
if (delayedTask != null) {
String os = delayedTask.getOutStr();
//可以随时添加新的延时任务
DelayedTask.queue.add(new DelayedTask(2, "hello"));
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " 消费服务 ,传参" + os);
}
}
}
public DelayedTask(int delay) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, delay);
this.executeTime = (int) (calendar.getTimeInMillis());
}
// 业务所需的参数构造方法
public DelayedTask(int delay, String str) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, delay);
this.executeTime = (int) (calendar.getTimeInMillis());
this.outStr = str;
}
/**
* 元素在队列中的剩余时间
*
* @param unit
* @return
*/
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
return executeTime - (calendar.getTimeInMillis());
}
/**
* 元素排序
*
* @param o
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
long val = this.getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) - o.getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
return val == 0 ? 0 : (val < 0 ? -1 : 1);
}
public int getExecuteTime() {
return executeTime;
}
public void setExecuteTime(int executeTime) {
this.executeTime = executeTime;
}
public String getOutStr() {
return outStr;
}
public void setOutStr(String outStr) {
this.outStr = outStr;
}
}Semaphore(信号量)
class TestSema implements Runnable {
private final Semaphore semaphore;
public TestSema(Semaphore semaphore) {
this.semaphore = semaphore;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
boolean get = semaphore.tryAcquire();
if (!get) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",no get");
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",get");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
semaphore.release();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",release");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(2);
Thread aThread = new Thread(new TestSema(semaphore), "A");
Thread bThread = new Thread(new TestSema(semaphore), "B");
Thread cThread = new Thread(new TestSema(semaphore), "C");
aThread.start();
bThread.start();
cThread.start();
}Atomic
public final int getAndAddInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4) {
int var5;
do {
var5 = this.getIntVolatile(var1, var2);
} while(!this.compareAndSwapInt(var1, var2, var5, var5 + var4));
return var5;
}CountDownLatch
public class MyCountDownLatch {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
new MyTask(countDownLatch).start();
new MyTask(countDownLatch).start();
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("任务全部完成");
}
}
class MyTask extends Thread {
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public MyTask(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.println("任务完成");
}
}
原理:当主线程调用await()时, 会判断count==0 如果不等于0 则将当前节点放入等待队列,阻塞当前线程,
然后自旋,不断判断count==0, 当满足时,取出等待队列中的节点进行释放对应线程
子线程每执行countDown则count-1
使用场景:比赛时各个队员全部准备就绪后 开始比赛
CyclicBarrier(循环栅(zha)栏)
public class MyCyclicBarrier {
static class MyTask extends Thread {
private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier;
public MyTask(CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier) {
this.cyclicBarrier = cyclicBarrier;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "到达");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "离开");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "到达");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "离开");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(5, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("完成");
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new MyTask(cyclicBarrier).start();
}
}
}
原理:每次调用await() count-1, 当count==0 时, 执行回调函数, 并重置count
CompletionService
主要是针对需要返回结果的异步任务进行设计的,一边生成任务,一边获取任务的返回值。让两件事分开执行,任务之间不会互相阻塞,可以实现先执行完的先取结果,不再依赖任务顺序了。
多线程计算累加和
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ConcurrentAccumulation {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int total = 100000;
int threads = 10;
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threads);
CompletionService<Integer> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executor);
int increment = total / threads;
for (int i = 0; i < threads; i++) {
final int start = i * increment;
final int end = (i == threads - 1) ? total : (i + 1) * increment;
completionService.submit(new AccumulationTask(start, end));
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < threads; i++) {
try {
sum += completionService.take().get();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);
executor.shutdown();
}
static class AccumulationTask implements Callable<Integer> {
private final int start;
private final int end;
public AccumulationTask(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
}= Executor + LinkedBlockingQueue
典型的适配器模式
线程池
实现多线程的方式

execute

线程池的种类
-
FixedThreadPool:这是一个定长线程池,核心线程数和最大线程数相同,线程数量固定。当线程达到核心线程数后,如果任务队列满了,不会创建额外的非核心线程去执行任务,而是执行拒绝策略。任务队列为链表结构的有界队列,用于控制线程的最大并发数。
-
CachedThreadPool:也称为缓存线程池,无核心线程,非核心线程数量无限。线程在执行完毕后如果闲置超过60秒会被回收。任务队列为不存储元素的阻塞队列,适合执行大量、耗时少的任务。
-
ScheduledThreadPool:支持定时或周期性执行任务。核心线程数量固定,非核心线程数量无限,执行完闲置10秒后回收。任务队列为延时阻塞队列,用于执行定时或周期性任务。
-
自定义线程池,指定队列大小
-
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 3, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100)); -
动态调整线程池核心线程数
-
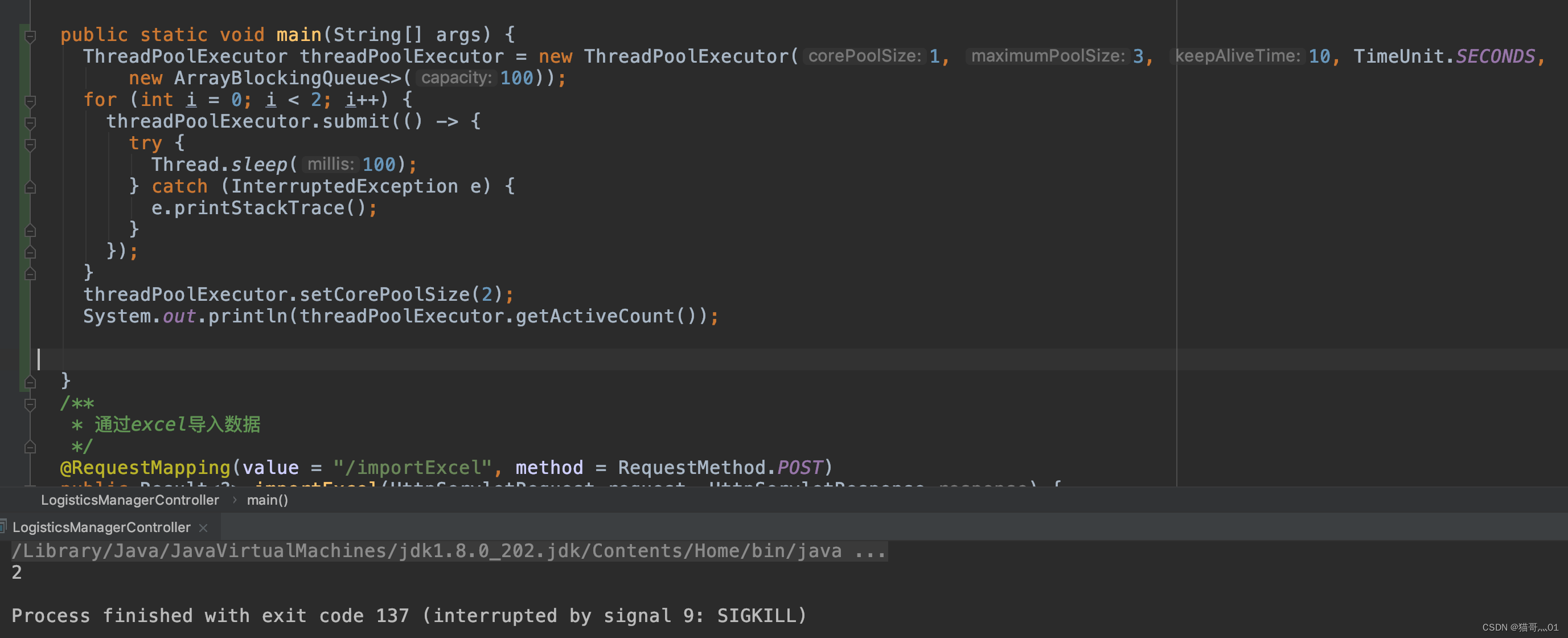
ThreadFactory(自定义)
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class CustomThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
public CustomThreadFactory(String namePrefix) {
this.namePrefix = namePrefix;
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
this.group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + "-thread-" + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
























 876
876











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








